What are the Points of Tensions Between India and Bangladesh? - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are the Points of Tensions Between India and Bangladesh?
Medium⏱️ 9 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
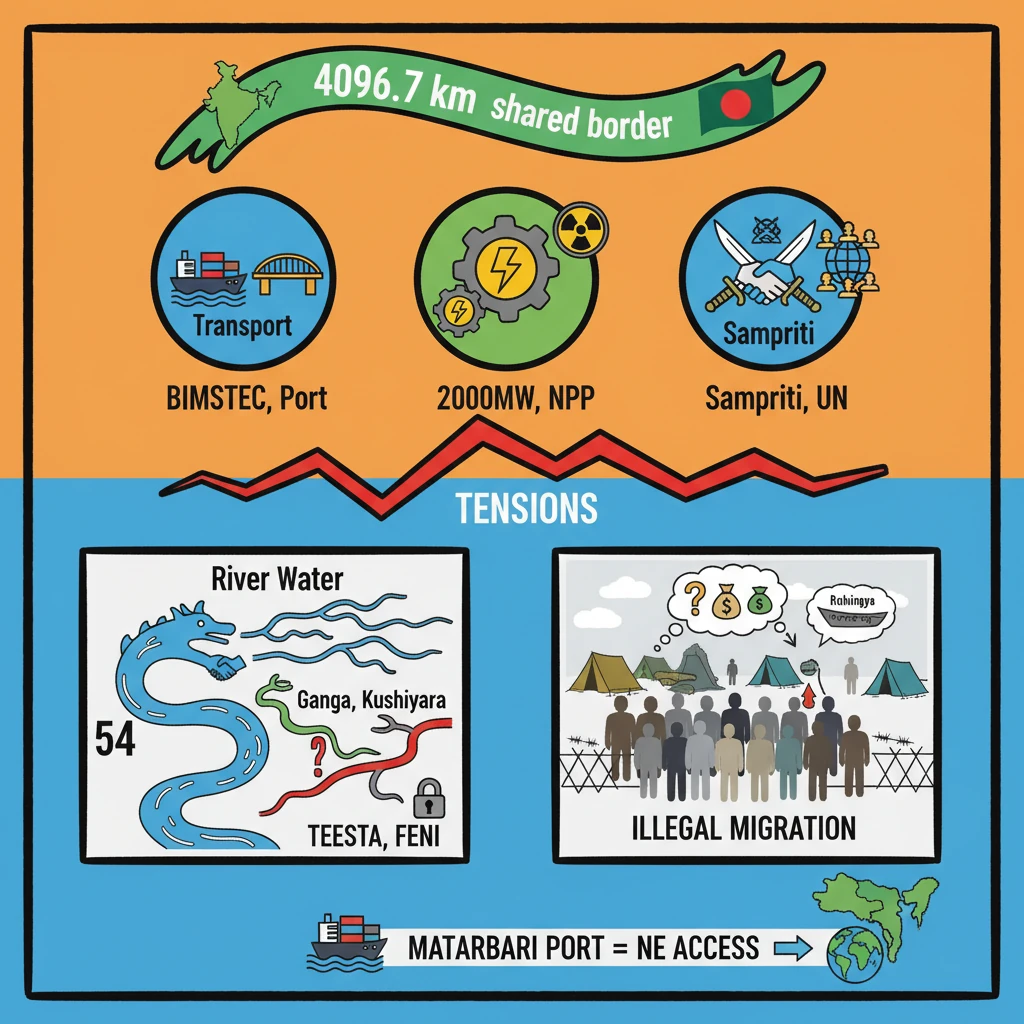
<h4>Introduction to India-Bangladesh Relations</h4><p>India and Bangladesh share a <strong>long-standing relationship</strong> marked by both cooperation and areas of tension. This dynamic partnership is crucial for regional stability and development in South Asia.</p><p>The shared <strong>border</strong> and common cultural ties underscore the importance of understanding the various facets of this bilateral engagement.</p><h4>Areas of Cooperation</h4><h4>Transport Connectivity Initiatives</h4><p>The <strong>BIMSTEC Master Plan for Transport Connectivity</strong> is a key initiative aiming to establish a robust shipping network across India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Thailand.</p><p>India is actively focusing on the <strong>Matarbari Port</strong>, which is being developed by Bangladesh. This port is strategically located approximately <strong>100 km from Tripura</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>Matarbari Port</strong> is envisioned to create a vital <strong>industrial corridor</strong> connecting <strong>Dhaka</strong> and <strong>Northeast India</strong>, significantly boosting trade and regional integration.</p></div><h4>Energy Sector Collaboration</h4><p>Bangladesh currently imports a substantial amount of electricity from India, highlighting significant energy cooperation.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Bangladesh imports nearly <strong>2,000 megawatts (MW) of electricity</strong> from India, demonstrating a strong energy interdependence.</p></div><p>A landmark agreement in <strong>2018</strong> saw <strong>Russia, Bangladesh, and India</strong> sign a memorandum for cooperation in the <strong>Rooppur Nuclear Power Plant project</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>Rooppur Nuclear Power Plant</strong> is significant as it represents <strong>Bangladesh’s first nuclear power reactor</strong>, with India playing a crucial supportive role.