19th East Asia Summit (EAS) - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

19th East Asia Summit (EAS)
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
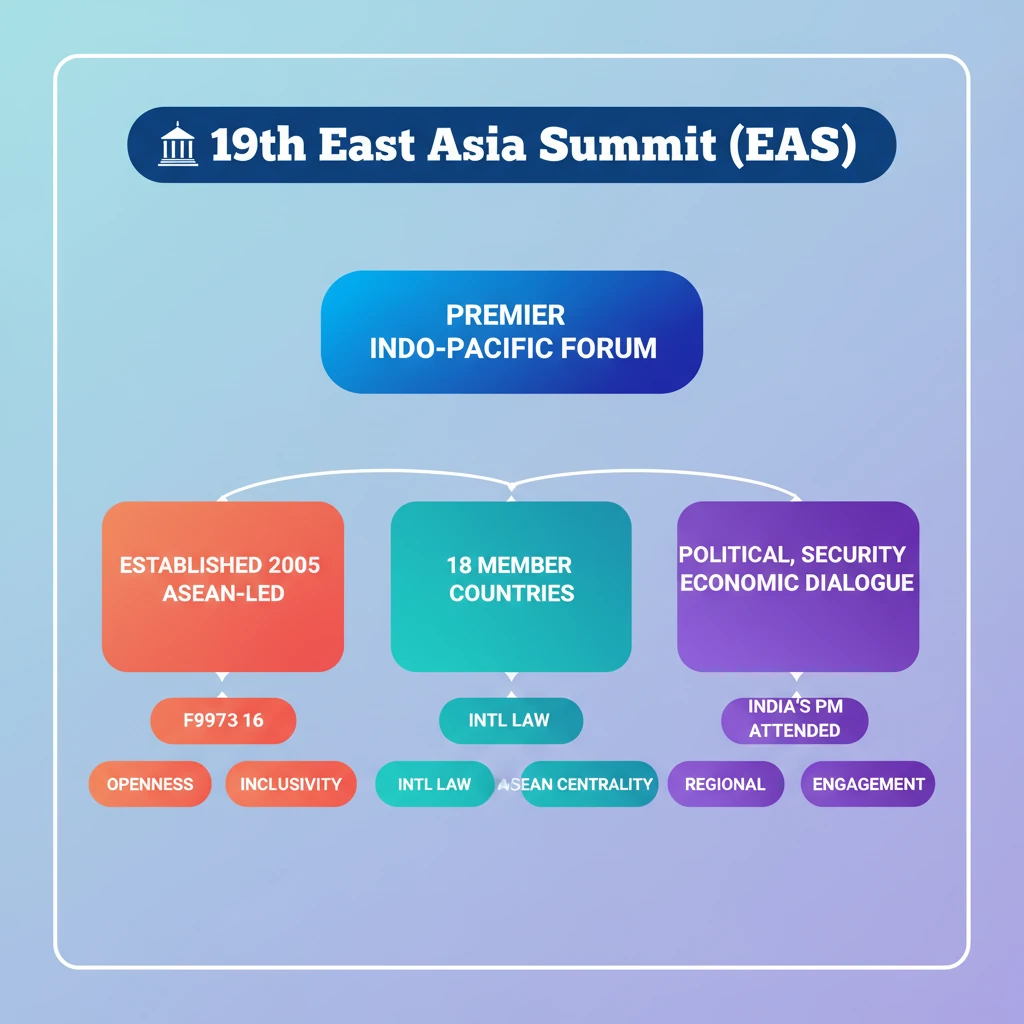
<h4>Recent Developments: India's Participation</h4><p>Recently, the <strong>Prime Minister of India</strong> attended the <strong>19th East Asia Summit (EAS)</strong> in <strong>Vientiane, Lao PDR</strong>. This participation underscores India's continued engagement with key regional forums.</p><h4>Understanding the East Asia Summit (EAS)</h4><p>The <strong>East Asia Summit (EAS)</strong> was formally established in <strong>2005</strong>. It was initiated as an <strong>Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)-led initiative</strong>, highlighting ASEAN's central role in regional diplomacy.</p><div class='key-point-box'>The EAS stands out as the <strong>only leader-led forum</strong> in the <strong>Indo-Pacific</strong> region. It brings together all key partners to discuss a wide array of issues, including <strong>political, security, and economic matters</strong> of strategic importance.</div><p>The foundational idea of an <strong>East Asia Grouping</strong> was first proposed by then <strong>Malaysian Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad</strong> in <strong>1991</strong>, setting the stage for its eventual formation.</p><p>The <strong>first summit</strong> was successfully held in <strong>Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia</strong>, on <strong>14th December 2005</strong>, officially launching the forum.</p><h4>Core Objectives and Principles of EAS</h4><p>The EAS operates on a set of fundamental principles that guide its discussions and collaborations:</p><ul><li><strong>Openness</strong>: Encouraging broad participation and transparency.</li><li><strong>Inclusiveness</strong>: Welcoming diverse perspectives from all member states.</li><li><strong>Respect for international law</strong>: Upholding global norms and regulations.</li><li><strong>ASEAN centrality</strong>: Recognizing ASEAN as the driving force and core of the forum.</li><li><strong>ASEAN’s role as the driving force</strong>: Affirming ASEAN's leadership in setting the agenda and direction.</li></ul><h4>EAS Membership: A Strategic Indo-Pacific Forum</h4><p>The EAS is a crucial forum for <strong>strategic dialogue</strong> within the expansive <strong>Indo-Pacific region</strong>. It comprises a total of <strong>18 countries</strong>, including all ASEAN members and key dialogue partners.</p><div class='info-box'><strong>EAS Member Countries:</strong><ul><li><strong>10 ASEAN Countries:</strong> Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.</li><li><strong>8 Dialogue Partners:</strong> Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russia, and the United States.</li></ul></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The East Asia Summit (EAS) was established in 2005 as an ASEAN-led initiative.
- •It is the only leader-led forum in the Indo-Pacific, discussing political, security, and economic issues.
- •The EAS comprises 10 ASEAN countries and 8 dialogue partners (Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, ROK, Russia, US).
- •Its principles include openness, inclusiveness, respect for international law, and ASEAN centrality.
- •India's Prime Minister recently attended the 19th EAS, highlighting its importance for India's regional engagement.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content