Dispute Settlement Body (DSB) - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Dispute Settlement Body (DSB)
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
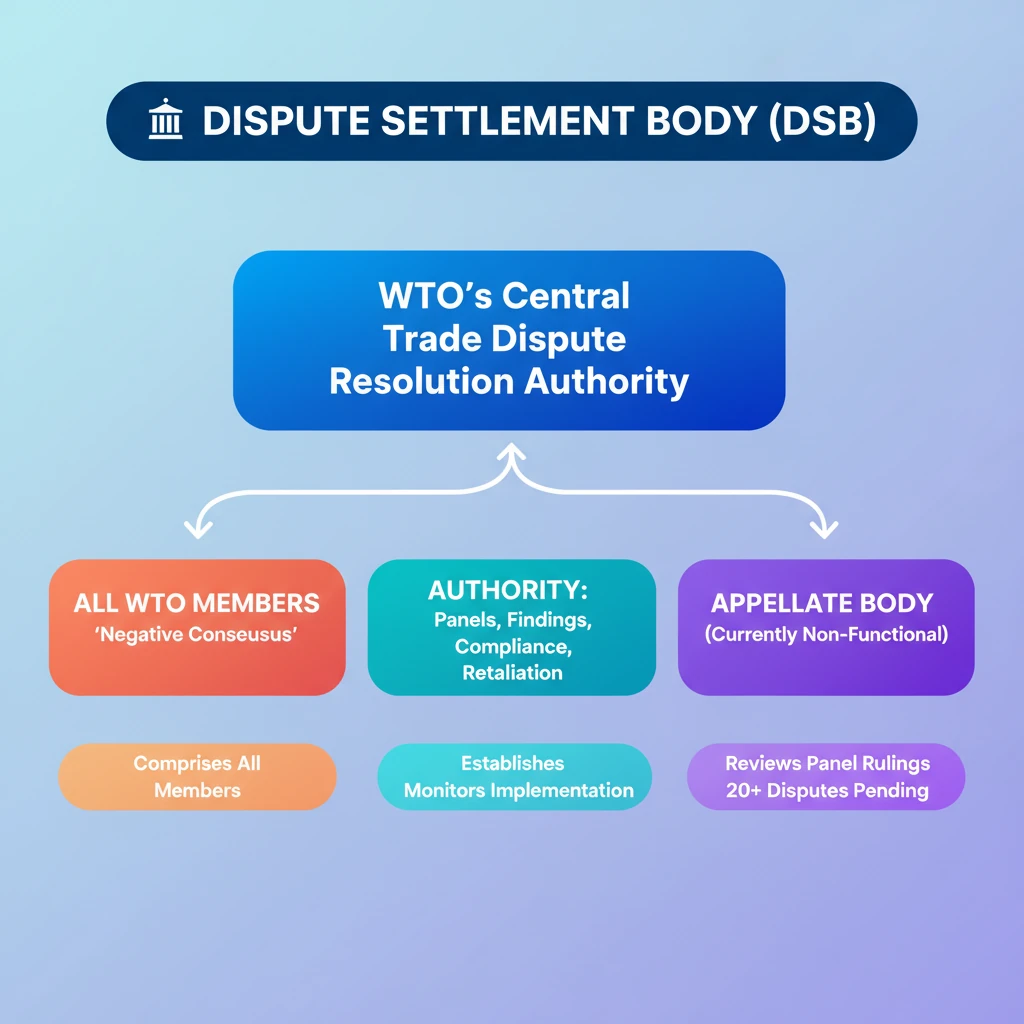
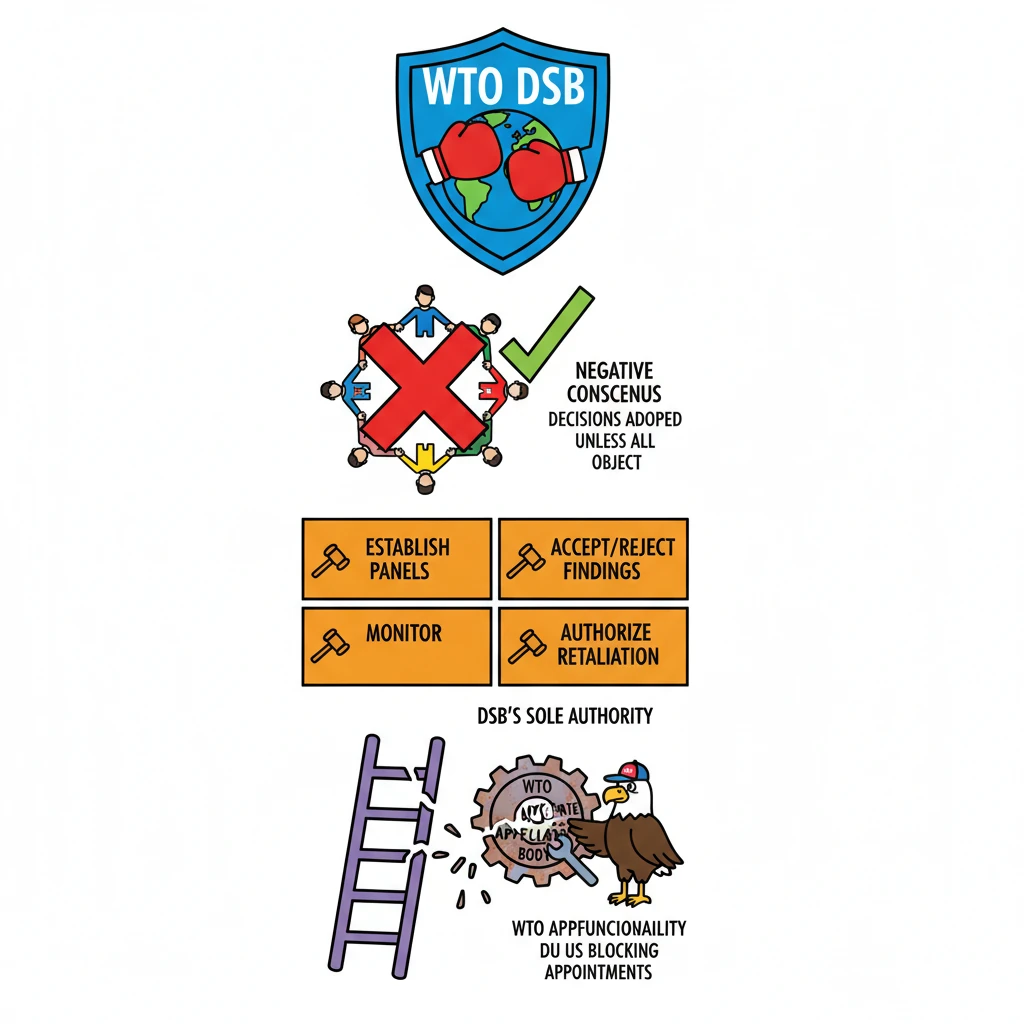
<h4>Introduction to the Dispute Settlement Body (DSB)</h4><p>The <strong>Dispute Settlement Body (DSB)</strong> is a pivotal institution within the <strong>World Trade Organization (WTO)</strong>. Its primary function is to manage and resolve trade disputes that arise between various <strong>member countries</strong> of the WTO.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>DSB</strong> comprises representatives from <strong>all WTO member countries</strong>, ensuring broad participation and legitimacy in its decision-making processes regarding international trade disagreements.</p></div><h4>Decision-Making by Consensus</h4><p>A distinctive feature of the <strong>DSB's</strong> operation is its decision-making mechanism. All decisions made by the <strong>DSB</strong> are achieved through <strong>consensus</strong>. This means that a decision is adopted unless there is an explicit objection from all members present.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>consensus</strong> rule implies that a decision is adopted unless *all* members explicitly object, a mechanism often referred to as <strong>'reverse consensus'</strong> or <strong>'negative consensus'</strong>, making it difficult to block rulings.</p></div><h4>Powers and Authority of the DSB</h4><p>The <strong>DSB</strong> holds exclusive authority over several critical stages of the dispute settlement process. This centralized power ensures consistency and adherence to WTO rules.</p><ul><li>It has the <strong>sole authority</strong> to <strong>establish panels of experts</strong>. These panels are tasked with thoroughly examining specific trade disputes brought before the WTO.</li><li>The <strong>DSB</strong> also possesses the power to either <strong>accept or reject the findings</strong> presented by these expert panels. This oversight ensures the integrity of the dispute resolution process.</li><li>Furthermore, it can accept or reject the <strong>results of an appeal</strong>, once a panel's finding has been reviewed by the Appellate Body.</li></ul><h4>Monitoring and Enforcement</h4><p>Beyond initial rulings, the <strong>DSB</strong> plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance with its decisions. It actively monitors how member countries implement the rulings and recommendations issued.