India and Uzbekistan Signed BIT - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
India and Uzbekistan Signed BIT
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
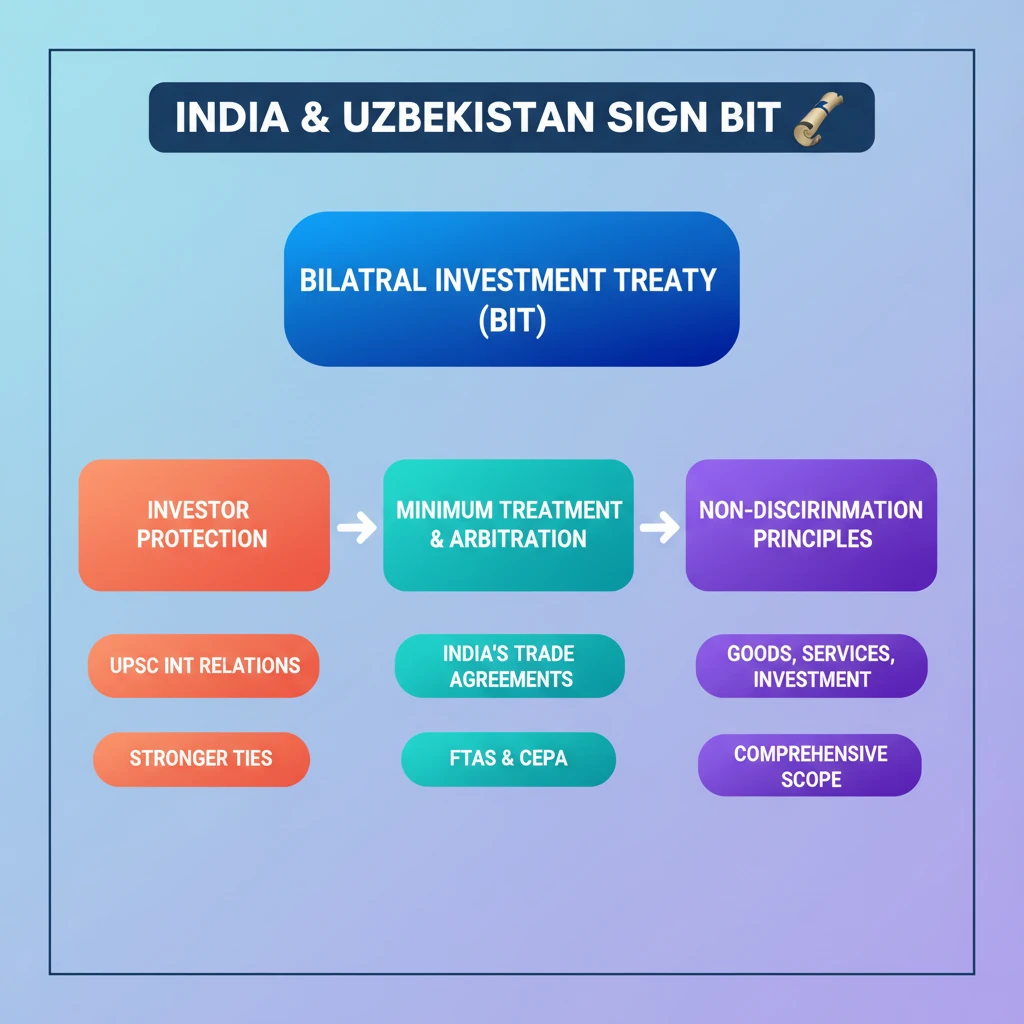
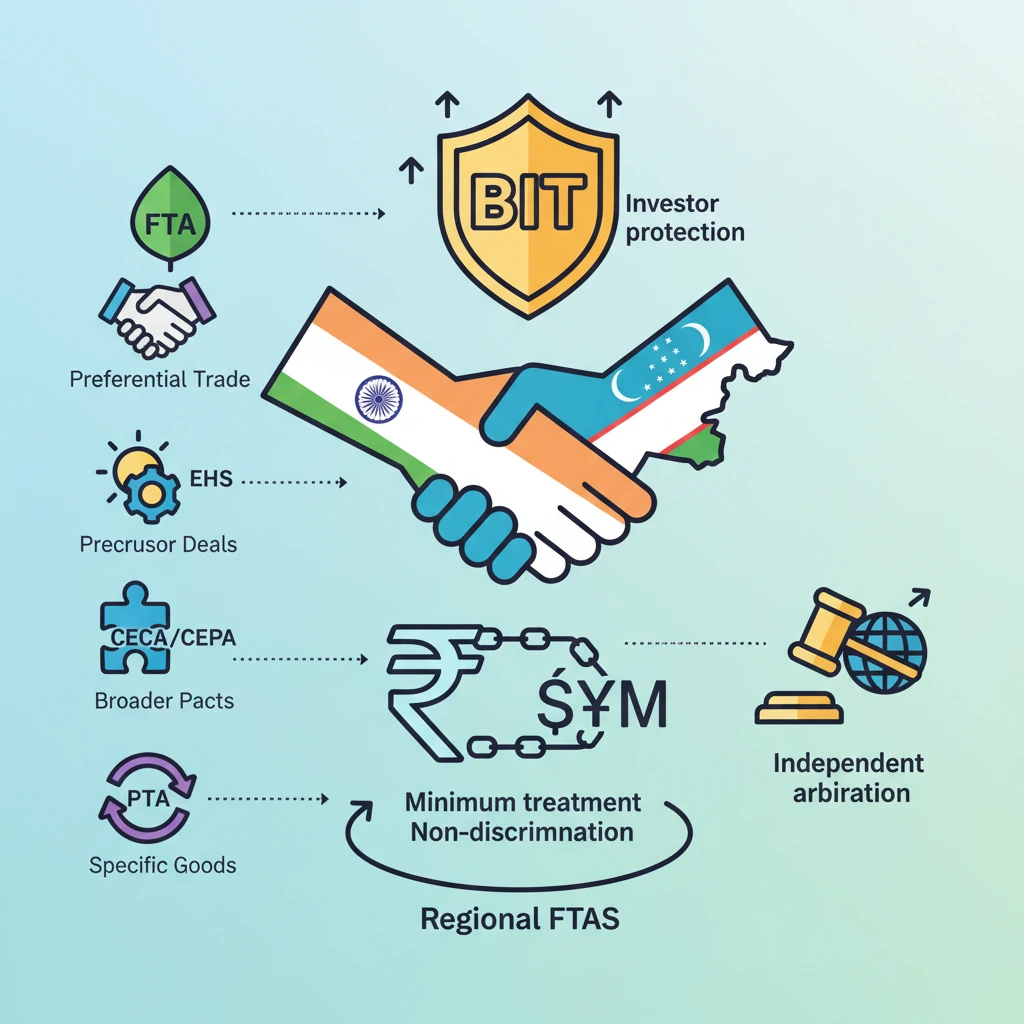
<h4>India and Uzbekistan Sign Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT)</h4><p><strong>India</strong> and <strong>Uzbekistan</strong> have signed a <strong>Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT)</strong>. This significant agreement aims to foster greater economic cooperation between the two nations.</p><p>The primary objective of this <strong>BIT</strong> is to assure <strong>appropriate protection</strong> for investors from both countries. It creates a stable and predictable environment for cross-border investments.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>A <strong>Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT)</strong> typically assures a <strong>minimum standard of treatment</strong> and <strong>non-discrimination</strong> for investors. It also offers mechanisms for <strong>independent arbitration</strong> for dispute resolution, enhancing investor confidence.</p></div><p>However, the treaty also acknowledges the right of both countries to <strong>regulate</strong>. It provides adequate <strong>policy space</strong> for public interest regulation, without compromising the fundamental principles of investor protection.</p><h4>Major Trade Agreements of India</h4><p>India engages in various types of trade and investment agreements to boost its economic ties globally. These agreements range from bilateral to regional and multilateral frameworks.</p><h5>Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)</h5><p>An <strong>FTA</strong> is a comprehensive deal between countries offering <strong>preferential trade terms</strong> and <strong>tariff concessions</strong>. It typically includes a <strong>negative list</strong> of products and services that are excluded from these concessions.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>India's FTAs with Neighbouring Countries:</strong><ul><li><strong>India-Sri Lanka FTA</strong></li><li><strong>India-Nepal Treaty of Trade</strong></li><li><strong>India-Bhutan Agreement on Trade, Commerce, and Transit</strong></li></ul></p></div><h5>Early Harvest Schemes (EHS)</h5><p>An <strong>EHS</strong> is a precursor to a broader agreement like an <strong>FTA</strong>, <strong>CECA</strong>, or <strong>CEPA</strong>. Negotiating countries select specific products for <strong>tariff liberalisation</strong> in the initial phase.