Why International Cooperation is Needed in Promotion of Green Hydrogen? - International Relations | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Why International Cooperation is Needed in Promotion of Green Hydrogen?
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
international relations
📖 Introduction
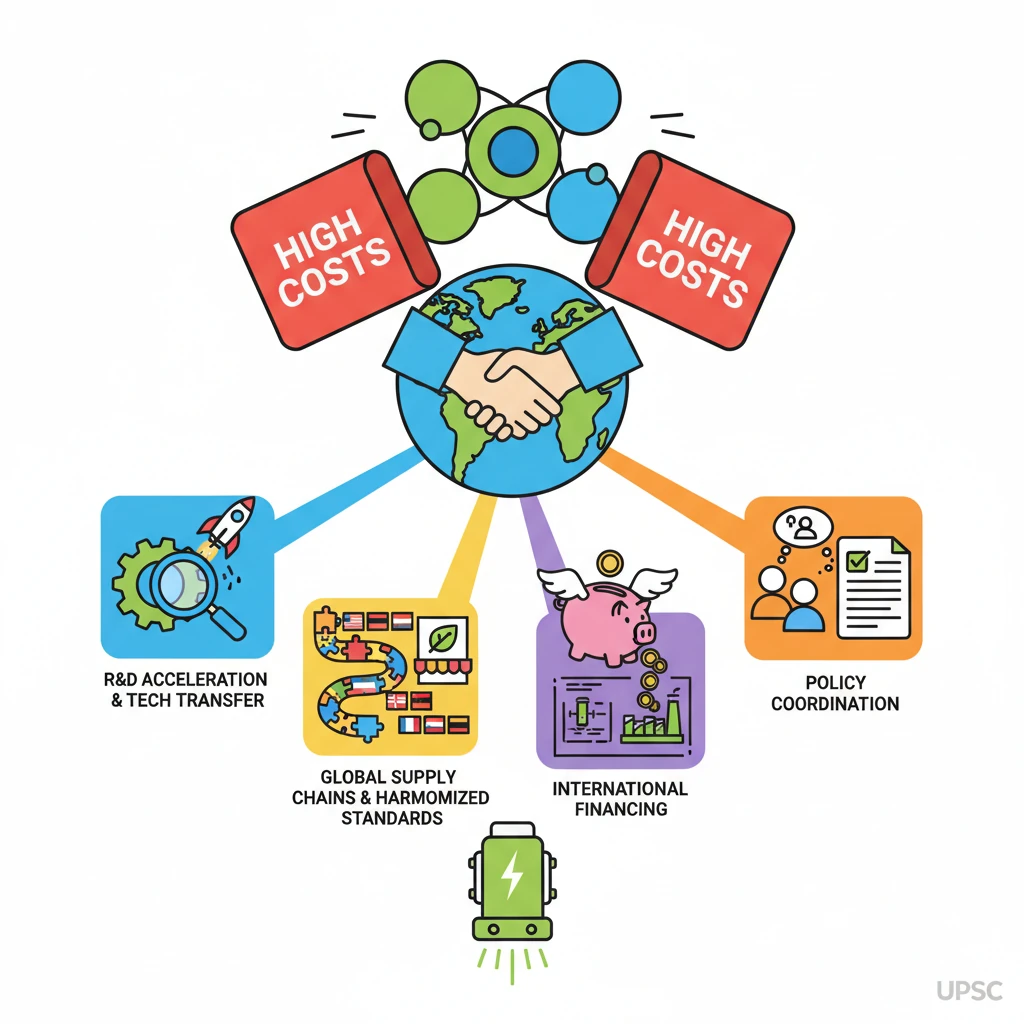
<h4>The Imperative of International Cooperation in Green Hydrogen</h4><p>The global transition to a sustainable energy future critically depends on scaling up <strong>Green Hydrogen</strong> production and deployment. This clean energy carrier, produced via electrolysis using renewable electricity, holds immense promise for decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>However, realizing its full potential requires concerted global efforts, making <strong>international cooperation</strong> absolutely essential across various fronts.</p></div><h4>High Production Costs: A Global Challenge</h4><p>One of the primary barriers to widespread adoption of <strong>Green Hydrogen</strong> is its significantly <strong>high production cost</strong>. This economic hurdle necessitates collaborative approaches to drive down expenses and make it competitive with fossil fuel-derived alternatives.</p><div class='info-box'><p>According to the <strong>International Energy Agency (IEA)</strong>, the cost of producing <strong>Green Hydrogen</strong> currently ranges from <strong>USD 3 to USD 8 per kilogram</strong>. This figure is considerably higher than that of <strong>Grey Hydrogen</strong>, which is produced from fossil fuels like natural gas without carbon capture.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Mains (GS III: Economy, Environment)</strong>: Understanding cost differentials and market barriers is crucial for analyzing energy policy questions. Mentioning IEA data adds credibility to your arguments.</p></div><h4>Accelerating Research and Development (R&D)</h4><p>International collaboration is vital for accelerating <strong>research and development</strong> in key areas. This includes improving electrolysis efficiency, developing advanced materials, and optimizing storage and transportation technologies for <strong>Green Hydrogen</strong>.</p><p>Sharing knowledge and resources among nations can prevent duplication of efforts and speed up technological breakthroughs, making <strong>Green Hydrogen</strong> more viable sooner.</p><h4>Establishing Global Supply Chains</h4><p>Developing robust and efficient <strong>global supply chains</strong> for <strong>Green Hydrogen</strong> and its derivatives (like green ammonia) requires international coordination. This involves identifying potential production hubs, establishing trade routes, and standardizing logistics.</p><p>Countries with abundant renewable energy resources can become exporters, while others can become importers, creating a global market that benefits all participants.