What is the UN Charter? - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What is the UN Charter?
Easy⏱️ 8 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
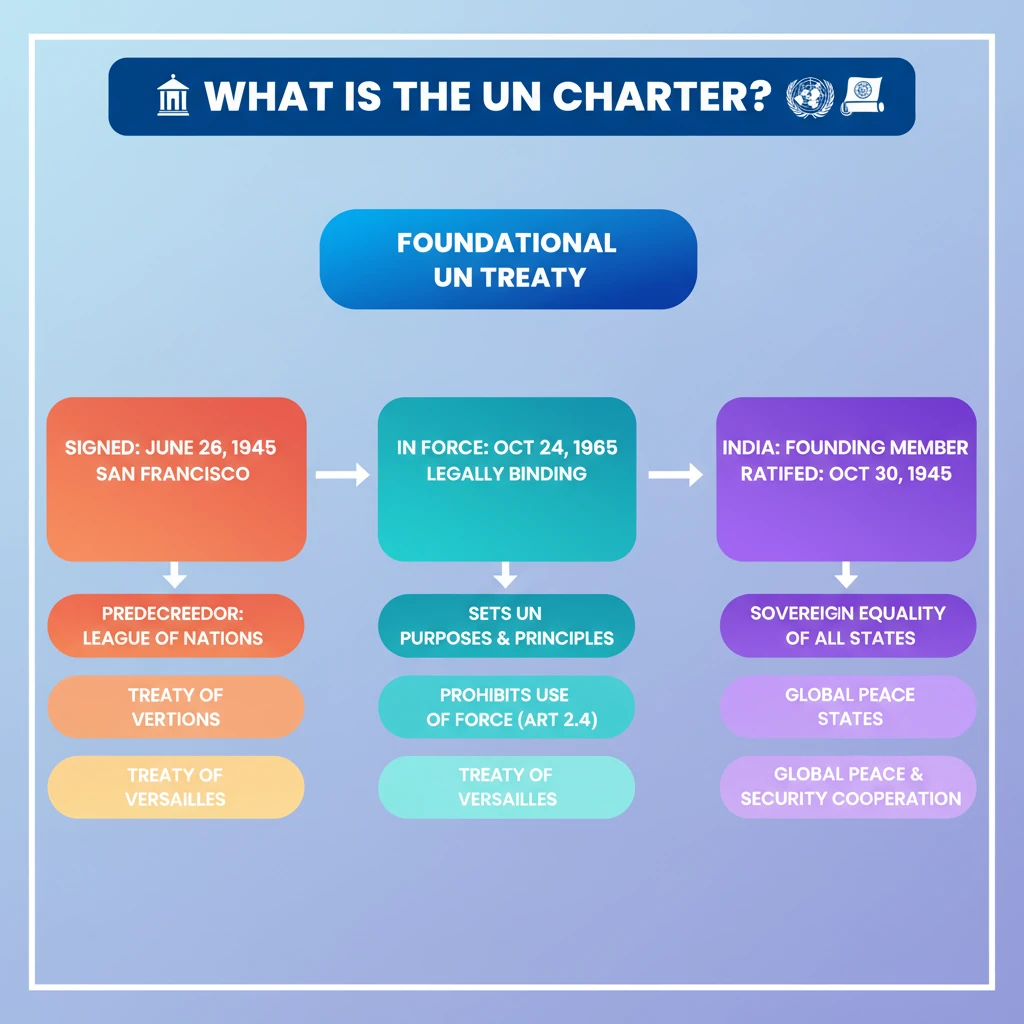
<h4>Origin and Adoption of the UN Charter</h4><p>The <strong>United Nations Charter</strong> is the foundational treaty of the <strong>United Nations (UN)</strong>. It was a landmark agreement established to prevent future global conflicts and foster international cooperation.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Signed:</strong> <strong>June 26, 1945</strong>, in <strong>San Francisco</strong>, at the conclusion of the <strong>UN Conference on International Organization</strong>.</p><p><strong>Came into Force:</strong> <strong>October 24, 1945</strong>. This date is now celebrated annually as <strong>United Nations Day</strong>.</p></div><p><strong>India</strong> played a significant role as one of the <strong>founding members</strong> of the United Nations. India officially ratified the <strong>UN Charter</strong> on <strong>October 30, 1945</strong>, shortly after its entry into force, demonstrating its early commitment to multilateralism.</p><h4>Predecessor: The League of Nations</h4><p>The concept of a global organization for peace emerged after devastating world wars. The immediate predecessor to the <strong>UN</strong> was the <strong>League of Nations</strong>, established after the first global conflict.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Established:</strong> <strong>1919</strong>, following the end of <strong>World War I</strong>.</li><li><strong>Foundation:</strong> Under the provisions of the <strong>Treaty of Versailles</strong>.</li><li><strong>Primary Objective:</strong> To “promote international cooperation and to achieve peace and security.”</li></ul></div><p>The experiences and shortcomings of the <strong>League of Nations</strong>, particularly its inability to prevent <strong>World War II</strong>, heavily influenced the structure and principles embedded within the <strong>UN Charter</strong>, aiming for a more robust and effective international body.</p><h4>Core Nature and Principles of the UN Charter</h4><p>The <strong>UN Charter</strong> serves as the fundamental constitutional document for the entire <strong>United Nations</strong> system. It delineates the rights and obligations of member states and guides their conduct on the international stage.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The Charter is a binding <strong>instrument of international law</strong>. All <strong>UN Member States</strong> are legally obligated to adhere to its principles and provisions, making it a cornerstone of global governance.</p></div><p>It lays down the bedrock principles that govern modern international relations. These principles are crucial for fostering a stable and cooperative global environment and preventing conflicts.</p><ul><li><strong>Equal Rights of All Countries:</strong> Emphasizes the sovereign equality of all member states, regardless of their size or economic power.</li><li><strong>Ban on Using Force:</strong> Prohibits the threat or use of force against the territorial integrity or political independence of any state, except in self-defense or under UN Security Council authorization.