India's Claim over Kalapani Region: Historical Basis - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
India's Claim over Kalapani Region: Historical Basis
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
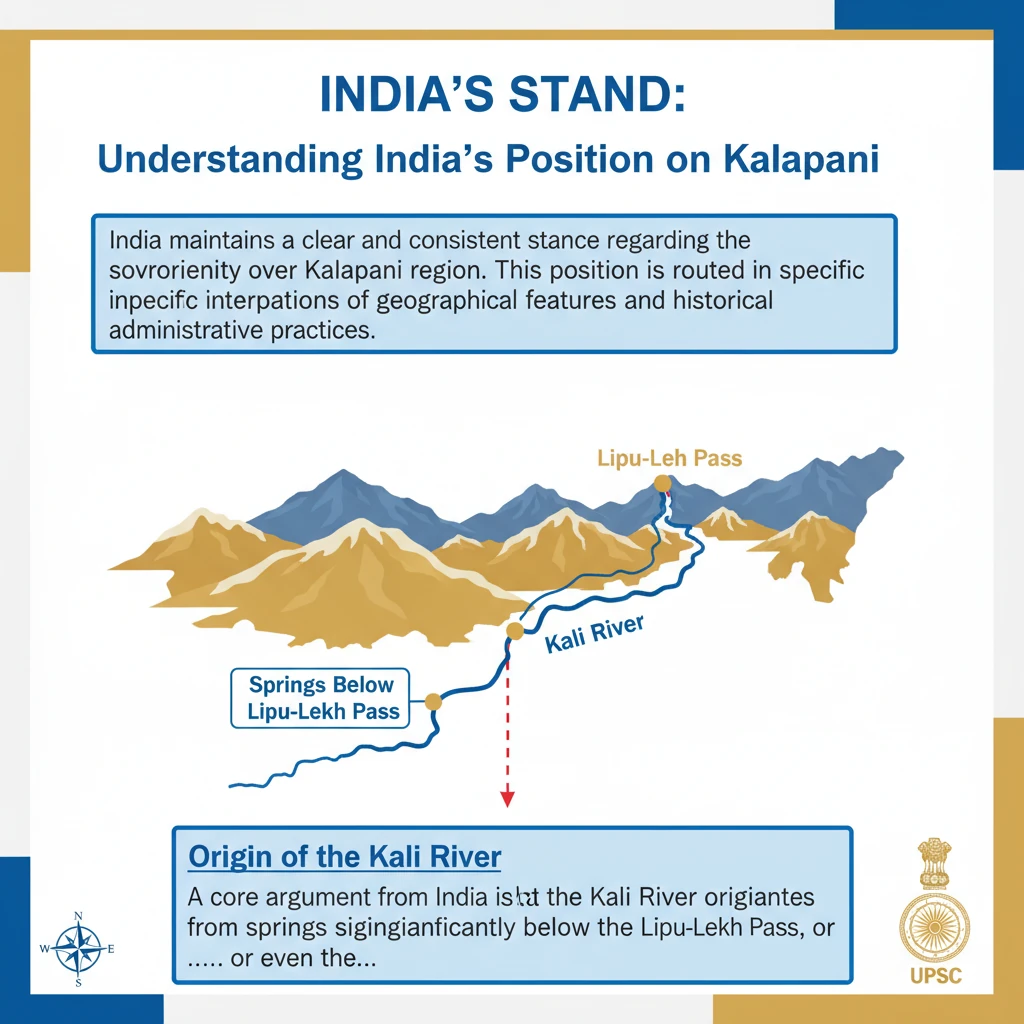
<h4>Understanding India's Position on Kalapani</h4><p>India maintains a clear and consistent stance regarding the sovereignty over the <strong>Kalapani region</strong>. This position is rooted in specific interpretations of geographical features and historical administrative practices.</p><h4>Origin of the Kali River</h4><p>A core argument from India is that the <strong>Kali River</strong> originates from springs located significantly below the <strong>Lipu-Lekh Pass</strong>, or even the <strong>Lipulekh Pass</strong> itself. This geographical interpretation is crucial to India's claim.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Claim:</strong> India asserts the <strong>Kali River</strong>'s source is south of the disputed area, effectively placing the <strong>Kalapani region</strong> within Indian territory.</p></div><h4>Interpretation of the Sugauli Treaty</h4><p>India highlights that the <strong>Sugauli Treaty</strong>, signed in <strong>1816</strong>, which defines the boundary between India (then British India) and Nepal, does not explicitly demarcate the area located north of these specific streams identified as the source of the <strong>Kali River</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The ambiguity in the <strong>Sugauli Treaty</strong> regarding the precise northernmost origin of the <strong>Kali River</strong> is central to the ongoing dispute.</p></div><h4>Historical Administrative Records</h4><p>Further supporting its claim, India refers to extensive administrative and revenue records from the <strong>nineteenth century</strong>. These historical documents consistently indicate that the <strong>Kalapani region</strong> was administered as part of India.</p><p>Specifically, these records show <strong>Kalapani</strong> being counted as an integral part of the <strong>Pithoragarh district</strong>, which falls within the present-day state of <strong>Uttarakhand</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>When discussing border disputes, always cite multiple forms of evidence: geographical, treaty-based, and historical administrative records. This strengthens your argument for <strong>UPSC Mains GS Paper 2</strong>.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •India claims Kalapani region based on the Kali River's origin being south of Lipu-Lekh Pass.
- •The 1816 Sugauli Treaty lacks clear demarcation of the Kali River's northern headwaters.
- •Nineteenth-century administrative records show Kalapani as part of India's Pithoragarh district.
- •The dispute highlights the complexities of interpreting historical treaties and geographical features.
- •Kalapani remains a key point of contention in India-Nepal relations, requiring diplomatic resolution.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Official government statements on India-Nepal border issues
•Historical texts on the Sugauli Treaty and Anglo-Nepalese War