</p></div><h4>Defence and Border Management</h4><p>India and Bangladesh share the <strong>longest land boundary</strong> that India has with any of its neighbors, necessitating strong defence cooperation.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The shared border spans <strong>4096.7 km</strong>. Indian states bordering Bangladesh include <strong>Assam, West Bengal, Mizoram, Meghalaya, and Tripura</strong>.</p></div><p>Both nations regularly conduct joint military exercises to enhance interoperability and strengthen security ties.</p><ul><li><strong>Army Exercise:</strong> <strong>Exercise Sampriti</strong></li><li><strong>Navy Exercise:</strong> <strong>Exercise Bongo Sagar</strong></li></ul><h4>Multilateral Engagement</h4><p>India and Bangladesh actively participate in various regional forums, reinforcing their commitment to multilateral cooperation.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Key multilateral forums include <strong>SAARC</strong> (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation), <strong>BIMSTEC</strong> (Bay of Bengal Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation), and <strong>IORA</strong> (Indian Ocean Rim Association).</p></div><h4>Points of Tension Between India and Bangladesh</h4><h4>Sharing of Transboundary River Waters</h4><p>A significant point of contention revolves around the equitable sharing of waters from numerous common rivers.</p><div class='info-box'><p>India and Bangladesh share <strong>54 common rivers</strong>. However, only two major treaties have been signed to date.</p></div><p>These treaties are the <strong>Ganga Waters Treaty</strong> and the more recent <strong>Kushiyara River Treaty</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Major rivers like the <strong>Teesta</strong> and <strong>Feni</strong> are still subjects of ongoing negotiations, posing a challenge to bilateral relations.