</li></ul><h4>Amendments to the Charter</h4><p>Despite its foundational status, the <strong>UN Charter</strong> is not immutable. It has undergone several amendments to adapt to changing global realities and the expanding membership of the organization, ensuring its continued relevance.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The Charter has been amended <strong>three times</strong> since its initial incorporation:</p><ol><li><strong>1963:</strong> Amendments to Articles 23, 27, and 61, primarily concerning the enlargement of the <strong>Security Council</strong> and <strong>Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)</strong>.</li><li><strong>1965:</strong> Further amendment to Article 109, regarding the review conference.</li><li><strong>1973:</strong> Amendment to Article 61, concerning the enlargement of the <strong>Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)</strong> once more.</li></ol></div><h4>Significance and Role of the UN Charter</h4><p>For over <strong>75 years</strong>, the <strong>UN Charter</strong> has been instrumental in shaping global governance and promoting collective action on critical international issues, demonstrating its enduring impact.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>UN</strong>, guided by its Charter, focuses on several core pillars to achieve its overarching goals of peace, development, and human rights:</p><ul><li><strong>Maintaining International Peace and Security:</strong> Through diplomatic efforts, peacekeeping missions, and sanctions.</li><li><strong>Providing Humanitarian Assistance:</strong> Responding to crises, conflicts, and natural disasters worldwide.</li><li><strong>Protecting Human Rights:</strong> Upholding universal human rights and fundamental freedoms for all individuals.</li><li><strong>Upholding International Law:</strong> Promoting justice and respect for obligations arising from treaties and other sources of international law.</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding the <strong>UN Charter's principles</strong> is vital for UPSC aspirants, especially for questions related to <strong>International Relations (GS Paper 2)</strong>, global governance, and India's foreign policy. It forms the basis for many contemporary international debates.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The UN Charter was signed on June 26, 1945, in San Francisco, and came into force on October 24, 1945.
- •It is the foundational, legally binding treaty of the United Nations, setting its purposes and principles.
- •India is a founding member of the UN and ratified the Charter on October 30, 1945.
- •The League of Nations, established after World War I under the Treaty of Versailles, was its direct predecessor.
- •Key principles include the sovereign equality of all states and the prohibition on the use of force in international relations.
- •The Charter has been amended three times (1963, 1965, 1973) to adapt to changing global realities and UN membership.
- •Its significance lies in maintaining international peace and security, providing humanitarian assistance, protecting human rights, and upholding international law for over 75 years.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Official United Nations Website (un.org) - Charter of the United Nations