What is Act East Policy? - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
What is Act East Policy?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
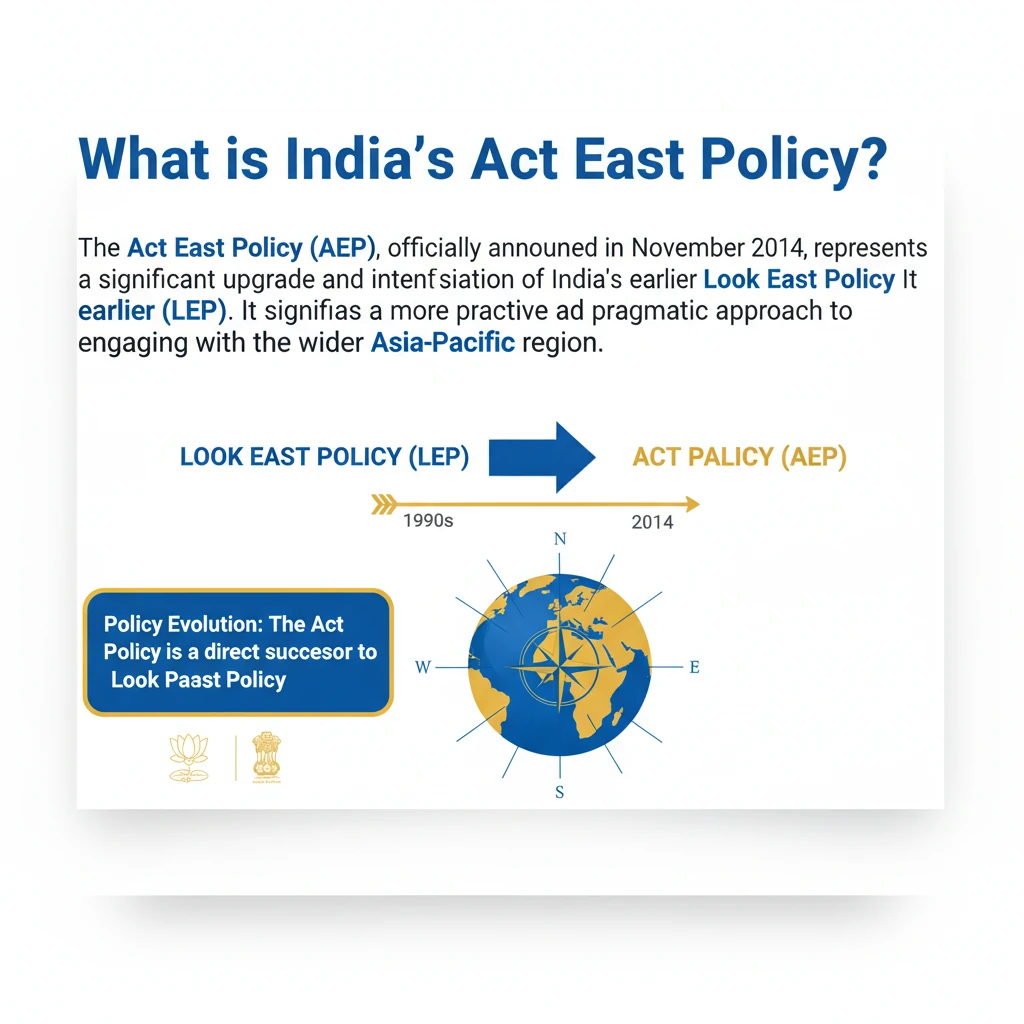
<h4>What is India's Act East Policy?</h4><p>The <strong>Act East Policy (AEP)</strong>, officially announced in <strong>November 2014</strong>, represents a significant upgrade and intensification of India's earlier <strong>Look East Policy (LEP)</strong>. It signifies a more proactive and pragmatic approach to engaging with the wider <strong>Asia-Pacific region</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Policy Evolution:</strong> The <strong>Act East Policy</strong> is a direct successor to the <strong>Look East Policy</strong>, which was initiated in the early 1990s. AEP aims for deeper, more comprehensive engagement.</p></div><h4>Diplomatic Initiative and Scope</h4><p>The <strong>Act East Policy</strong> is a comprehensive diplomatic initiative designed to foster robust <strong>economic, strategic, and cultural relations</strong>. It targets the vast <strong>Indo-Pacific region</strong>, engaging countries at bilateral, regional, and multilateral levels.</p><p>Its scope involves intensive and continuous engagement across various critical sectors. This multi-faceted approach ensures a holistic development of ties with partner nations.</p><h4>Key Pillars of Engagement</h4><ul><li><strong>Connectivity:</strong> Enhancing physical and digital links, including infrastructure projects.</li><li><strong>Trade:</strong> Promoting economic cooperation and boosting bilateral and regional commerce.</li><li><strong>Culture:</strong> Strengthening people-to-people contact and cultural exchanges.</li><li><strong>Defence:</strong> Fostering security cooperation and joint exercises.</li><li><strong>People-to-People Contact:</strong> Encouraging tourism, educational exchanges, and cultural understanding.