What are the Reasons for the Iran-Israel Conflict? - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are the Reasons for the Iran-Israel Conflict?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
<h4>Recent Escalation: Iran's Attacks on Israel</h4><p>In a significant escalation, <strong>Iran</strong> launched over <strong>300 projectiles</strong> against <strong>Israel</strong>. These included a combination of <strong>drones, cruise missiles, and ballistic missiles</strong>, marking a direct military engagement between the two nations.</p><div class='info-box'><p>This large-scale attack by <strong>Iran</strong> was widely perceived as direct retaliation for a previous deadly strike. The strike targeted <strong>Iran’s consulate in Damascus, Syria</strong>, which resulted in significant casualties.</p></div><p>The immediate aftermath of this escalation has led to increased tensions. It has also created an additional risk of <strong>piracy and hostage-taking</strong> within the critical <strong>Gulf region</strong>, impacting global maritime security.</p><h4>Historical Roots of Hostility</h4><p>The relationship between <strong>Iran</strong> and <strong>Israel</strong> has been profoundly tumultuous for decades. A pivotal turning point was the <strong>Iranian Revolution of 1979</strong>, which fundamentally reshaped Iran's political and ideological landscape.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Before <strong>1979</strong>, <strong>Iran</strong>, under the rule of the <strong>Shah</strong>, maintained a relatively close alliance with <strong>Israel</strong>. The revolution transformed <strong>Iran</strong> into an <strong>Islamic Republic</strong>, adopting an openly hostile stance towards <strong>Israel</strong>.</p></div><h4>Religious and Ideological Divide</h4><p>At the core of the conflict lie deep-seated <strong>religious and ideological differences</strong>. <strong>Iran</strong> is constitutionally an <strong>Islamic Republic</strong>, primarily governed by the principles of <strong>Shia Islam</strong>.</p><p>Conversely, <strong>Israel</strong> defines itself as a <strong>predominantly Jewish state</strong>. These contrasting foundational identities contribute significantly to their mutual distrust and animosity.</p><h4>The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict Dimension</h4><p><strong>Iran's unwavering support</strong> for <strong>Palestinian causes</strong> is a major flashpoint. This includes substantial backing for various militant groups operating in the region.</p><ul><li><strong>Hamas:</strong> A Palestinian Sunni-Islamist fundamentalist organization.</li><li><strong>Hezbollah:</strong> A Shia Islamist political party and militant group based in Lebanon.</li></ul><div class='key-point-box'><p>Both <strong>Hamas</strong> and <strong>Hezbollah</strong> are designated as <strong>terrorist organizations</strong> by <strong>Israel</strong>, the <strong>United States</strong>, and several other Western nations. Iran's support for these groups directly challenges Israel's security interests.