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding the <strong>water diplomacy challenges</strong> is crucial for Mains answers, especially regarding regional cooperation and environmental security.</p></div><h4>Illegal Migration Concerns</h4><p>The issue of <strong>illegal migration</strong> from Bangladesh into India remains a persistent and significant concern for India.</p><p>This influx includes both <strong>refugees</strong> and <strong>economic migrants</strong>, placing considerable strain on India's border states.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Illegal migration impacts local <strong>resources</strong>, creates demographic shifts, and raises serious <strong>security concerns</strong> in states like <strong>Assam</strong> and <strong>West Bengal</strong>.</p></div><p>The problem was further exacerbated by the entry of <strong>Rohingya refugees</strong> into India, often transiting through Bangladesh, adding another layer of complexity.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>The topic of <strong>cross-border migration</strong> and its socio-economic and security implications is frequently tested in <strong>UPSC Mains GS-II and GS-III</strong>.</p></div>
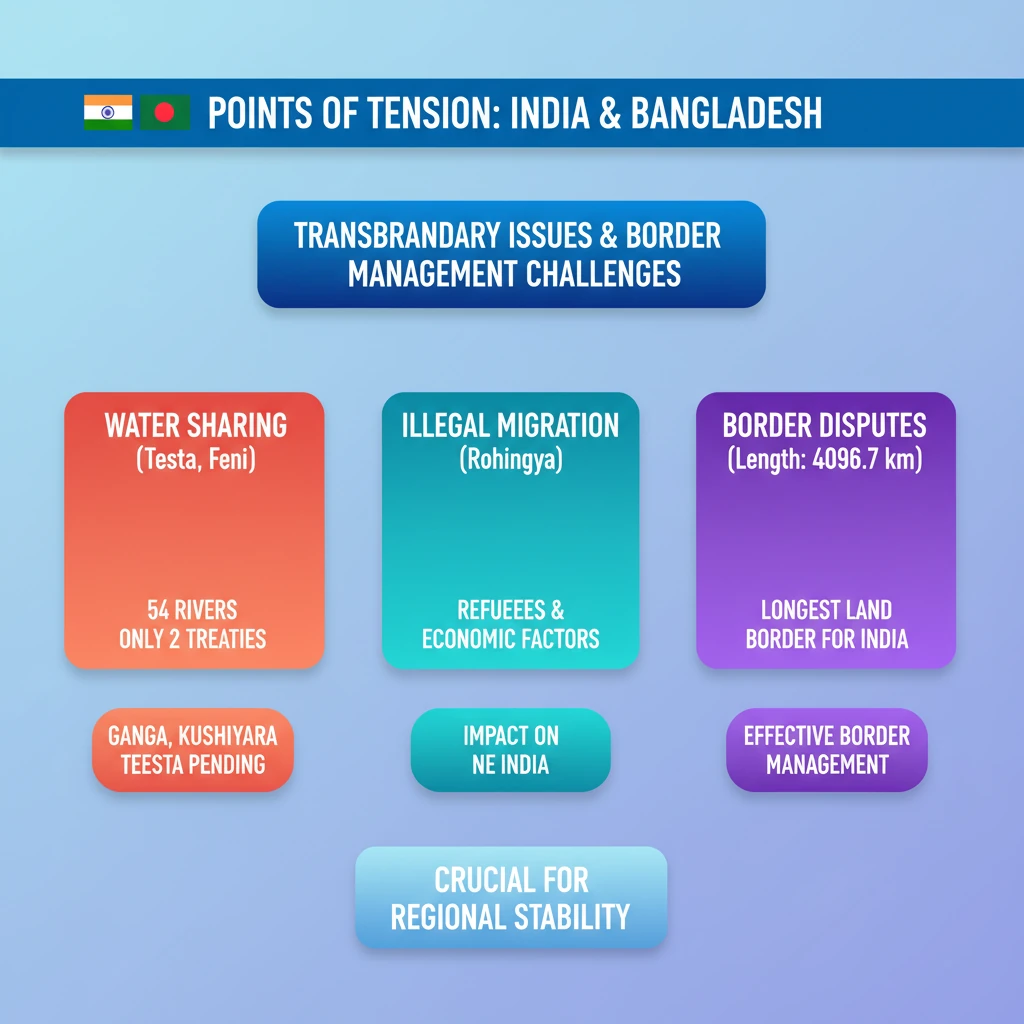
💡 Key Takeaways
- •India and Bangladesh share a 4096.7 km border, India's longest.
- •Cooperation areas include transport (BIMSTEC, Matarbari Port), energy (2000 MW import, Rooppur NPP), defence (Sampriti, Bongo Sagar), and multilateral forums.
- •Key tensions are transboundary river water sharing (54 rivers, only Ganga and Kushiyara treaties; Teesta, Feni pending) and illegal migration (refugees, economic migrants, Rohingya).
- •Connectivity projects like Matarbari Port are vital for Northeast India's access to global markets.
- •Effective border management and water diplomacy are crucial for long-term bilateral stability.
🧠 Memory Techniques
90% Verified Content