Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India Pipeline - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India Pipeline
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
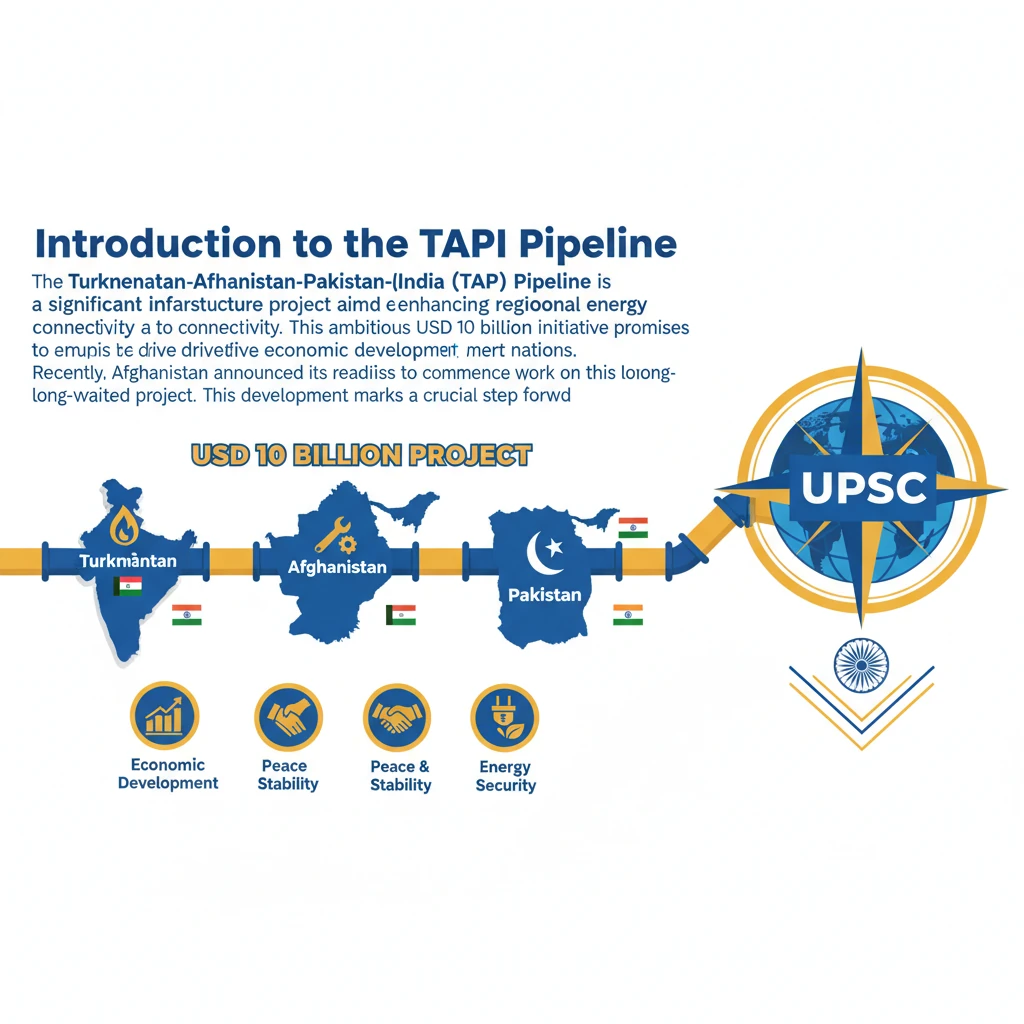
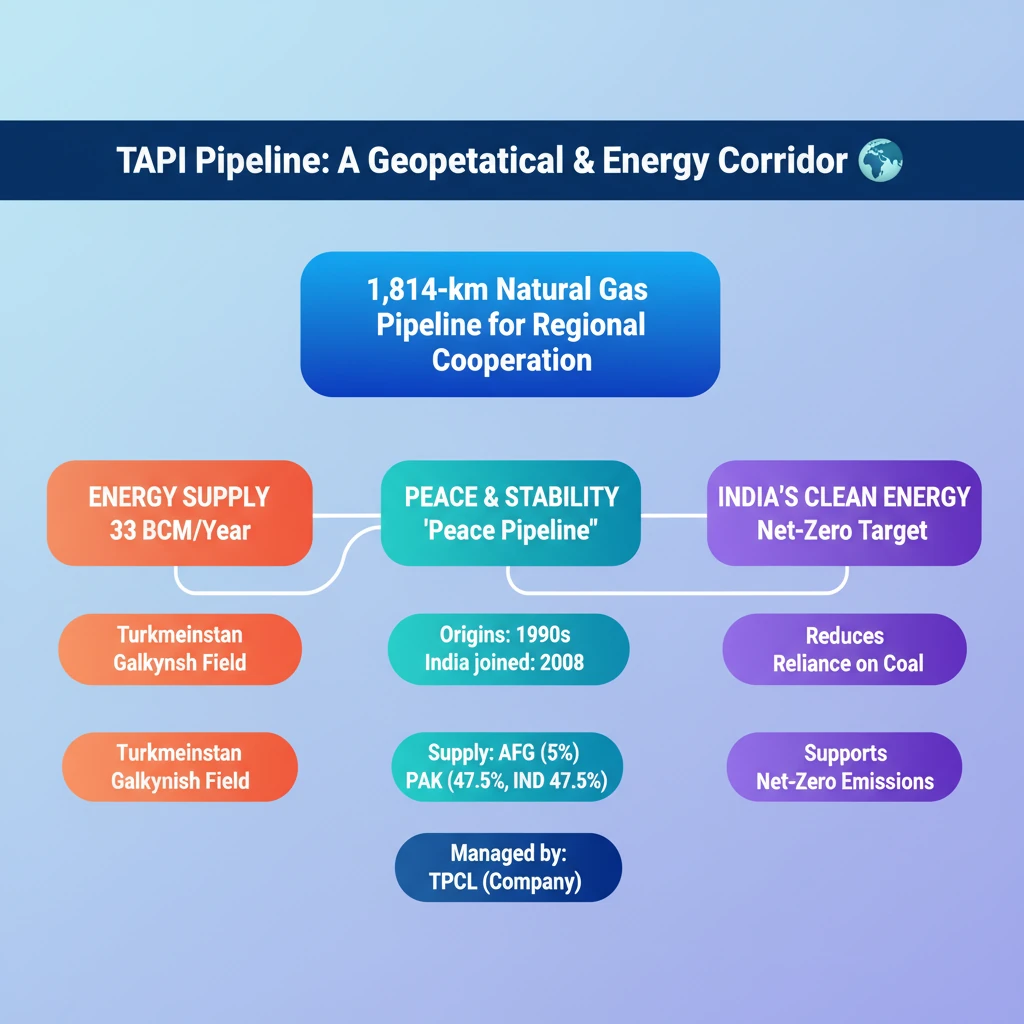
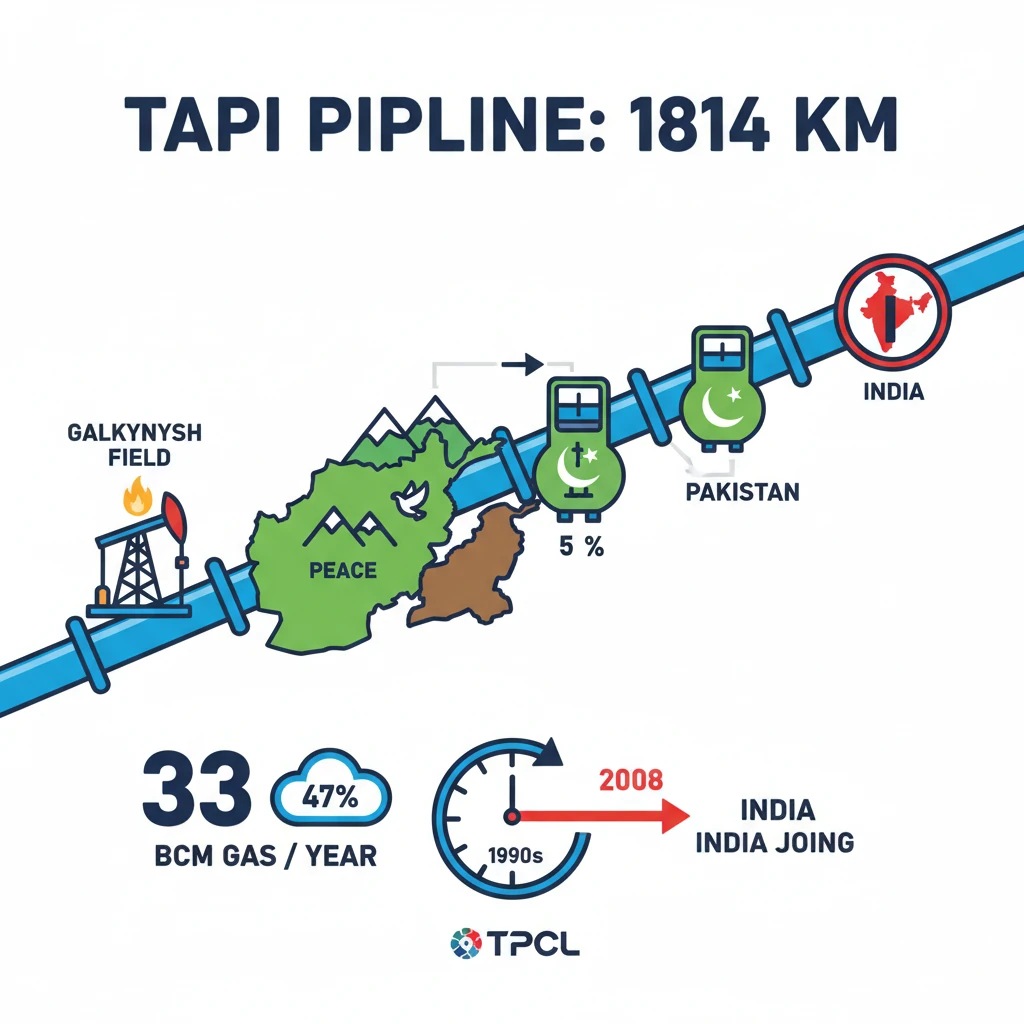
<h4>Introduction to the TAPI Pipeline</h4><p>The <strong>Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India (TAPI) Pipeline</strong> is a significant infrastructure project aimed at enhancing regional energy connectivity. This ambitious <strong>USD 10 billion</strong> initiative promises to drive economic development across the participating nations.</p><p>Recently, <strong>Afghanistan</strong> announced its readiness to commence work on this long-awaited project. This development marks a crucial step forward after years of delays, primarily attributed to prevailing security concerns within Afghanistan.</p><h4>What is the TAPI Pipeline?</h4><p>The <strong>TAPI Pipeline</strong> is an extensive natural gas pipeline designed to transport gas from <strong>Turkmenistan's Galkynysh gas field</strong>. It will traverse through <strong>Afghanistan</strong> and <strong>Pakistan</strong> before reaching <strong>India</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Specifications:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Length:</strong> Approximately <strong>1,814-kilometres</strong></li><li><strong>Annual Capacity:</strong> Expected to deliver around <strong>33 billion cubic metres (BCM)</strong> of natural gas</li><li><strong>Operational Period:</strong> Projected to operate for <strong>30 years</strong></li></ul></div><p>The pipeline is also widely known as the <strong>‘Peace Pipeline’</strong>. This moniker reflects its significant potential to foster greater regional cooperation and contribute to stability among the involved countries.