The AfCFTA is a free trade agreement designed to facilitate duty-free trade within Africa - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

The AfCFTA is a free trade agreement designed to facilitate duty-free trade within Africa
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
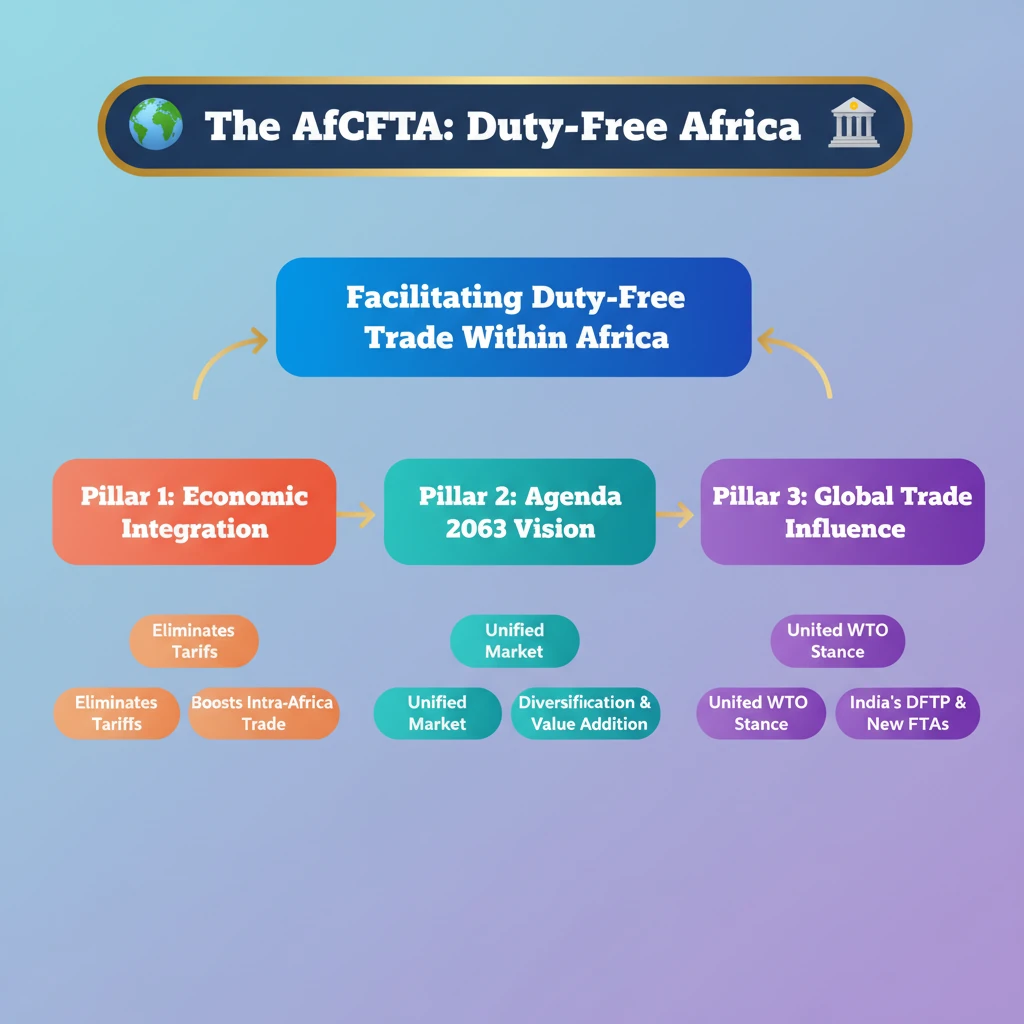
<h4>Introduction to AfCFTA</h4><p>The <strong>African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA)</strong> is a landmark free trade agreement designed to foster duty-free trade across the African continent. Its primary goal is to dismantle both <strong>tariffs</strong> and <strong>non-tariff barriers</strong> among its member states, thereby facilitating the unrestricted movement of goods, services, and people.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>AfCFTA</strong> represents a crucial step towards deeper economic integration in Africa, aiming to create a single continental market.</p></div><h4>Alignment with Africa's Development Framework</h4><p>This ambitious initiative is an integral component of <strong>Africa’s Development Framework Agenda 2063</strong>. This overarching vision seeks to establish a unified economic market throughout the entire African continent, promoting prosperity and sustainable development.</p><h4>India's Trade Relationship with Africa</h4><p>India currently engages in extensive trade with Africa, encompassing a diverse array of products. These range from essential commodities like <strong>crude oil</strong> to various <strong>chemicals</strong> and <strong>textiles</strong>.</p><p>The advent of the <strong>AfCFTA</strong> presents significant opportunities for Africa to pursue trade diversification and value addition. This strategic shift aligns seamlessly with India’s existing export interests and long-term investment strategies on the continent.</p><h4>African Stance on WTO Reforms</h4><p>The <strong>AfCFTA</strong> has the potential to foster a unified African stance on crucial <strong>World Trade Organisation (WTO) reforms</strong>. Key areas of focus include global challenges such as <strong>food security</strong>, agricultural policies, and the equitable transfer of technology.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>A coordinated approach from African nations is vital to advocate for necessary changes in the global trade environment, which has recently shown an increasing trend towards <strong>protectionism</strong>.</p></div><h4>India's Duty-Free Tariff Preference (DFTP) and FTAs</h4><p>India extends its <strong>Duty-Free Tariff Preference (DFTP)</strong> scheme to <strong>27 Least Developed Countries (LDCs)</strong> in Africa. This preference is granted on a <strong>non-reciprocal basis</strong>, meaning these countries benefit without having to offer reciprocal concessions to India.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>DFTP Scheme</strong> by India provides tariff preferences on imports from LDCs. These are countries identified by the UN as disadvantaging nations with the lowest socio-economic indicators, aiming to support their economic development.</p></div><p>Beyond the DFTP, India is actively exploring the possibility of establishing new <strong>Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)</strong> with various African nations. This includes significant economies such as <strong>South Africa</strong>, with the aim of boosting trade volumes and diversifying the range of goods exchanged.</p><h4>Strategic Cooperation with Africa</h4><p>India's engagement with Africa extends beyond trade, encompassing several strategic cooperation initiatives:</p><ul><li><strong>Support for African Union (AU)</strong>: India has been a strong advocate for the <strong>African Union’s full membership in the G20</strong>. This commitment underscores India's dedication to amplifying African voices and concerns on the global stage.</li><li><strong>Special Economic Zones (SEZs)</strong>: India actively encourages its investors to establish a robust presence in Africa’s manufacturing zones. Expanding <strong>SEZs</strong> is viewed as a crucial mechanism for deepening bilateral economic ties and fostering industrial growth.</li><li><strong>Global South Representation</strong>: India positions itself as a leading voice for the <strong>Global South</strong>. In this role, it advocates for policies that promote equitable and inclusive growth within multilateral forums and international organizations.</li></ul>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •AfCFTA aims for duty-free trade within Africa, eliminating tariffs and non-tariff barriers.
- •It's a key pillar of Africa's Agenda 2063, envisioning a unified economic market.
- •India's trade interests align with AfCFTA's push for diversification and value addition.
- •AfCFTA can foster a unified African stance on WTO reforms (food security, agriculture, tech transfer).
- •India offers Duty-Free Tariff Preference (DFTP) to 27 African LDCs and seeks new FTAs.
- •India strategically supports the African Union (AU's G20 membership), promotes SEZs, and champions the Global South.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content