Deepening India-Brazil Relations - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Deepening India-Brazil Relations
Medium⏱️ 9 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
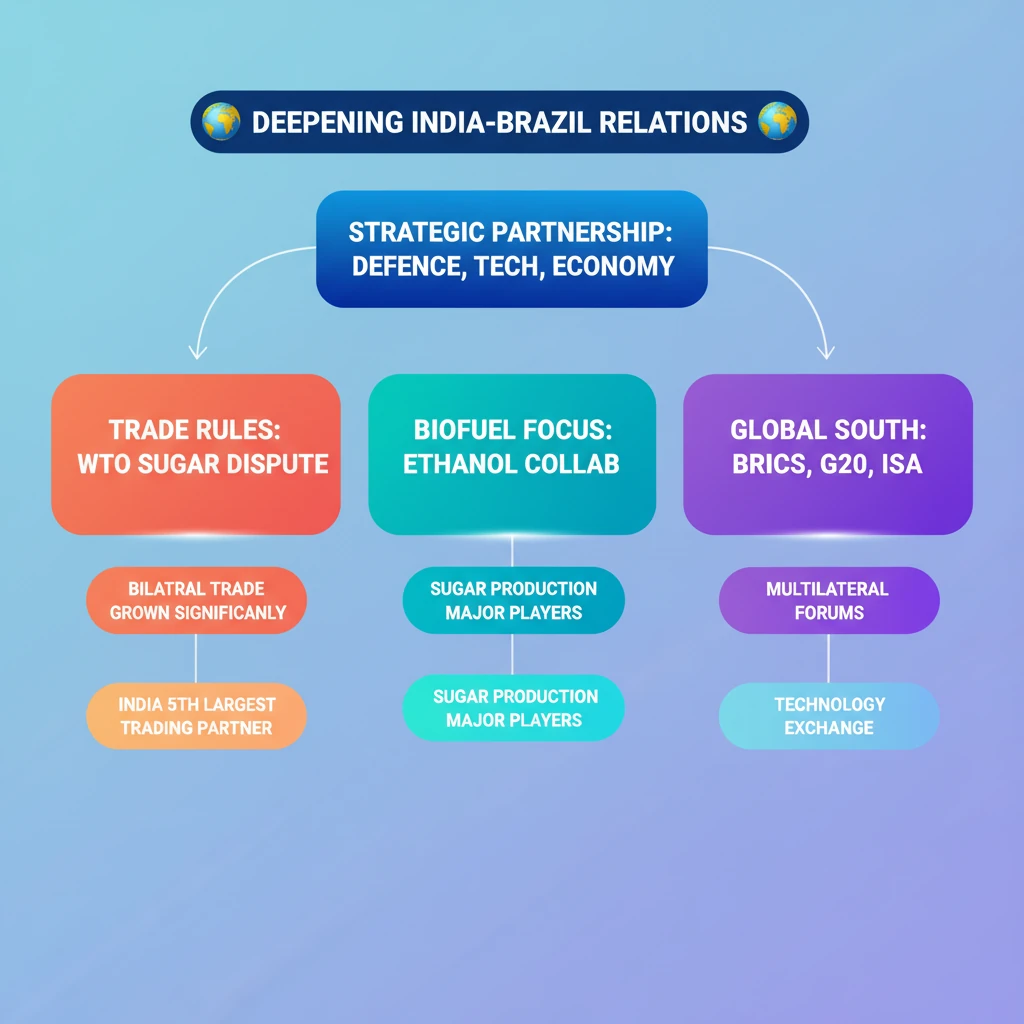
<h4>Deepening India-Brazil Relations: An Overview</h4><p>The <strong>India-Brazil strategic partnership</strong> has significantly <strong>deepened and diversified</strong> over recent years.</p><p>This robust relationship spans critical domains including <strong>defence, space, security, technology</strong>, and strong <strong>people-to-people connections</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Recently, <strong>India</strong> and <strong>Brazil</strong>, both major players in <strong>global sugar production</strong>, successfully resolved their long-standing <strong>WTO trade dispute</strong> concerning <strong>sugar subsidies</strong>.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'><p>This resolution aligns with their expanding collaboration in <strong>ethanol technology</strong> and addresses broader issues impacting <strong>global sugar supply and prices</strong>.</p></div><h4>The India-Brazil WTO Sugar Subsidies Dispute</h4><h5>Background of the Dispute</h5><p>In <strong>2019</strong>, <strong>Brazil</strong>, alongside <strong>Australia</strong> and <strong>Guatemala</strong>, initiated a challenge against <strong>India’s sugar subsidy measures</strong> at the <strong>World Trade Organization (WTO)</strong>.</p><p>They contended that these subsidies were inconsistent with various articles of the <strong>WTO’s Agreement on Agriculture</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>US</strong> and <strong>Australia</strong> also highlighted a significant reporting gap, claiming <strong>India</strong> had not included <strong>sugarcane or its derivatives</strong> in domestic support notifications since the <strong>marketing year 1995-96</strong>.</p></div><h5>India's Defence and Resolution</h5><p><strong>India</strong> defended its policies, asserting that <strong>sugarcane procurement</strong> is managed by <strong>private mills</strong>, not the government, which aligns with <strong>fair trade practices</strong>.</p><p><strong>India</strong> also pointed out an error in the <strong>US-Australia analysis</strong>, which used the entire <strong>sugarcane production</strong> in a given year for subsidy calculations, irrespective of whether it was delivered to mills under the <strong>Sugarcane (Control) Order</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>The resolution of this dispute demonstrates the commitment of both nations to multilateral trade rules and can set a precedent for resolving similar trade disagreements through dialogue.</p></div><h4>Major Areas of Cooperation</h4><h5>Institutional Level Engagements</h5><p><strong>India</strong> and <strong>Brazil</strong> share a deeply <strong>multifaceted relationship</strong>, engaging closely both bilaterally and within numerous <strong>multilateral forums</strong>.</p><p>Key multilateral platforms include <strong>BRICS, IBSA, G4, G20, BASIC, International Solar Alliance (ISA), WTO, UNESCO</strong>, and <strong>WIPO</strong>.