East Asia Summit - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

East Asia Summit
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to the East Asia Summit (EAS)</h4><p>The <strong>East Asia Summit (EAS)</strong> is a premier leaders-led forum in the Indo-Pacific region. It serves as a platform for strategic dialogue and cooperation on key political, security, and economic challenges.</p><p>Established in <strong>2005</strong>, the EAS comprises <strong>18 members</strong>: the ten ASEAN member states (Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, Indonesia, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam) and eight dialogue partners (Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russia, and the United States).</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>EAS</strong> plays a crucial role in fostering regional stability and prosperity by addressing issues of common interest and concern.</p></div><h4>Economic Importance of EAS</h4><p>The <strong>EAS member countries</strong> collectively represent a significant portion of the global economy. Their combined economic power makes the forum vital for international trade and investment.</p><div class='info-box'><p>In <strong>2023</strong>, EAS members accounted for approximately <strong>53% of the world's population</strong> and contributed roughly <strong>60% of global GDP</strong>.</p></div><p><strong>India's economic ties with ASEAN</strong>, a core component of EAS, are particularly strong. <strong>ASEAN</strong> is India's <strong>fourth-largest trading partner</strong>, highlighting the robust commercial relationship.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>India</strong> is <strong>ASEAN's seventh-largest trading partner</strong>. Over the last decade, <strong>India-ASEAN trade</strong> has more than doubled, reaching over <strong>USD 130 billion</strong>.</p></div><h4>Strategic Importance of EAS</h4><p>The <strong>EAS</strong> is strategically vital for India's foreign policy, particularly its <strong>Act East Policy</strong>. It provides a platform for enhancing connectivity and security in the Southeast Asian region.</p><p><strong>Connectivity projects</strong>, encompassing both physical infrastructure and digital links, are central to India's engagement. These initiatives aim to boost regional integration and strengthen ties with <strong>East Asian nations</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Major initiatives include the <strong>India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway</strong> and the <strong>Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project</strong>. These projects are crucial for improving regional links.</p></div><p>Beyond infrastructure, India also focuses on <strong>capacity-building</strong> through programs like the <strong>Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC)</strong>. This initiative supports countries such as <strong>Cambodia</strong>, <strong>Laos</strong>, and <strong>Vietnam</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding the strategic projects like <strong>Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport</strong> is key for questions on India's connectivity initiatives and <strong>Act East Policy</strong> in <strong>GS Paper 2</strong>.</p></div><h4>Cultural Importance of EAS</h4><p>Cultural ties form another significant pillar of India's engagement with <strong>EAS nations</strong>. <strong>Buddhism</strong>, originating in India, serves as a major cultural and religious bridge connecting many <strong>Southeast Asian</strong> and <strong>East Asian countries</strong>.</p><p>India actively promotes these shared heritage links. Initiatives like the <strong>restoration of Nalanda University</strong> and support for the <strong>International Buddhist Confederation</strong> reinforce these spiritual and cultural bonds.</p><div class='info-box'><p>These efforts enhance India's cultural diplomacy with nations such as <strong>Myanmar</strong>, <strong>Thailand</strong>, and <strong>Cambodia</strong>, showcasing its commitment to promoting <strong>Buddhist traditions</strong> globally.</p></div>
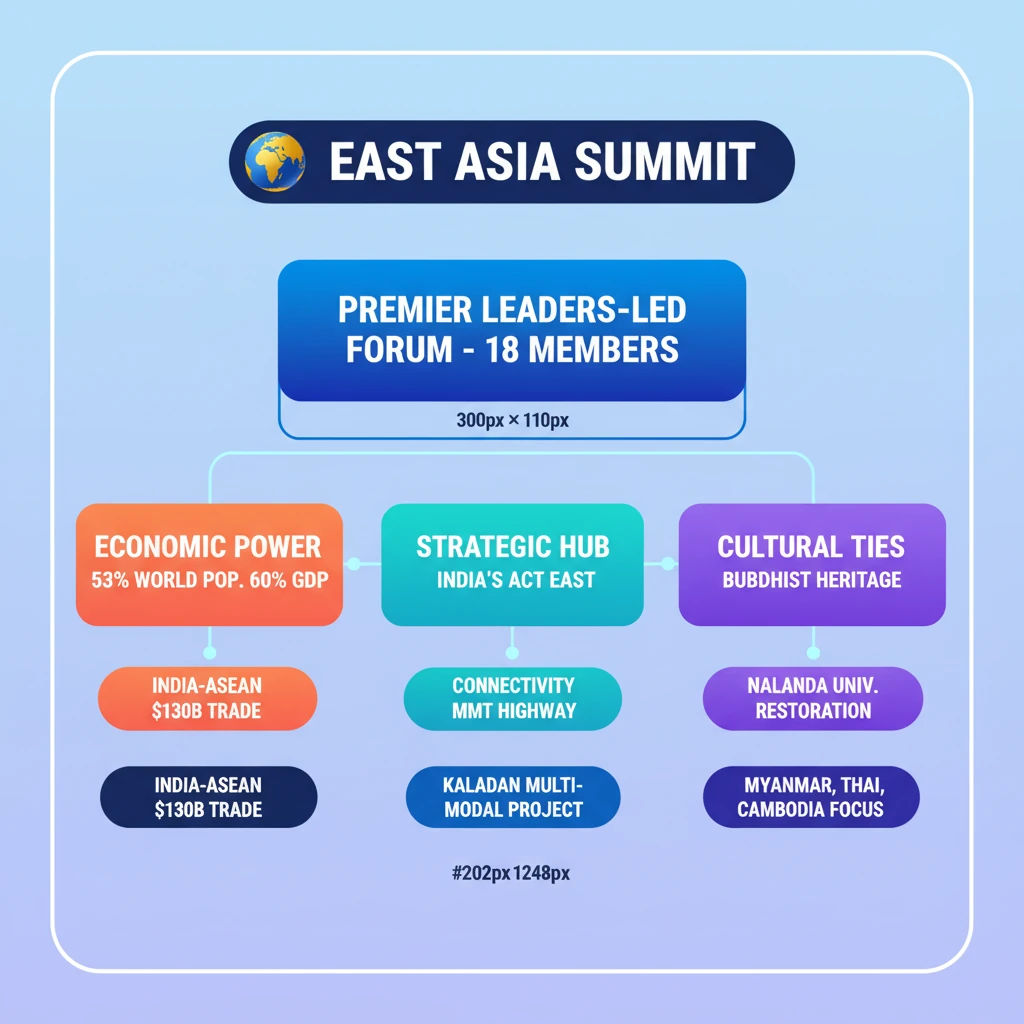
💡 Key Takeaways
- •EAS is a premier leaders-led forum with 18 members, including 10 ASEAN states and 8 dialogue partners (India, US, China, Russia, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand).
- •Economically, EAS members represent 53% of world population and 60% of global GDP; India-ASEAN trade exceeds USD 130 billion.
- •Strategically, EAS is vital for India's Act East Policy, supporting connectivity projects like the India-Myanmar-Thailand Highway and Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport.
- •Culturally, India leverages shared Buddhist heritage, with initiatives like Nalanda University restoration strengthening ties with Myanmar, Thailand, and Cambodia.
- •EAS facilitates comprehensive dialogue on political, security, and economic issues, upholding ASEAN centrality and contributing to regional stability and prosperity.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Official ASEAN and Ministry of External Affairs (India) publications for general EAS context and membership details.