India’s Act East Policy - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

India’s Act East Policy
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
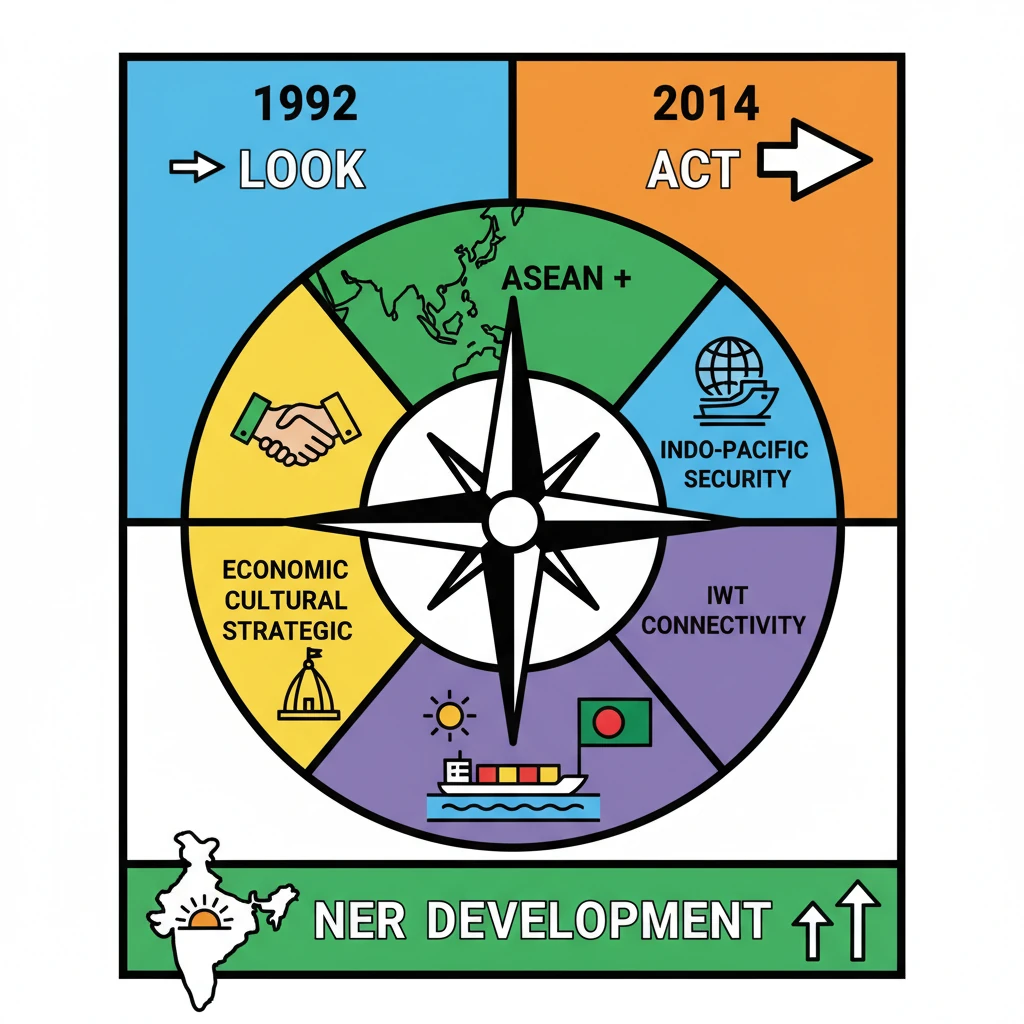
<h4>Introduction: Act East Policy and Inland Water Transport</h4><p>India's <strong>Act East Policy</strong> is a pivotal diplomatic initiative focused on strengthening ties with the vast <strong>Asia-Pacific region</strong>.</p><p>Recently, the policy gained significant momentum with the flagging off of <strong>trial cargo vessels</strong>, emphasizing the crucial role of <strong>Inland Water Transport (IWT)</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>first batch of trial Cargo Vessels</strong> was flagged off from <strong>Mala Inland Custom Port</strong> in West Bengal to <strong>Sultanganj Port</strong> in Bangladesh, marking a key step under the <strong>Act East Policy</strong>.</p></div><h4>Understanding Inland Water Transport (IWT)</h4><p><strong>Inland Water Transport (IWT)</strong> refers to the transportation of goods and passengers via navigable rivers, canals, lakes, and other inland waterways.</p><p>This mode utilizes various watercraft such as <strong>boats, barges, and ships</strong> to move cargo and people within a country's interior regions, connecting various ports and terminals.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>IWT Significance:</strong> It is a highly <strong>cost-effective</strong> mode of transportation, particularly beneficial for <strong>bulk cargo</strong>.</p></div><p>Common bulk cargoes include <strong>coal, iron ore, cement, food grains, and fertilizers</strong>, making IWT vital for industrial and agricultural logistics.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li>Current share in India's modal mix: Only <strong>2%</strong>.</li><li>Government's target by <strong>2030</strong> (under <strong>Maritime India Vision (MIV)-2030</strong>): To increase this share to <strong>5%</strong>.</li><li>The <strong>Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI)</strong> has identified <strong>25 new National Waterways (NWs)</strong> through feasibility studies to make them navigable.