FMR Review: Security Concerns - Infiltration, Drugs, Insurgency - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

FMR Review: Security Concerns - Infiltration, Drugs, Insurgency
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
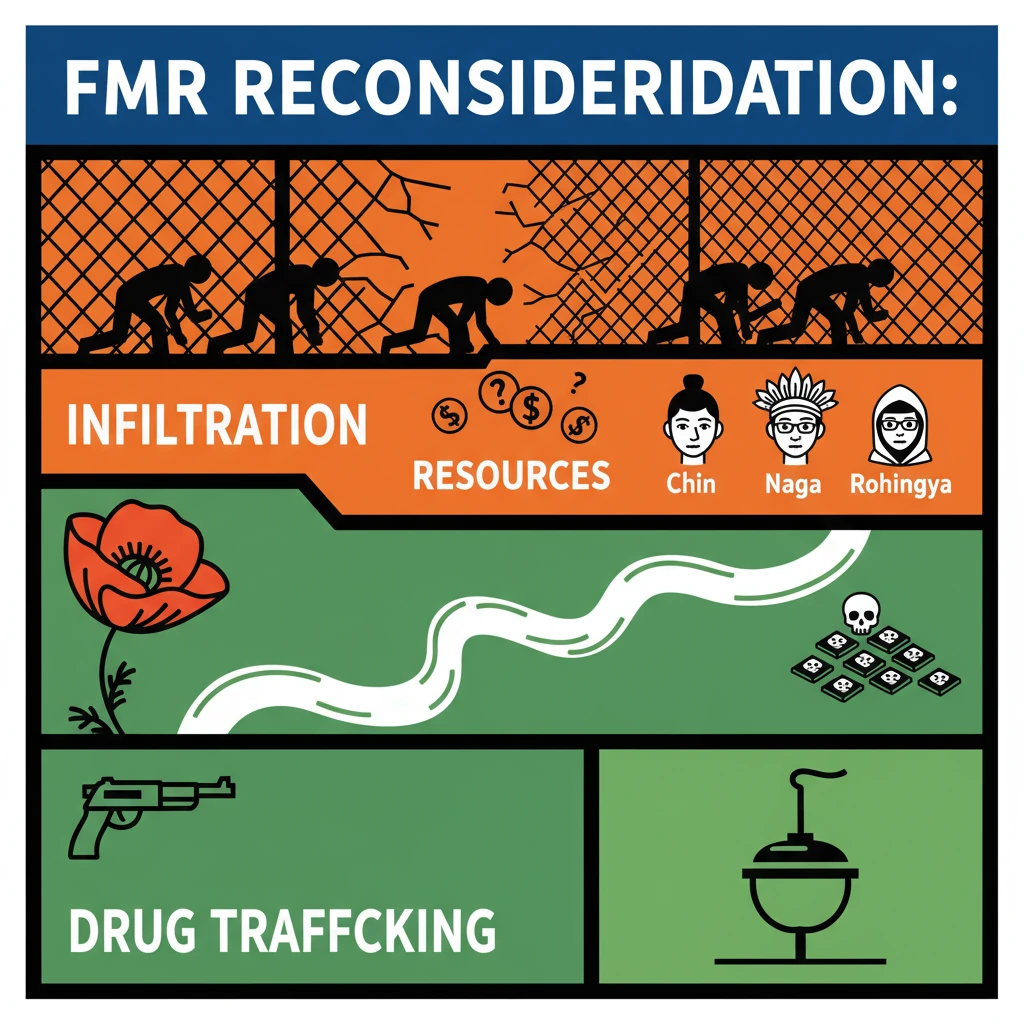
<h4>Potential Reasons for Reconsidering the Free Movement Regime (FMR)</h4><p>The <strong>Free Movement Regime (FMR)</strong>, a unique arrangement between <strong>India</strong> and <strong>Myanmar</strong>, is currently under scrutiny. Several pressing concerns necessitate a re-evaluation of its continued implementation along the shared border.</p><h4>Security Concerns</h4><p>The porous nature of the <strong>India-Myanmar border</strong>, facilitated by the FMR, has raised significant security challenges for India's northeastern states. These issues directly impact national security and regional stability.</p><h4>Increased Infiltration</h4><p>There are growing concerns regarding the influx of <strong>illegal immigrants</strong> into India. Communities such as the <strong>Chin</strong> and <strong>Naga</strong>, along with <strong>Rohingyas</strong>, are migrating from <strong>Myanmar</strong>.</p><p>This unchecked migration places a considerable strain on local resources and significantly impacts the demographic balance in border regions, leading to potential social unrest.</p><h4>Drug Trafficking and Arms Smuggling</h4><p>The open border is frequently exploited for the illegal movement of contraband. This includes widespread <strong>drug trafficking</strong> and the smuggling of <strong>weapons</strong>, which poses a severe threat to India's internal security.</p><p>These illicit activities fuel crime within the border states and destabilize the region. The flow of narcotics, in particular, has devastating social consequences.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Factual Data: Drug Cases in Manipur</strong></p><ul><li>In <strong>2022</strong>, <strong>Manipur</strong> recorded <strong>500 cases</strong> filed under the <strong>Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act</strong>.</li><li>A total of <strong>625 individuals</strong> were arrested in connection with these drug-related offenses, according to data from the Chief Minister’s Office.</li></ul></div><h4>Insurgency Activities</h4><p>The FMR has been consistently misused by various <strong>insurgent groups</strong> operating in <strong>northeastern India</strong>. The ease of cross-border movement allows them to evade capture by Indian security forces.</p><p>These groups exploit the FMR to establish hideouts, procure arms, and conduct cross-border operations, complicating counter-insurgency efforts.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Examples of Insurgent Groups Misusing FMR:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Kuki National Organisation (KNO)</strong> in <strong>Manipur</strong>.