India's Nuclear Disarmament Policy & Export Control Regimes - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

India's Nuclear Disarmament Policy & Export Control Regimes
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
<h4>India's Stance on Nuclear Disarmament and Non-Proliferation</h4><p>India has consistently advocated for a comprehensive approach to nuclear issues on the global stage. Its policy centers on achieving <strong>universal</strong>, <strong>non-discriminatory</strong>, and <strong>verifiable nuclear disarmament</strong>. This objective is pursued within a clearly defined <strong>time-bound framework</strong>.</p><p>Alongside its disarmament advocacy, India also actively supports the principles of <strong>non-proliferation</strong>. This dual approach underscores India's commitment to global peace and security, ensuring that nuclear weapons do not spread while working towards their eventual elimination.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>India's Nuclear Doctrine:</strong> India maintains a <strong>credible minimum deterrence</strong> and a <strong>No First Use (NFU) policy</strong>. This doctrine emphasizes a responsible and restrained approach to its nuclear capabilities.</p></div><h4>India's Role in Global Export Control Regimes</h4><p>To further its commitment to international security, India participates in various multilateral export control regimes. These groups are designed to prevent the transfer of sensitive <strong>technology</strong>, <strong>materials</strong>, or <strong>components</strong>.</p><p>The primary goal is to restrict these transfers to entities that pose a significant threat to <strong>international security and stability</strong>. India's membership in these regimes reflects its growing stature as a responsible global actor.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Export Control Regimes India is Part Of:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Wassenaar Arrangement</strong>: Controls conventional arms and dual-use goods and technologies.</li><li><strong>Australia Group (AG)</strong>: Aims to counter the proliferation of chemical and biological weapons.</li><li><strong>Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR)</strong>: Prevents the proliferation of missile and unmanned aerial vehicle technology capable of delivering weapons of mass destruction.</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding India's nuclear policy and its participation in export control regimes is crucial for <strong>GS Paper II (International Relations)</strong>. Questions often focus on India's role in global governance and its strategic autonomy.</p></div>
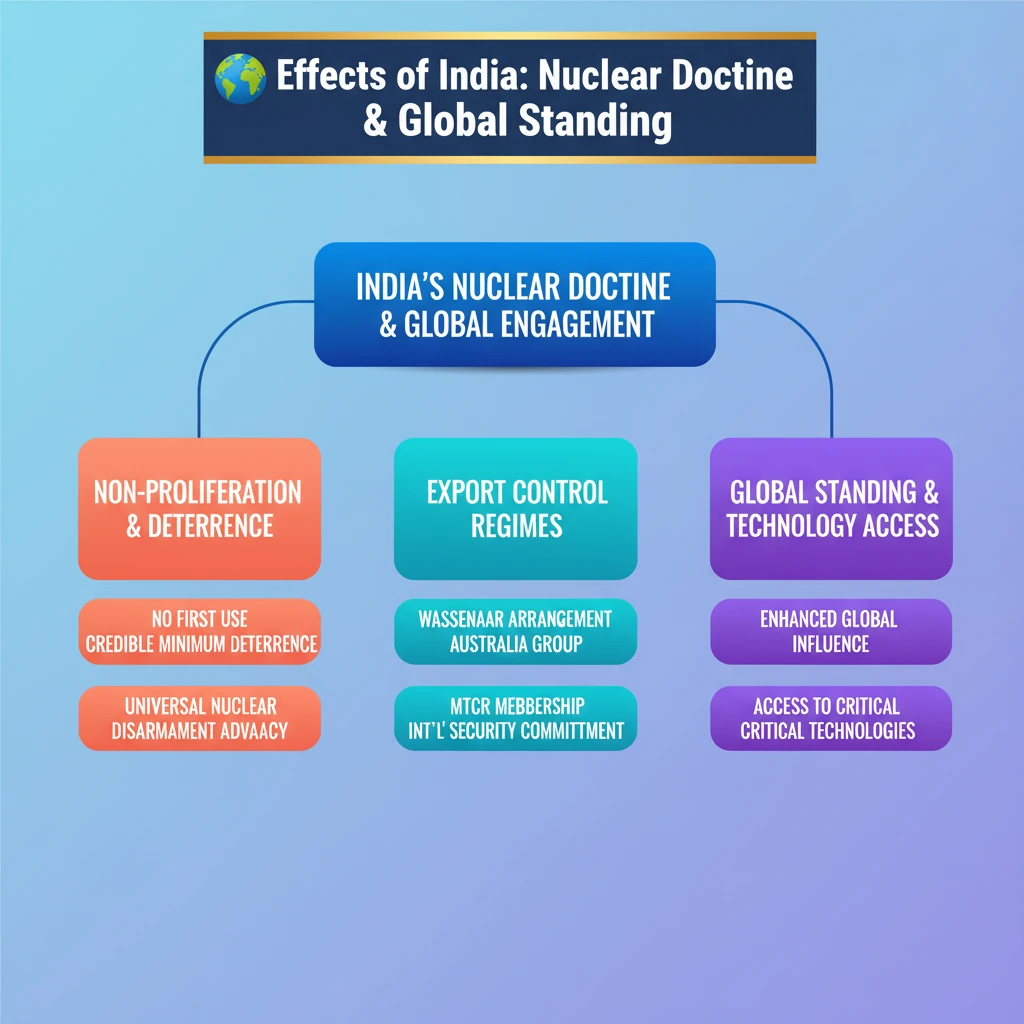
💡 Key Takeaways
- •India advocates for universal, non-discriminatory, time-bound nuclear disarmament.
- •India supports non-proliferation while maintaining a credible minimum deterrence and No First Use policy.
- •India is a member of key export control regimes: Wassenaar Arrangement, Australia Group, and MTCR.
- •These memberships enhance India's global standing and access to critical technologies.
- •India's participation in these regimes reflects its commitment to international security and stability.
- •Membership aids India's bid for Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG) entry.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India official statements
•United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs (UNODA)
•Official websites of Wassenaar Arrangement, Australia Group, MTCR