</p></div><h4>Geopolitical Rivalry and Regional Influence</h4><p><strong>Iran</strong> and <strong>Israel</strong> are formidable <strong>regional rivals</strong>, actively vying for influence across the <strong>Middle East</strong>. Their competing strategic interests fuel numerous proxy conflicts.</p><p>Key regional conflicts where their interests clash include the <strong>civil wars in Syria and Yemen</strong>. These theatres demonstrate their opposing objectives and alliances.</p><ul><li>In <strong>Syria</strong>, <strong>Iran</strong> strongly supports the <strong>Assad regime</strong>, providing military and financial aid.</li><li>In <strong>Yemen</strong>, <strong>Iran</strong> backs the <strong>Houthi rebels</strong>, who control significant parts of the country.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding these proxy conflicts is crucial for analyzing the broader <strong>Middle East geopolitics</strong>, often appearing in <strong>GS Paper 2 (International Relations)</strong> questions.</p></div><p><strong>Israel</strong>, on the other hand, actively opposes <strong>Iranian influence</strong> in these countries. It views Iran's expansion as a direct threat to its national security and regional stability.</p><h4>Iran's Nuclear Program</h4><p><strong>Iran's nuclear program</strong> remains a significant point of contention. <strong>Israel</strong> has been an exceptionally vocal critic of the <strong>Iran nuclear deal</strong>, formally known as the <strong>Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA)</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Israel</strong> views a nuclear-armed <strong>Iran</strong> as an existential threat. It has taken proactive measures, including alleged <strong>covert operations</strong>, to disrupt and delay <strong>Iran’s nuclear activities</strong>.</p></div>
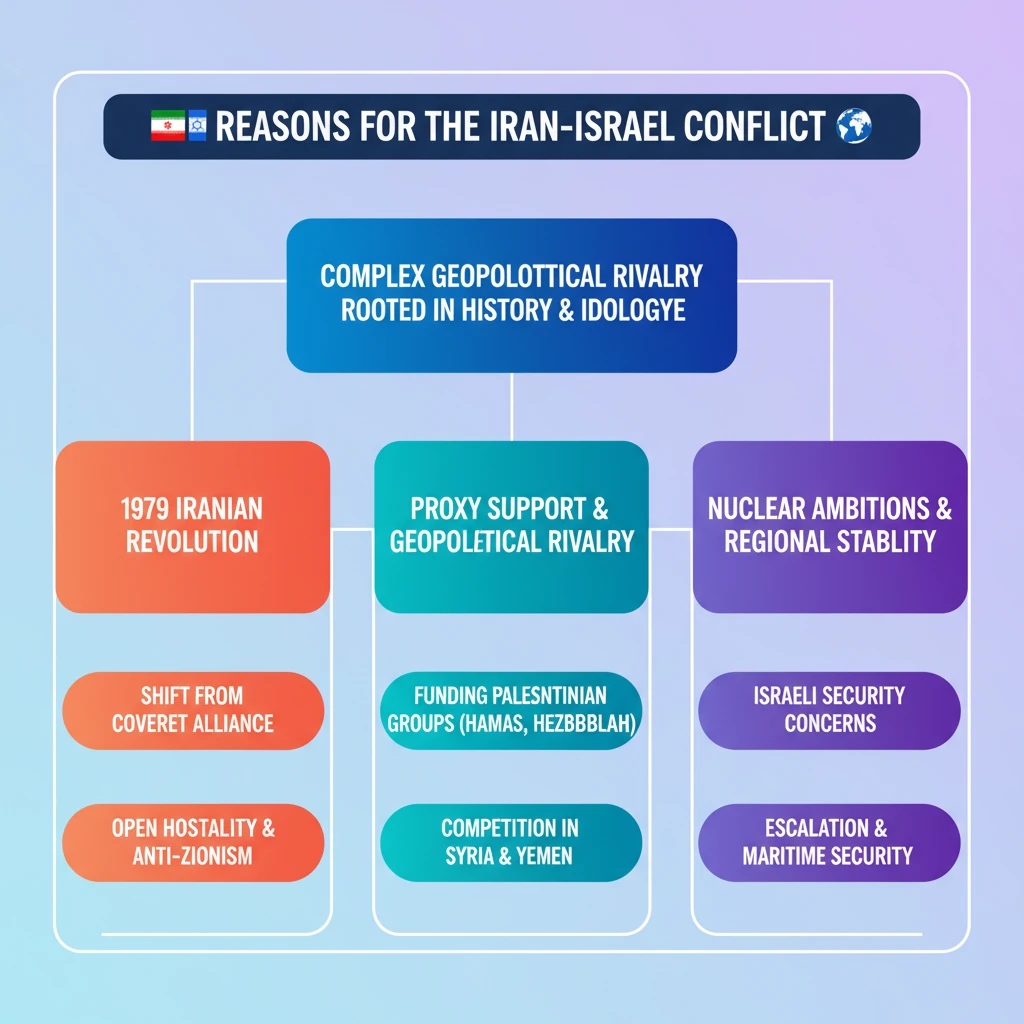
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The Iran-Israel conflict is a complex geopolitical rivalry rooted in historical, religious, and ideological differences.
- •The 1979 Iranian Revolution marked a pivotal shift from a covert alliance to open hostility.
- •Key drivers include Iran's support for Palestinian groups (Hamas, Hezbollah), geopolitical competition in Syria and Yemen, and Israel's concerns over Iran's nuclear program.
- •Recent direct military exchanges, like Iran's April 2024 strikes, signify a dangerous escalation from traditional proxy warfare.
- •The conflict poses significant risks to regional stability, maritime security in the Gulf, and international efforts for nuclear non-proliferation.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Council on Foreign Relations
•International Crisis Group reports
•UN Security Council resolutions (general context)