G7: Origin, Members, and Significance for International Relations - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

G7: Origin, Members, and Significance for International Relations
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
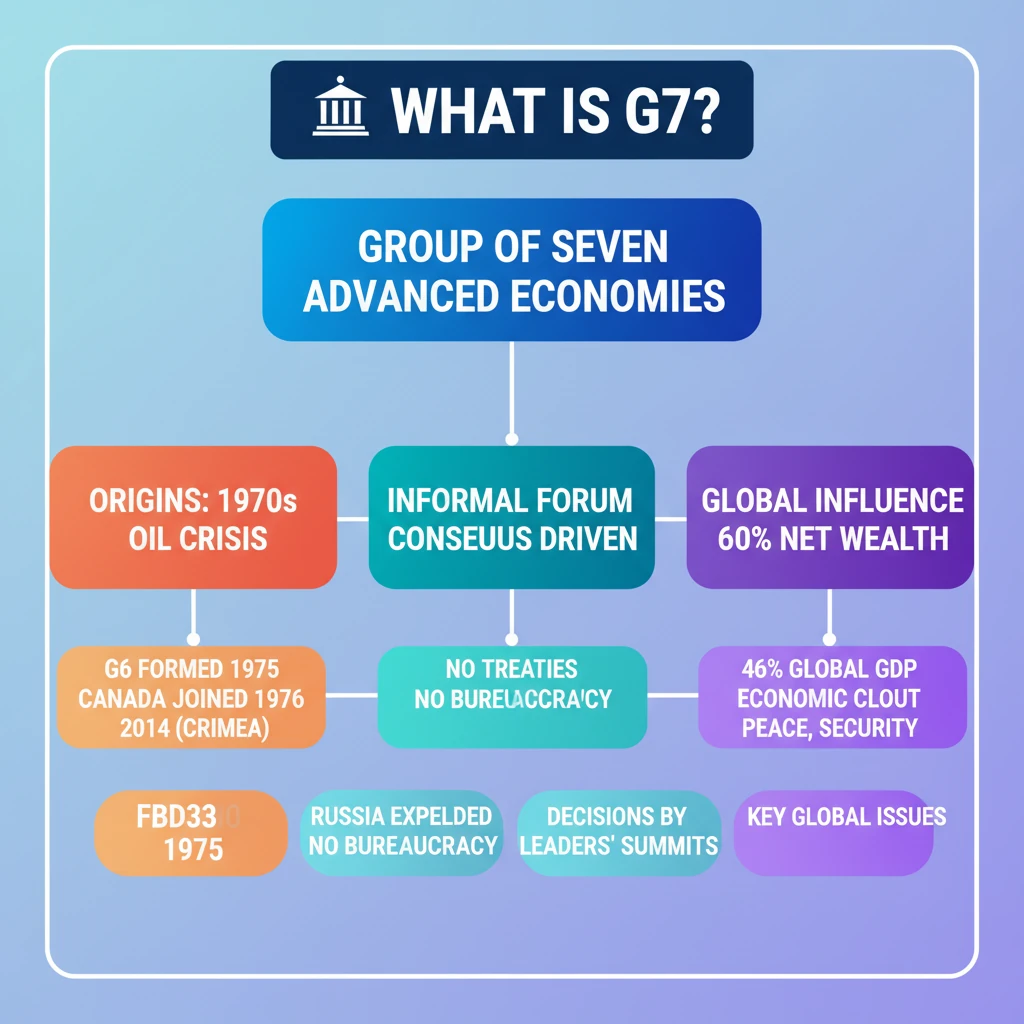
<h4>What is the G7?</h4><p>The <strong>Group of Seven (G7)</strong> is an informal forum comprising seven of the world's most advanced and developed economies. It serves as a platform for its member countries to discuss and coordinate solutions to global issues, particularly economic, security, and environmental challenges.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Core Members:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>France</strong></li><li><strong>Germany</strong></li><li><strong>Italy</strong></li><li><strong>Japan</strong></li><li><strong>The United Kingdom</strong></li><li><strong>The United States</strong></li><li><strong>Canada</strong></li></ul></div><p>Beyond its core members, the G7 also extends invitations to the heads of significant <strong>international organizations</strong>. These invitees participate in discussions, contributing their expertise and perspectives on global governance.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key International Organizations Invited:</strong></p><ul><li>The <strong>European Union (EU)</strong></li><li>The <strong>International Monetary Fund (IMF)</strong></li><li>The <strong>World Bank</strong></li><li>The <strong>United Nations (UN)</strong></li></ul></div><p><strong>G7 summits</strong> are held annually, providing a regular opportunity for leaders to meet. The hosting responsibility rotates among the member countries, ensuring shared leadership and diverse perspectives on the agenda.</p><h4>Origin of the G7</h4><p>The G7's inception was a direct response to a major global economic upheaval. The <strong>Oil Crisis of 1973</strong>, coupled with a subsequent financial crisis, highlighted the need for major industrial nations to coordinate their economic policies.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Foundational Event:</strong> The <strong>1973 Oil Crisis</strong> and subsequent financial instability prompted the creation of the G7.</p></div><p>In <strong>1975</strong>, the leaders of six major industrial nations convened for the first time. This initial grouping was known as the <strong>G6</strong>, laying the groundwork for future collaboration.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Original G6 Members (1975):</strong></p><ul><li><strong>United States</strong></li><li><strong>United Kingdom</strong></li><li><strong>France</strong></li><li><strong>West Germany</strong></li><li><strong>Japan</strong></li><li><strong>Italy</strong></li></ul></div><p>The group expanded in <strong>1976</strong> when <strong>Canada</strong> joined, transforming the <strong>G6</strong> into the <strong>G7</strong>. This marked the stable composition of the group for many years.