What were the Key Outcomes of PM’s Visit to Brunei Darussalam? - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What were the Key Outcomes of PM’s Visit to Brunei Darussalam?
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
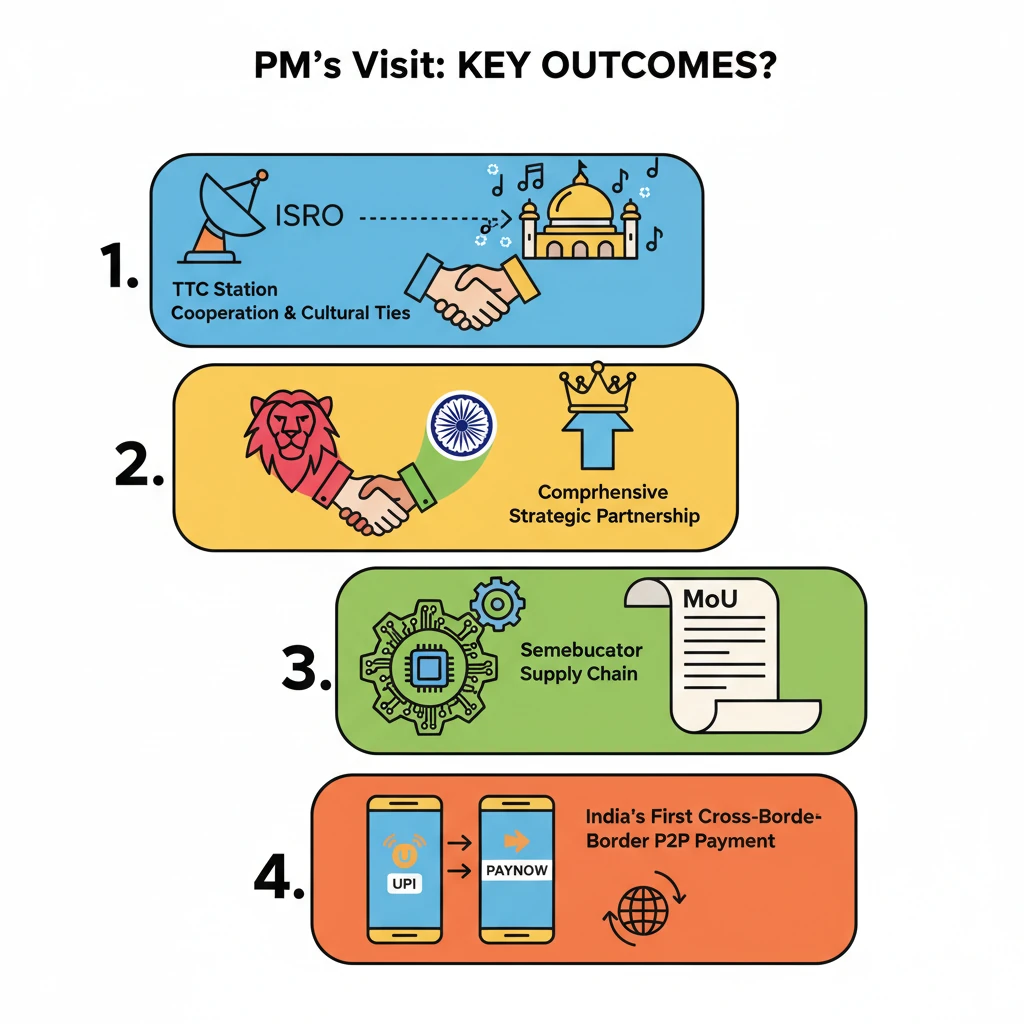
<h4>PM's Visit to Brunei Darussalam: Key Highlights</h4><p>During the visit, the Prime Minister visited the iconic <strong>Omar Ali Saifuddien Mosque</strong> in <strong>Bandar Seri Begawan</strong>. This mosque is a significant symbol of <strong>Brunei's Islamic heritage</strong> and is named after the <strong>28th Sultan of Brunei</strong>.</p><p>India expressed appreciation for <strong>Brunei's continued support</strong> in hosting <strong>ISRO's Telemetry Tracking and Telecommand (TTC) Station</strong>. Discussions were held to further cooperation under the recently reviewed <strong>Memorandum of Understanding (MoU)</strong>, highlighting ongoing space collaboration.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>ISRO Telemetry Tracking and Telecommand (TTC) Station</strong> in Brunei is crucial for India's space missions, providing vital communication and tracking support for satellites and spacecraft.</p></div><h4>PM's Visit to Singapore: Major Outcomes</h4><p>The Prime Minister's visit to Singapore yielded several significant outcomes, deepening the existing strong bilateral ties. A key focus was on enhancing economic and strategic partnerships across various sectors.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The visit underscored the growing importance of <strong>Southeast Asia</strong> in India's <strong>Act East Policy</strong> and its commitment to fostering robust relationships with key regional partners like Singapore.</p></div><h4>Semiconductor Ecosystem Partnership</h4><p>A landmark <strong>Memorandum of Understanding (MoU)</strong> was signed between India and Singapore aimed at developing a <strong>resilient semiconductor supply chain</strong>. This agreement marks a crucial new area of bilateral cooperation, vital for future technological advancements.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>This <strong>MoU</strong> holds immense <strong>geo-strategic significance</strong>. <strong>Semiconductor chips</strong> are globally critical components across various technologies, making a secure supply chain essential for national and economic security.</p></div><div class='info-box'><p>Singapore has a well-established and thriving <strong>semiconductor industry</strong> since the <strong>1970s</strong>. It accounts for approximately <strong>10% of global semiconductor output</strong> and <strong>20% of semiconductor equipment production</strong>, making it a key player.</p></div><h4>Elevation to Comprehensive Strategic Partnership</h4><p>India and Singapore mutually agreed to elevate their bilateral relationship to a <strong>'Comprehensive Strategic Partnership'</strong>. This upgrade signifies a broader and deeper level of cooperation across diverse sectors, from defense to economy and culture.</p><h4>Strengthening Cultural Linkages</h4><p>India announced the upcoming inauguration of the <strong>Thiruvalluvar Cultural Centre</strong> in Singapore. This centre will celebrate the rich legacy of the revered <strong>Tamil saint Thiruvalluvar</strong>, further enhancing people-to-people connections and cultural exchange.</p><h4>India-Singapore Bilateral Relations: A Deeper Dive</h4><p>Beyond the immediate visit outcomes, the existing India-Singapore relationship provides a strong foundation for future collaborations.</p><h4>Historical Connect</h4><p>India and Singapore share profound <strong>historical ties</strong> that span over a millennium, encompassing extensive commerce, vibrant cultural exchanges, and deep people-to-people connections.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The modern relationship traces back to <strong>1819</strong> when <strong>Stamford Raffles</strong>, a British East India administrator, established a trading post in Singapore. This post later became a <strong>British colony</strong>, governed from <strong>Kolkata until 1867</strong>.