</p><p>Bilateral engagements are structured through various high-level dialogues and committees:</p><ul><li><strong>Strategic Dialogue</strong>: Led by the <strong>National Security Advisor (NSA)</strong>, addressing mutual regional and global issues.</li><li><strong>India-Brazil Business Leaders Forum</strong>: Focuses on enhancing <strong>trade, investment</strong>, and broader <strong>economic cooperation</strong>.</li><li><strong>Trade Monitoring Mechanism (TMM)</strong>: Designed to track and resolve specific issues in <strong>bilateral trade</strong>.</li><li><strong>Economic and Financial Dialogue</strong>: Covers cooperation across <strong>investment, trade</strong>, and <strong>monetary policy</strong>.</li><li><strong>Joint Defence Commission</strong>: Facilitates robust <strong>defence cooperation</strong>, including <strong>joint exercises, equipment procurement</strong>, and <strong>intelligence sharing</strong>.</li><li><strong>Joint Committee on Science & Technology</strong>: Fosters collaboration in <strong>research, development</strong>, and <strong>knowledge exchange</strong>.</li></ul><h5>Trade and Investment Landscape</h5><p><strong>India</strong> has emerged as <strong>Brazil’s 5th largest trading partner</strong> in <strong>2021</strong>, reflecting significant growth in bilateral commerce.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Bilateral trade figures:</p><ul><li><strong>2020</strong>: <strong>USD 7.05 billion</strong></li><li><strong>2021</strong>: Increased to <strong>USD 11.53 billion</strong></li><li><strong>2022</strong>: Further grew to <strong>USD 15.15 billion</strong></li><li><strong>2023</strong>: <strong>India’s exports</strong> to Brazil stood at <strong>USD 6.08 billion</strong>, with <strong>imports</strong> at <strong>USD 4.17 billion</strong>.</li></ul></div><p><strong>Major Indian exports</strong> to Brazil include <strong>agrochemicals, synthetic yarns, auto components and parts</strong>.</p><p>Conversely, <strong>India’s imports</strong> from Brazil primarily consist of <strong>crude oil, gold, vegetable oil, sugar</strong>, and various <strong>bulk minerals and ores</strong>.</p><p>Both nations have attracted substantial investments across diverse sectors such as <strong>automobiles, IT, mining, energy, biofuels</strong>, and <strong>footwear</strong>.</p>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •India-Brazil strategic partnership is deepening across defence, space, security, technology, and economy.
- •The recent resolution of the WTO sugar subsidies dispute highlights mature bilateral engagement and commitment to trade rules.
- •Both nations are key players in global sugar production and are collaborating on ethanol technology.
- •Bilateral trade has significantly grown, with India becoming Brazil's 5th largest trading partner in 2021.
- •India and Brazil are crucial members of multilateral forums like BRICS, IBSA, G20, and ISA, amplifying the Global South's voice.
- •Cooperation spans diverse sectors including agrochemicals, auto components, crude oil, gold, and investments in IT, energy, and biofuels.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content