</li></ul></div><h4>The Act East Policy: Overview</h4><p>The <strong>'Act East Policy'</strong>, officially announced in <strong>November 2014</strong>, serves as an upgraded and more proactive version of the earlier <strong>“Look East Policy”</strong>.</p><p>It is a comprehensive diplomatic initiative designed to promote robust <strong>economic, strategic, and cultural relations</strong> with the broader <strong>Asia-Pacific region</strong> at various levels.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The policy involves intensive and continuous engagement with <strong>Southeast Asian countries</strong> across multiple critical domains.</p></div><p>Key areas of engagement include <strong>connectivity, trade, culture, defence, and people-to-people contact</strong>, pursued at bilateral, regional, and multilateral platforms.</p><h4>Aims of the Act East Policy</h4><p>The <strong>Act East Policy</strong> adopts a <strong>proactive and pragmatic approach</strong> to achieve several crucial objectives:</p><ul><li>To promote enhanced <strong>economic cooperation</strong> and strengthen <strong>cultural ties</strong> with partner nations.</li><li>To develop deep and enduring <strong>strategic relationships</strong> with countries in the <strong>Indo-Pacific region</strong>.</li><li>To significantly improve the <strong>economic development of the North Eastern Region (NER)</strong>, recognizing its pivotal role as India's gateway to the Southeast Asia Region.</li></ul><h4>Look East vs. Act East Policy: A Comparison</h4><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>Act East Policy</strong> represents an evolution and expansion of the <strong>Look East Policy</strong>, moving towards more comprehensive and dynamic engagement.</p></div><h5>Look East Policy (Launched 1992)</h5><p>The <strong>Look East Policy</strong> primarily focused on the <strong>Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries</strong>.</p><p>Its main emphasis was on fostering greater <strong>economic integration</strong> with these rapidly growing economies.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>1996:</strong> India became a <strong>dialogue partner of ASEAN</strong>.