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The purpose of an <strong>EHS</strong> is to pave the way for more comprehensive trade agreements and to build confidence between the negotiating parties.</p></div><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Example:</strong><ul><li><strong>India-Thailand Early Harvest Scheme (EHS)</strong></li></ul></p></div><h5>Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreements (CECAs) & Partnership Agreements (CEPAs)</h5><p><strong>CECA/CEPA</strong> agreements are broader in scope than traditional <strong>FTAs</strong>. They address a wider range of regulatory, trade, and economic aspects.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The key difference is that a <strong>CEPA</strong> has the widest scope, often including <strong>services</strong>, <strong>investment</strong>, and other areas. A <strong>CECA</strong> primarily focuses on <strong>tariff</strong> and <strong>Tariff Rate Quota (TQR)</strong> rates negotiation.</p></div><div class='info-box'><p><strong>India's CECAs and CEPAs:</strong><ul><li><strong>CEPA with UAE, South Korea, Japan</strong></li><li><strong>CECA with Singapore, Malaysia</strong></li><li><strong>India-Mauritius Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA)</strong></li></ul></p></div><h5>Preferential Trade Agreements (PTAs)</h5><p>In a <strong>PTA</strong>, partners grant <strong>preferential access</strong> to specified products by lowering duties on agreed tariff lines. These agreements maintain a <strong>positive list</strong> of products eligible for reduced or zero tariffs.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>India's PTAs:</strong><ul><li><strong>Asia Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA)</strong>: Involves <strong>Bangladesh, China, India, S. Korea, Lao PDR, Sri Lanka, and Mongolia</strong>.</li><li><strong>SAARC Preferential Trading Agreement (SAPTA)</strong>: Predecessor to SAFTA, involved <strong>SAARC member countries</strong>.