</p><h4>Gas Distribution and Beneficiaries</h4><p>The natural gas transported through the <strong>TAPI Pipeline</strong> will be distributed among the four participating nations. Each country has a specific share allocated for its energy needs.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Annual Gas Allocation:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Afghanistan:</strong> 5%</li><li><strong>Pakistan:</strong> 47.5%</li><li><strong>India:</strong> 47.5%</li></ul></div><h4>Historical Development and Ownership</h4><p>The concept of the <strong>TAPI Pipeline</strong> originated in the <strong>1990s</strong>, laying the groundwork for future energy collaboration. Significant progress on the project was achieved in <strong>2003</strong>, with strong backing from the <strong>Asian Development Bank (ADB)</strong>.</p><p><strong>India</strong> officially joined the initiative in <strong>2008</strong>, marking a pivotal moment in the pipeline's development and solidifying its regional scope. The project is managed by a dedicated entity.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>TAPI Pipeline Company Limited (TPCL)</strong> is responsible for both the construction and ongoing operation of the pipeline. It operates as a joint venture with shares held by <strong>Turkmengas</strong> (Turkmenistan), <strong>Afghan Gas</strong> (Afghanistan), and entities from <strong>Pakistan</strong> and <strong>India</strong>.</p></div><h4>Significance of the TAPI Pipeline</h4><p>The pipeline holds immense significance for energy security, environmental sustainability, and regional geopolitics. It presents a crucial alternative to traditional energy sources.