</li></ul><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Focus Region:</strong> While primarily focused on <strong>Southeast Asian countries</strong> (ASEAN), the policy's ambit extends to the broader <strong>Indo-Pacific region</strong>, including East Asia and Oceania.</p></div><h4>Primary Objectives of Act East Policy</h4><p>The overarching aim of the <strong>Act East Policy</strong> is to achieve multifaceted development. It seeks to promote <strong>economic cooperation</strong>, strengthen <strong>cultural ties</strong>, and develop a robust <strong>strategic relationship</strong> with countries across the <strong>Indo-Pacific region</strong>.</p><p>A critical component of the policy is the focus on the <strong>North Eastern Region (NER)</strong> of India. The NER is envisioned as the 'gateway' to Southeast Asia, and its economic development is a key strategic objective, leveraging its geographical proximity.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> When discussing <strong>Act East Policy</strong>, always highlight its distinction from <strong>Look East Policy</strong> (more proactive, broader scope) and emphasize the strategic importance of the <strong>North Eastern Region</strong> as a land bridge to ASEAN.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
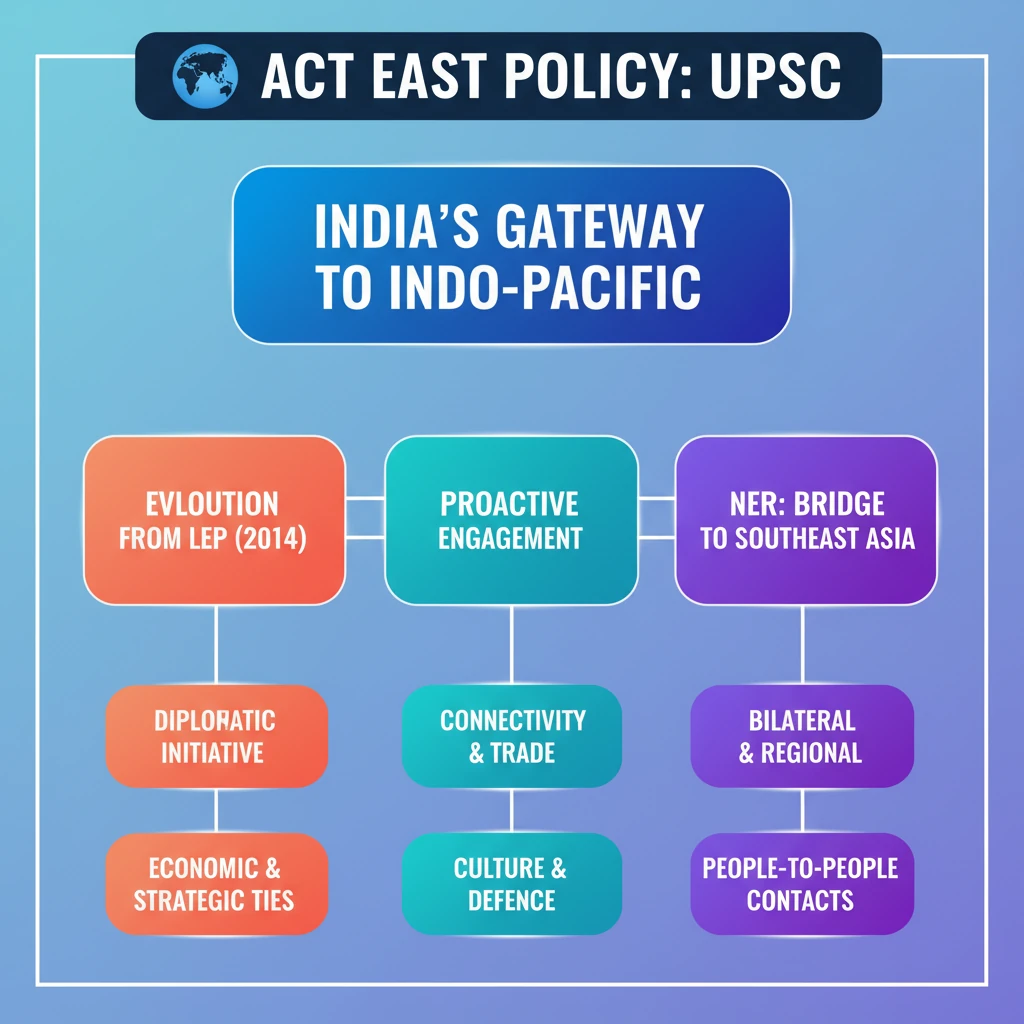
- •Act East Policy (AEP) was launched in November 2014, upgrading the Look East Policy (LEP).
- •It's a diplomatic initiative for economic, strategic, and cultural ties with the Indo-Pacific region.
- •Key engagement areas: connectivity, trade, culture, defence, and people-to-people contact.
- •AEP aims for proactive, pragmatic engagement at bilateral, regional, and multilateral levels.
- •A primary objective is the economic development of India's North Eastern Region (NER) as a gateway to Southeast Asia.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content