</li><li><strong>India-MERCOSUR PTA</strong>: Involves <strong>Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay and India</strong>.</li><li><strong>India's PTA with Chile, Afghanistan</strong></li></ul></p></div><h5>Regional FTAs of India</h5><p>India is also part of several regional free trade agreements, strengthening its economic integration within specific geographical blocs.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Regional FTAs:</strong><ul><li><strong>India-ASEAN Trade in Goods Agreement</strong>: Involves <strong>10 ASEAN countries + India</strong>.</li><li><strong>South Asia Free Trade Agreement (SAFTA)</strong>: Involves <strong>India, Pakistan, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Bhutan, and the Maldives</strong>.</li></ul></p></div><h5>Global System of Trade Preferences (GSTP)</h5><p>The <strong>GSTP</strong> is a framework for promoting trade among developing countries. India is a participant in this broader global initiative.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>GSTP</strong> involves <strong>43 countries + India</strong>, aiming to facilitate trade through preferential tariff arrangements among its members.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the nuances between <strong>FTA, EHS, CECA, CEPA, and PTA</strong> is crucial for both Prelims (definitions, examples) and Mains (implications for India's trade policy, economic diplomacy). Pay attention to the scope and depth of each agreement type.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •India and Uzbekistan signed a Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT) for investor protection.
- •BITs ensure minimum treatment, non-discrimination, and independent arbitration for investors.
- •India engages in various trade agreements: FTAs, EHS, CECAs/CEPAs, PTAs, and Regional FTAs.
- •FTAs offer preferential trade; EHS are precursors to broader deals.
- •CECAs/CEPAs are comprehensive, covering goods, services, and investment, with CEPA having the widest scope.
- •PTAs grant preferential access on a 'positive list' of products.
- •These agreements are crucial for India's economic diplomacy, FDI attraction, and market access.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India (general knowledge on trade agreements)
•Press Information Bureau (PIB) releases (for specific agreement details like India-UAE CEPA)