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Environmental Impact:</strong> The <strong>TAPI Pipeline</strong> offers a vital alternative to <strong>coal</strong>, which is a major contributor to carbon emissions. By facilitating the use of natural gas, it can significantly reduce <strong>carbon dioxide emissions</strong> compared to coal-fired energy generation.</p></div><p>For <strong>India</strong>, which currently relies heavily on <strong>coal</strong> for its energy requirements, <strong>TAPI</strong> could play a transformative role. It is expected to facilitate a smoother transition towards cleaner energy sources, thereby assisting India in achieving its ambitious <strong>emission reduction goals</strong> and its <strong>Net-Zero Emissions Target</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understand <strong>TAPI</strong> not just as an energy project, but as a geopolitical tool for regional stability and a key component of India's energy diversification strategy. Connect it to India's <strong>'Act East' policy</strong> and climate commitments like <strong>Net-Zero by 2070</strong>.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •TAPI is a 1,814-km natural gas pipeline from Turkmenistan (Galkynysh field) to India, via Afghanistan and Pakistan.
- •It aims to deliver 33 BCM of gas annually, supplying Afghanistan (5%), Pakistan (47.5%), and India (47.5%).
- •Known as the 'Peace Pipeline,' it promotes regional cooperation and stability.
- •Origins in the 1990s, with India joining in 2008; managed by TAPI Pipeline Company Limited (TPCL).
- •Significantly aids India's transition to cleaner energy, supporting its Net-Zero Emissions Target by reducing reliance on coal.
- •Recent Afghan commitment signals a potential breakthrough after years of security-related delays.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Asian Development Bank (ADB) official reports on TAPI
•Official websites/statements from TAPI Pipeline Company Limited (TPCL) member countries