India’s Push for Security Council Reform: The G4 Model - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

India’s Push for Security Council Reform: The G4 Model
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
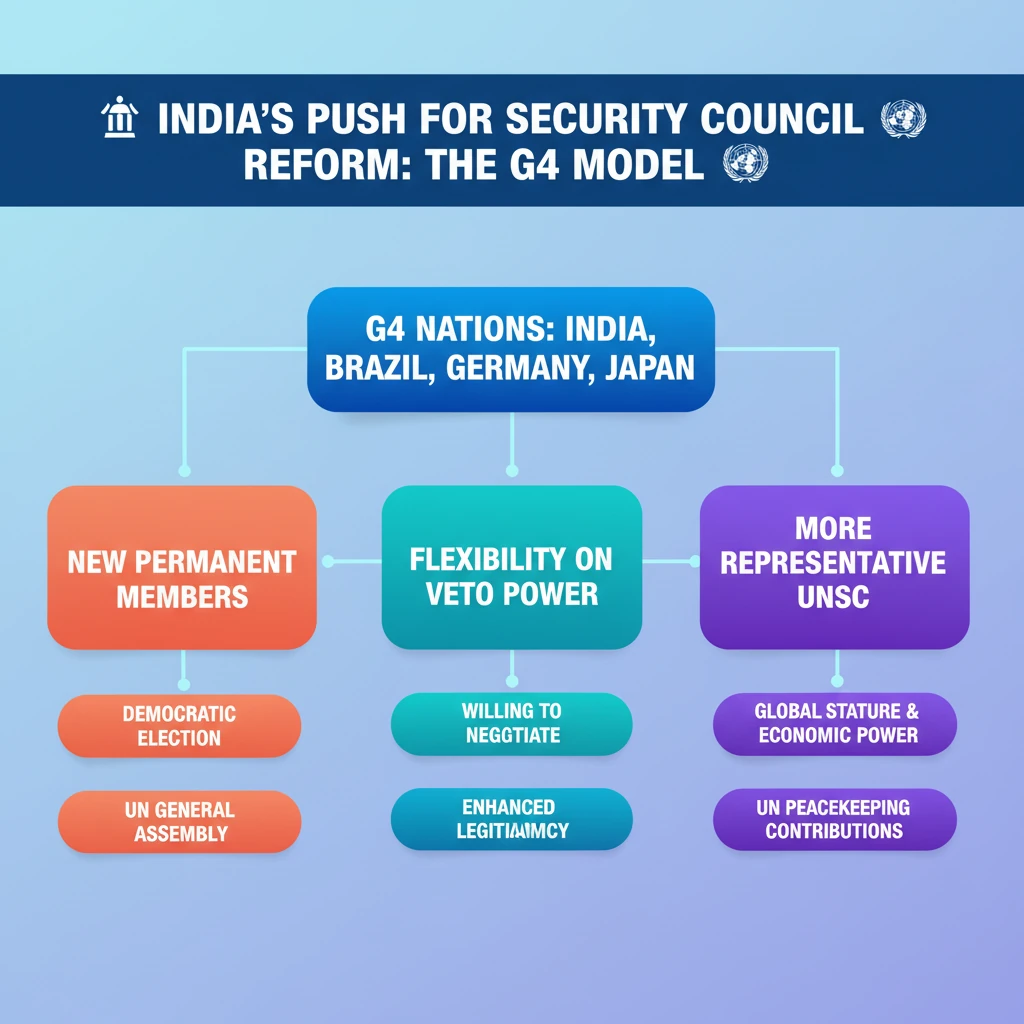
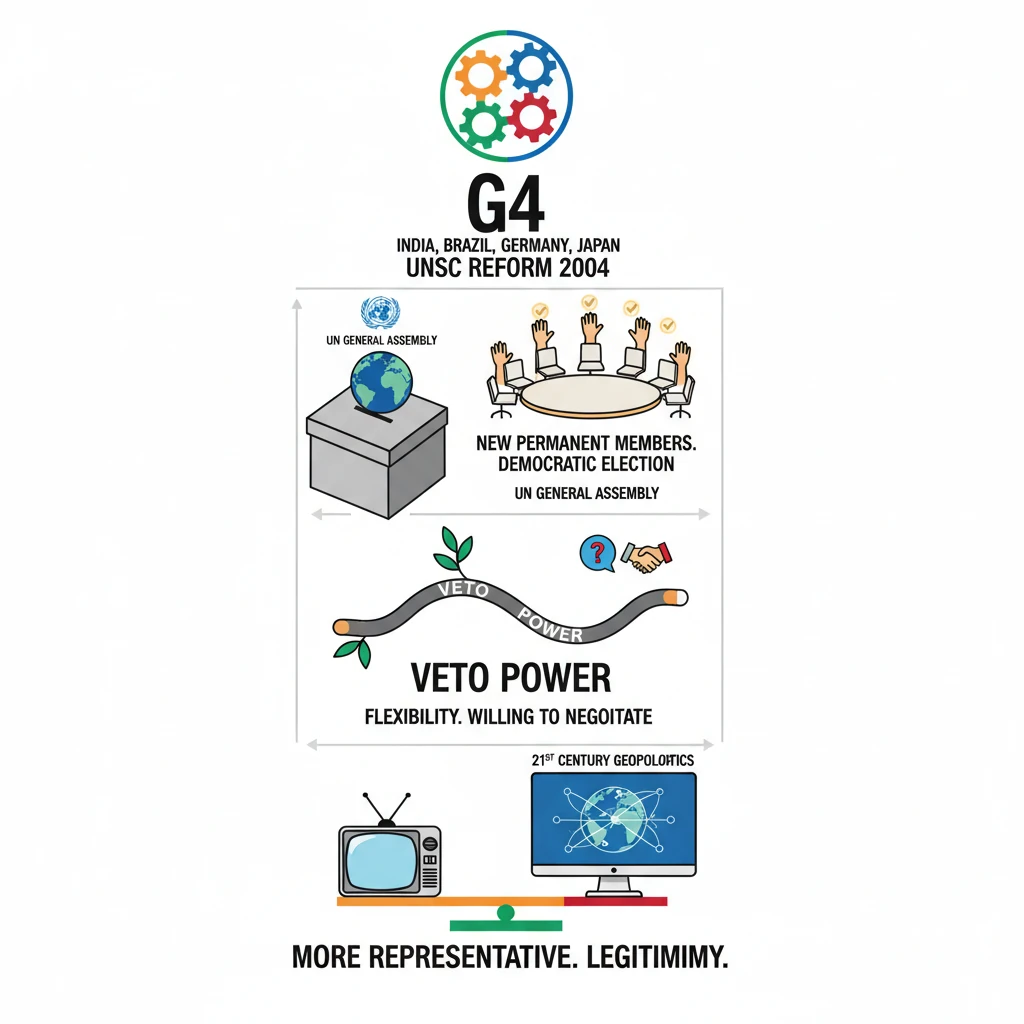
<h4>India's Push for UNSC Reform: The G4 Model</h4><p>India is actively advocating for the reform of the <strong>United Nations Security Council (UNSC)</strong>.</p><p>This push is articulated through a detailed model presented on behalf of the <strong>G4 nations</strong> during the <strong>Intergovernmental Negotiations (IGN)</strong> on Security Council Reform.</p><h4>Understanding the G4 Nations</h4><p>The <strong>G4</strong> is a group of four countries: <strong>Brazil</strong>, <strong>Germany</strong>, <strong>India</strong>, and <strong>Japan</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>G4 alliance</strong> was established in <strong>2004</strong> with the primary objective of promoting and achieving comprehensive reforms within the <strong>UN Security Council</strong>.</p></div><h4>Key Features of the G4 Model for Reform</h4><p>The model proposed by the <strong>G4 nations</strong> outlines significant changes to the current structure of the <strong>UNSC</strong>.</p><ul><li>It advocates for the inclusion of <strong>new permanent members</strong> to reflect contemporary global realities.</li><li>These new permanent members would be elected democratically by the <strong>UN General Assembly</strong>, ensuring broader representation.</li></ul><div class='key-point-box'><p>A crucial aspect of the <strong>G4 model</strong> is its expressed <strong>flexibility on the veto issue</strong>. This indicates a willingness to negotiate the specifics of veto power for new permanent members.</p></div><h4>India's Rationale for Permanent Membership</h4><p>India's demand for a permanent seat in the <strong>UNSC</strong> is underpinned by its growing global stature, economic power, and significant contributions to UN peacekeeping operations.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>UPSC aspirants should note that India's internal strengthening (e.g., <strong>National Investigation Agency</strong>, <strong>Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Amendment Act</strong>, <strong>National Intelligence Grid (NATGRID)</strong>, <strong>National Security Guard</strong>) also contributes to its credentials as a responsible global power deserving of a greater role in global governance.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •India, Brazil, Germany, and Japan form the G4, advocating for UN Security Council reform since 2004.
- •The G4 model proposes new permanent members, democratically elected by the UN General Assembly.
- •The model shows flexibility on the controversial veto power issue, indicating a willingness to negotiate.
- •Reform aims to make the UNSC more representative of 21st-century geopolitical realities and enhance its legitimacy.
- •India's growing global stature, economic power, and contributions to UN peacekeeping strengthen its claim for a permanent seat.
🧠 Memory Techniques
90% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of External Affairs (India) official statements and reports
•Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) analyses
•Academic journals on International Relations and UN Studies