Economic Community of West African States - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Economic Community of West African States
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
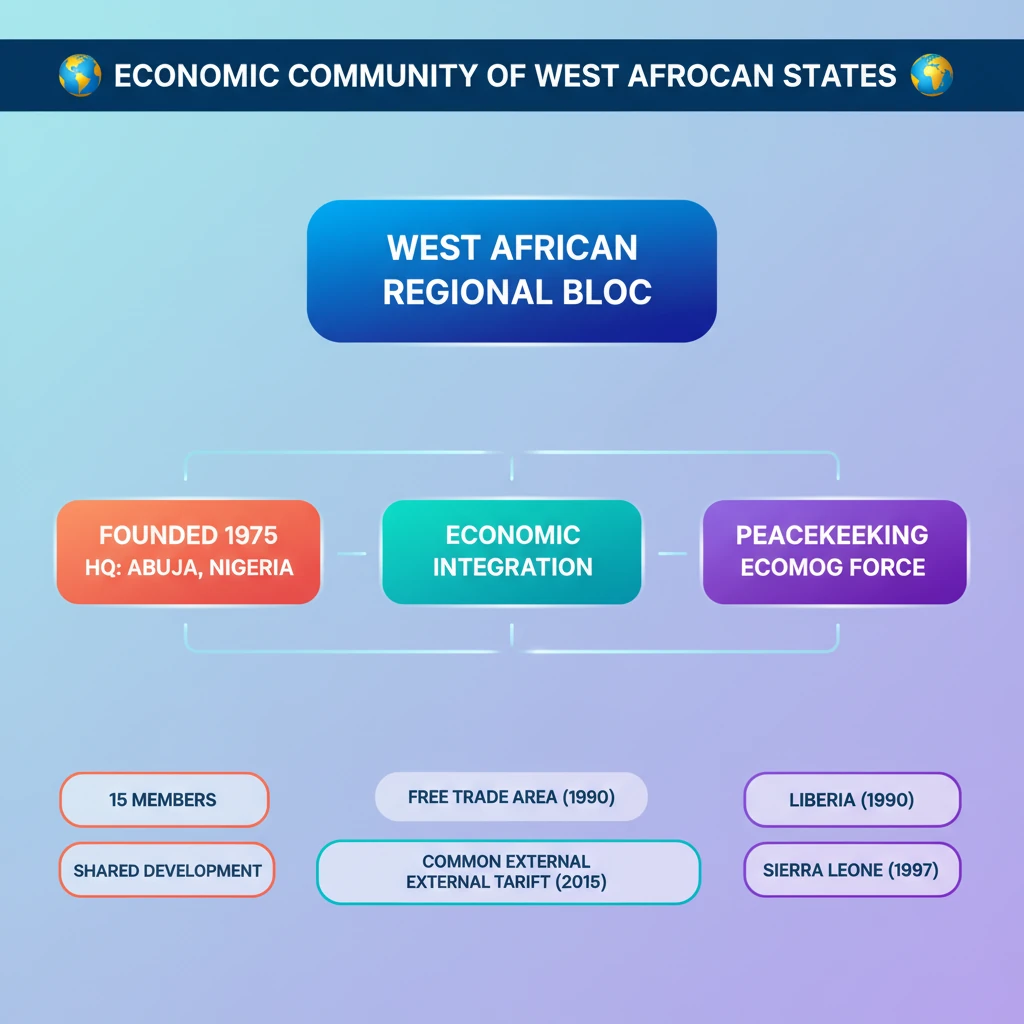
<h4>Introduction to ECOWAS</h4><p>The <strong>Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)</strong> is a prominent regional political and economic union of fifteen countries located in <strong>West Africa</strong>. Established on <strong>May 28, 1975</strong>, with the signing of the <strong>Treaty of Lagos</strong>, its primary goal is to promote economic integration across the region.</p><p><strong>ECOWAS</strong> aims to create a large, unified trading bloc, fostering economic growth and development among its member states. It also plays a significant role in regional peace and security initiatives.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Founding Date:</strong> <strong>May 28, 1975</strong></p><p><strong>Founding Treaty:</strong> <strong>Treaty of Lagos</strong></p><p><strong>Headquarters:</strong> <strong>Abuja, Nigeria</strong></p><p><strong>Current Members (before recent withdrawals):</strong> 15 West African nations</p></div><h4>Objectives of ECOWAS</h4><p>The core objectives of <strong>ECOWAS</strong> are multifaceted, encompassing economic, social, and political dimensions. These aims are designed to uplift the living standards of its citizens and maintain regional stability.</p><ul><li>To promote <strong>cooperation and integration</strong>, leading to the establishment of an economic union in <strong>West Africa</strong>.</li><li>To foster the creation of a <strong>single common market</strong> through the liberalization of trade.</li><li>To ensure <strong>regional peace and security</strong> through various protocols and mechanisms.</li><li>To facilitate the <strong>free movement of people, goods, and services</strong> within the sub-region.</li><li>To harmonize agricultural, industrial, monetary, and social policies among member states.</li></ul><h4>Institutional Structure</h4><p><strong>ECOWAS</strong> operates through a robust institutional framework designed to implement its policies and achieve its objectives. Key institutions include the <strong>Authority of Heads of State and Government</strong>, the <strong>Council of Ministers</strong>, and the <strong>ECOWAS Commission</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>Authority of Heads of State and Government</strong> is the supreme decision-making body, providing overall policy direction. The <strong>ECOWAS Commission</strong> serves as the executive arm, managing daily affairs and implementing decisions.</p></div><p>Other vital institutions include the <strong>Community Parliament</strong>, the <strong>Community Court of Justice</strong>, and the <strong>ECOWAS Bank for Investment and Development (EBID)</strong>. These bodies ensure legislative oversight, legal redress, and financial support for regional projects.</p><h4>Key Achievements</h4><p>Over the decades, <strong>ECOWAS</strong> has achieved several notable milestones in regional integration and conflict resolution. Its efforts have contributed to stability and economic growth in the sub-region.</p><ul><li>Successful implementation of a <strong>free movement protocol</strong>, allowing citizens to travel and reside in member states without visas.</li><li>Establishment of the <strong>ECOWAS Cease-fire Monitoring Group (ECOMOG)</strong>, which intervened in conflicts in <strong>Liberia</strong> and <strong>Sierra Leone</strong>.</li><li>Progress towards a <strong>single currency zone (Eco)</strong>, though this objective has faced significant delays.</li><li>Promotion of democratic governance and constitutional rule through various protocols and election monitoring missions.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>For <strong>UPSC Mains GS-II (International Relations)</strong>, understanding the institutional mechanisms and intervention capabilities of regional blocs like <strong>ECOWAS</strong> is crucial. Focus on its role in both economic integration and peace-keeping.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •ECOWAS is a West African regional economic and political union, established in 1975 by the Treaty of Lagos.
- •Its core objectives are economic integration (common market, free movement) and regional peace/security.
- •The 1993 Revised Treaty expanded its mandate to include political and security cooperation, leading to interventions like ECOMOG.
- •Recent withdrawals by Burkina Faso, Mali, and Niger highlight challenges to ECOWAS's unity and its approach to military coups.
- •ECOWAS plays a critical role in 'African solutions to African problems' but faces significant internal and external pressures.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•African Union (AU) publications on regional economic communities
•Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) analyses on West Africa
•Reputable international news agencies (e.g., Reuters, BBC, Al Jazeera) for recent developments.