</p><p>Later, in <strong>1997</strong>, <strong>Russia</strong> was invited to join, leading to the formation of the <strong>G8</strong>. However, this expanded format was not permanent.</p><p>In <strong>2014</strong>, <strong>Russia</strong> was expelled from the group following its <strong>annexation of the Crimea region of Ukraine</strong>. This event led to the group reverting to its original <strong>G7</strong> format, which it maintains today.</p><h4>Nature of the G7 Grouping</h4><p>The <strong>G7</strong> is characterized by its informal structure. It operates without formal treaties or a permanent bureaucratic apparatus, distinguishing it from traditional international organizations.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Informal Grouping:</strong> The G7 functions outside formal treaties and lacks a permanent bureaucracy. Each member nation takes turns leading discussions.</p></div><p>Decisions within the <strong>G7</strong> are reached through <strong>consensus</strong> among its members. While these decisions are not legally binding, they carry significant weight due to the economic and political influence of the member states.</p><p>Despite its lack of direct legislative power, the <strong>G7's pronouncements</strong> and coordinated actions can profoundly influence international policies. Their agreements often shape global agendas and set precedents for multilateral cooperation.</p><h4>Significance and Global Impact</h4><p>The collective economic strength of the <strong>G7 nations</strong> gives the group considerable influence on the global stage. Their combined resources and policy coordination efforts have far-reaching implications for international trade, finance, and development.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>G7's Global Economic Footprint:</strong></p><ul><li>Controls approximately <strong>60% of global net wealth</strong>.</li><li>Drives about <strong>46% of global GDP</strong>.</li><li>Represents roughly <strong>10% of the world’s population</strong>.</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>For <strong>UPSC Mains (GS-II)</strong>, understanding the <strong>G7's informal nature</strong> and its <strong>influence through consensus</strong> is crucial. Be prepared to discuss how such groupings impact global governance without formal legal backing.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •G7 comprises 7 advanced economies: France, Germany, Italy, Japan, UK, USA, Canada.
- •It originated from the 1973 Oil Crisis, with the G6 forming in 1975 and Canada joining in 1976.
- •Russia joined in 1997 (G8) but was expelled in 2014 after annexing Crimea, reverting to G7.
- •It is an informal grouping, operating without treaties or permanent bureaucracy, making decisions by consensus.
- •G7 members collectively control 60% of global net wealth and drive 46% of global GDP, giving it significant global influence.
- •Despite its informal nature, G7 plays a crucial role in coordinating responses to global economic, health, and geopolitical challenges.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content