</p></div><p>Significantly, India was among the first countries to officially recognise <strong>Singapore's independence in 1965</strong>, underscoring the enduring bond between the two nations.</p><h4>Trade and Economic Cooperation</h4><p>Trade relations are a cornerstone of the bilateral partnership. Singapore is a vital economic partner for India.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Singapore stands as <strong>India's 6th largest trade partner</strong>, contributing a significant <strong>3.2%</strong> to India's overall trade volume.</p></div><p>Investment flows are equally robust, with Singapore being a top source of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into India.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Since <strong>2018-19</strong>, <strong>Singapore</strong> has consistently been the <strong>largest contributor of FDI into India</strong>. Key sectors attracting this investment include <strong>Services, Computer Software & Hardware, Trading, Telecommunications, and Drugs & Pharmaceuticals</strong>.</p></div><h4>Fintech Advancements</h4><p>Significant strides have been made in fintech cooperation, facilitating easier cross-border transactions.</p><p>Commercial and technical arrangements have been successfully implemented for the acceptance of <strong>RuPay cards in Singapore</strong>. This enhances convenience for Indian tourists and businesses.</p><p>The <strong>UPI-PayNow linkage</strong> represents a landmark development in cross-border fintech. It enables instant, low-cost fund transfers between the two countries' fast payment systems.</p><div class='highlight-box'><p>Singapore is the <strong>first nation</strong> with which India has launched this cross-border <strong>Person-to-Person (P2P) payment facility</strong>, marking a significant milestone in digital payment integration.</p></div><h4>Science and Technology Cooperation</h4><p>Cooperation in science and technology, particularly in space, has been a strong area of collaboration.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation)</strong> has successfully launched several <strong>Singaporean satellites</strong>. This includes <strong>Singapore's first indigenous built micro-satellite in 2011</strong>, demonstrating robust partnership in space technology.</p></div><h4>Multilateral Cooperation</h4><p>Both nations actively participate in various multilateral forums, contributing to regional and global stability and development.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Singapore has joined key Indian initiatives such as the <strong>International Solar Alliance (ISA)</strong> and the <strong>Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI)</strong>. India and Singapore are also active members of regional groups like the <strong>Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA)</strong>.</p></div><h4>Indian Community and Cultural Ties</h4><p>The presence of a significant Indian diaspora further strengthens the cultural and social fabric connecting the two countries.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Ethnic Indians</strong> constitute approximately <strong>9.1%</strong> of Singapore's <strong>3.9 million residents</strong>. Reflecting this cultural diversity, <strong>Tamil</strong> is one of the <strong>four official languages of Singapore</strong>.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •PM's visit to Brunei reaffirmed ISRO's TTC Station cooperation and cultural ties.
- •Singapore visit elevated relationship to 'Comprehensive Strategic Partnership'.
- •Landmark MoU signed with Singapore for resilient semiconductor supply chain.
- •UPI-PayNow linkage with Singapore is India's first cross-border P2P payment facility.
- •India and Singapore share deep historical, economic (6th largest trade partner, top FDI source), and cultural ties.
- •Both nations collaborate on multilateral forums like ISA, CDRI, and IORA.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content