</p><p>In cases where a country fails to comply with a ruling, the <strong>DSB</strong> is empowered to <strong>authorize retaliation</strong>. This can involve allowing the aggrieved country to impose trade sanctions on the non-compliant member, providing a robust mechanism for enforcement.</p><h4>The Appellate Body and Its Current Crisis</h4><p>Panel rulings or reports can be challenged at the <strong>WTO's Appellate Body (WTOAB)</strong>. The <strong>Appellate Body</strong> serves as the highest judicial authority in the WTO's dispute settlement system, reviewing points of law in panel reports.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Currently, the <strong>WTO Appellate Body</strong> is <strong>not functioning</strong>. This critical situation stems from significant differences among <strong>member countries</strong> regarding the appointment of new members to this body.</p></div><p>The <strong>United States (US)</strong> has been consistently blocking the appointment of new members, leading to a shortage of judges required for the Appellate Body to hear new cases. As a result, <strong>over 20 disputes</strong> are presently pending without resolution at the Appellate Body level.</p><div class='highlight-box'><p>The paralysis of the <strong>Appellate Body</strong> represents a major challenge to the <strong>rule-based multilateral trading system</strong> and is a frequently discussed topic in international relations and global governance.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The Dispute Settlement Body (DSB) is the WTO's central authority for resolving trade disputes among member countries.
- •It comprises all WTO members and makes decisions by 'negative consensus' (decisions adopted unless all members object).
- •The DSB has sole authority to establish expert panels, accept/reject findings, monitor implementation, and authorize retaliation for non-compliance.
- •The WTO Appellate Body (WTOAB) reviews panel rulings but is currently non-functional due to the US blocking appointments of new members.
- •Over 20 disputes are pending at the Appellate Body, significantly challenging the effectiveness and credibility of the multilateral trading system.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•World Trade Organization (WTO) official website (for general structure and functions and Appellate Body status)