</li><li><strong>Kangleipak Communist Party-Lamphel (KCP-Lamphel)</strong>, also active in <strong>Manipur</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Socio-economic and Regional Issues</h4><p>Beyond immediate security concerns, the FMR also presents significant socio-economic and regional challenges that affect the delicate balance of life in border communities.</p><h4>Impact on Cultural Identity</h4><p>Increased migration from <strong>Myanmar</strong> raises concerns about the preservation of <strong>indigenous culture</strong> and <strong>traditions</strong> in India's border areas. Local communities fear the dilution of their unique heritage.</p><p>The demographic changes brought about by migration can lead to social tensions and a loss of distinct cultural identities over time.</p><h4>Environmental Degradation</h4><p>Unregulated cross-border movements are often linked to environmental damage. This includes extensive <strong>deforestation</strong> along the border regions.</p><p>Illegal resource extraction, such as logging and poaching, is also attributed to the ease of movement, leading to significant ecological imbalances.</p><h4>Regional Dynamics</h4><p>The evolving geopolitical landscape adds another layer of complexity. <strong>China's growing influence</strong> in <strong>Myanmar</strong> is a critical factor.</p><p>This increasing influence has potential implications for <strong>India's border security</strong> and regional stability, necessitating a strategic re-evaluation of border policies like the FMR.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight: Multidimensional Challenge</strong></p><p>When analyzing the FMR, remember it's not just a security issue. It's a complex challenge involving <strong>geopolitics</strong>, <strong>socio-cultural dynamics</strong>, and <strong>environmental concerns</strong>. A holistic approach is key for mains answers.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Reconsideration of FMR driven by security, socio-economic, and regional concerns.
- •Increased infiltration of illegal immigrants (Chin, Naga, Rohingyas) strains resources and impacts demographics.
- •Porous border facilitates drug trafficking (e.g., Manipur NDPS cases) and arms smuggling, threatening internal security.
- •Insurgent groups (KNO, KCP-Lamphel) exploit FMR for cross-border movement and evasion.
- •Concerns exist over dilution of indigenous cultural identity and environmental degradation (deforestation, illegal extraction).
- •China's growing influence in Myanmar adds a geopolitical dimension to border security challenges.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•General knowledge on India-Myanmar Free Movement Regime and border dynamics
•Publicly available reports on NDPS cases in Manipur (as referenced in source)