</p><h4>Harmonizing Standards and Regulations</h4><p>For <strong>Green Hydrogen</strong> to become a globally traded commodity, there is an urgent need for <strong>harmonized international standards</strong> and regulations. This includes certification schemes for 'green' origin, safety protocols, and technical specifications for infrastructure.</p><p>Such harmonization reduces trade barriers, builds investor confidence, and ensures interoperability across different national systems.</p><h4>Mobilizing Investment and Financing</h4><p>The massive upfront capital investment required for <strong>Green Hydrogen</strong> projects necessitates international financial mechanisms and investment flows. Multilateral development banks, climate funds, and cross-border private investments play a crucial role.</p><p>International cooperation can facilitate blended finance models, risk-sharing mechanisms, and attract the necessary capital to scale up projects globally.</p><h4>Policy Coordination and Market Creation</h4><p>Coordinated policy frameworks among nations can create a stronger global market for <strong>Green Hydrogen</strong>. This includes aligning incentives, subsidies, and carbon pricing mechanisms to support its adoption.</p><p>International dialogues help in sharing best practices and developing supportive regulatory environments that foster demand and supply for this emerging energy source.</p><h4>Addressing Climate Change Goals</h4><p>Ultimately, <strong>Green Hydrogen</strong> is a critical tool in the fight against <strong>climate change</strong>. International cooperation is indispensable to collectively achieve ambitious <strong>net-zero emissions targets</strong> and limit global warming.</p><p>By working together, countries can ensure a faster, more equitable, and effective transition away from fossil fuels, leveraging <strong>Green Hydrogen</strong>'s potential across diverse sectors.</p>
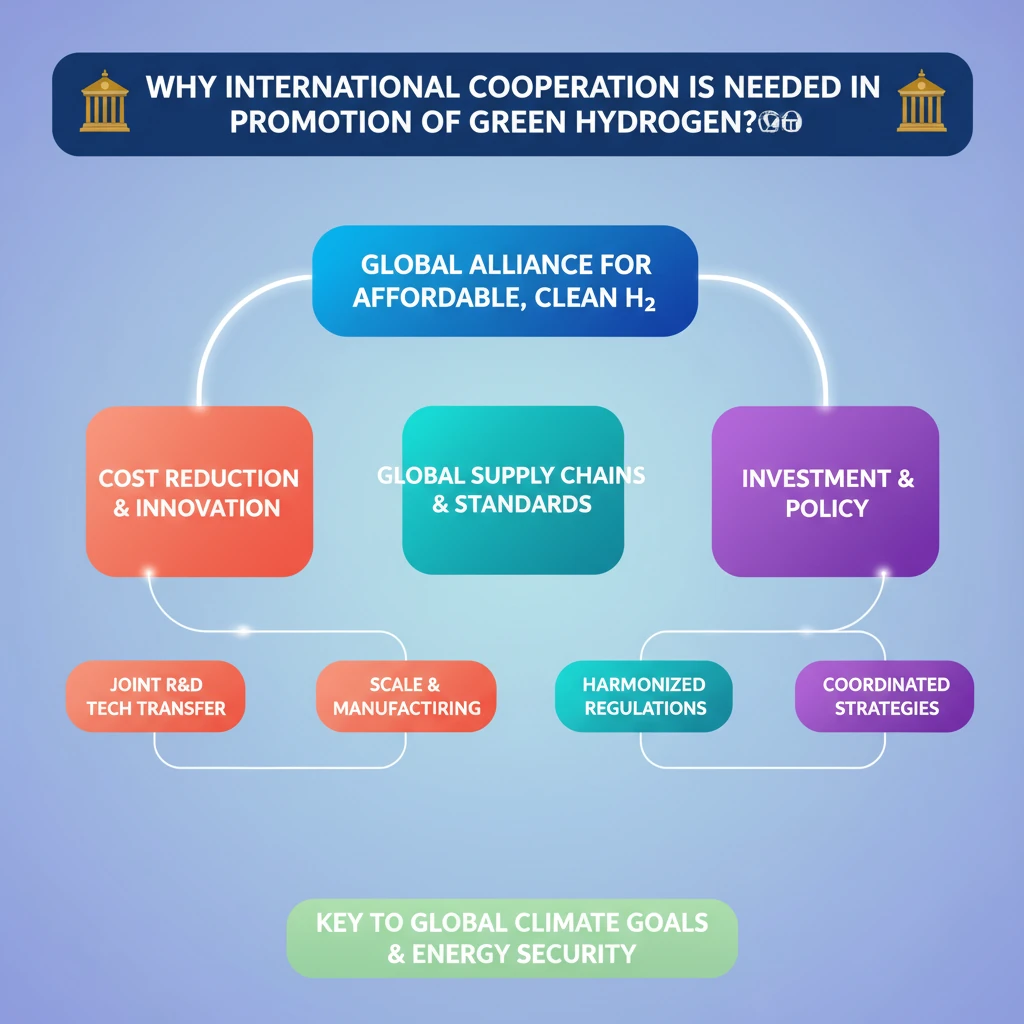
💡 Key Takeaways
- •High production costs are the primary barrier for Green Hydrogen adoption.
- •International cooperation is crucial for cost reduction, R&D acceleration, and technology transfer.
- •Global supply chains and harmonized standards are vital for a thriving Green Hydrogen market.
- •International financing and policy coordination are needed to mobilize investments.
- •Green Hydrogen is key to achieving global climate goals and enhancing energy security.
- •India's National Green Hydrogen Mission is a significant step towards becoming a global hub.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•International Energy Agency (IEA) reports on Hydrogen
•Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India - National Green Hydrogen Mission documents
•European Commission - EU Hydrogen Strategy documents
•News articles and official statements regarding India-Germany Green Hydrogen Task Force