</li><li><strong>2002:</strong> India's relationship with ASEAN was upgraded to a <strong>summit-level partner</strong>.</li><li><strong>2012:</strong> The relationship was further elevated to a <strong>Strategic Partnership</strong>.</li><li><strong>Trade Growth:</strong> India's trade with ASEAN grew from <strong>USD 2 billion</strong> (1992) to <strong>USD 72 billion</strong> (2017-18) after the signing of the <strong>Free Trade Agreement (FTA) in 2010</strong>.</li></ul></div><p>India was also an active participant in several regional forums during this period, including the <strong>East Asia Summit (EAS)</strong> and the <strong>ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF)</strong>.</p><h5>Act East Policy (Launched 2014)</h5><p>The <strong>Act East Policy</strong> expands its geographical focus to include not only <strong>ASEAN countries</strong> but also the broader <strong>East Asian countries</strong> and the entire <strong>Indo-Pacific region</strong>.</p><p>Beyond economic integration, a key differentiator is its strong emphasis on <strong>security cooperation</strong> and strategic partnerships.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> The shift from 'Look' to 'Act' signifies a move from passive observation to a more <strong>proactive, multi-dimensional, and results-oriented strategy</strong>, encompassing defence, security, and strategic partnerships alongside economic and cultural ties.</p></div>
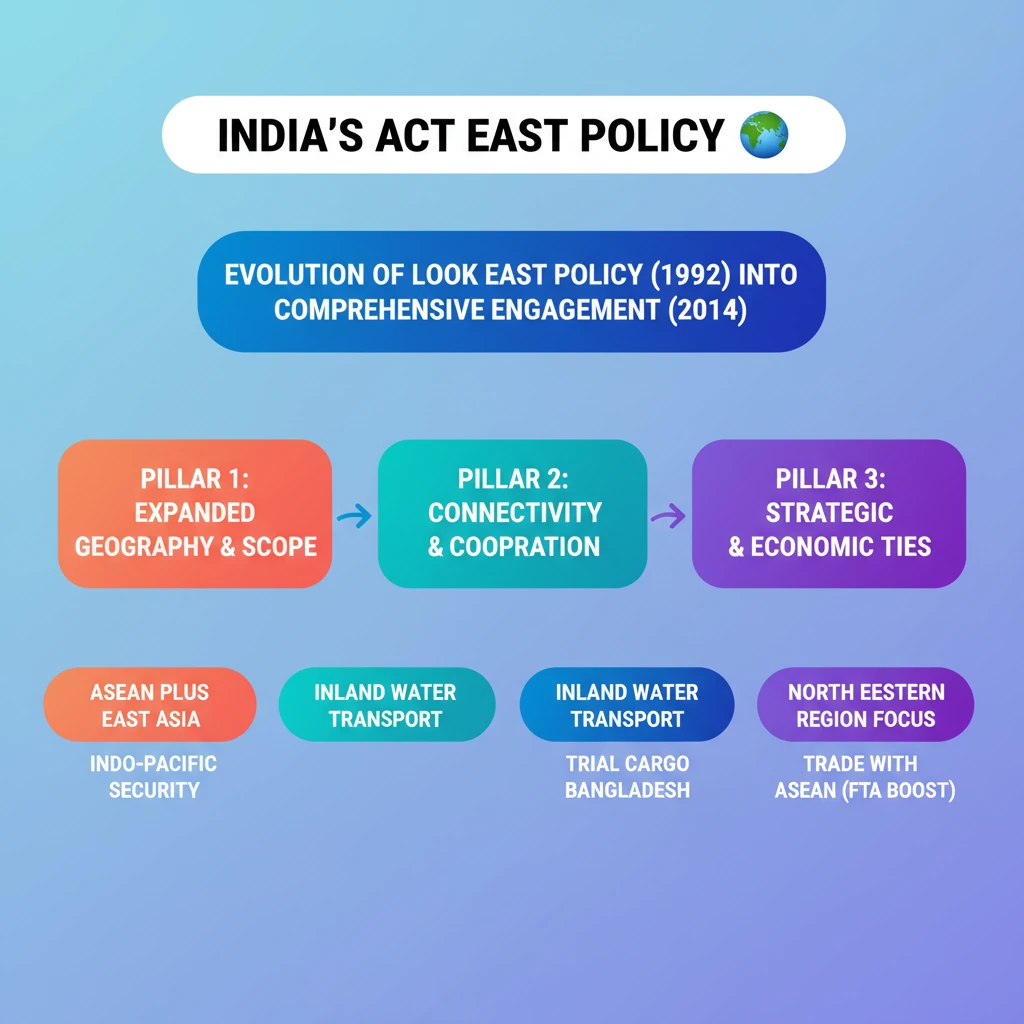
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Act East Policy (2014) is an upgrade of Look East Policy (1992), expanding geographical and thematic scope.
- •Shift from primarily economic integration with ASEAN to comprehensive engagement including East Asia, Indo-Pacific, and security cooperation.
- •Inland Water Transport (IWT) is a key connectivity pillar, exemplified by trial cargo vessels to Bangladesh.
- •AEP aims to promote economic cooperation, cultural ties, strategic relations, and significantly develop India's North Eastern Region (NER).
- •India's trade with ASEAN grew substantially post-FTA, highlighting the economic success of the earlier policy and setting the stage for AEP's expansion.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content