99% of human history - History | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

99% of human history
Easy⏱️ 6 min read
history
📖 Introduction
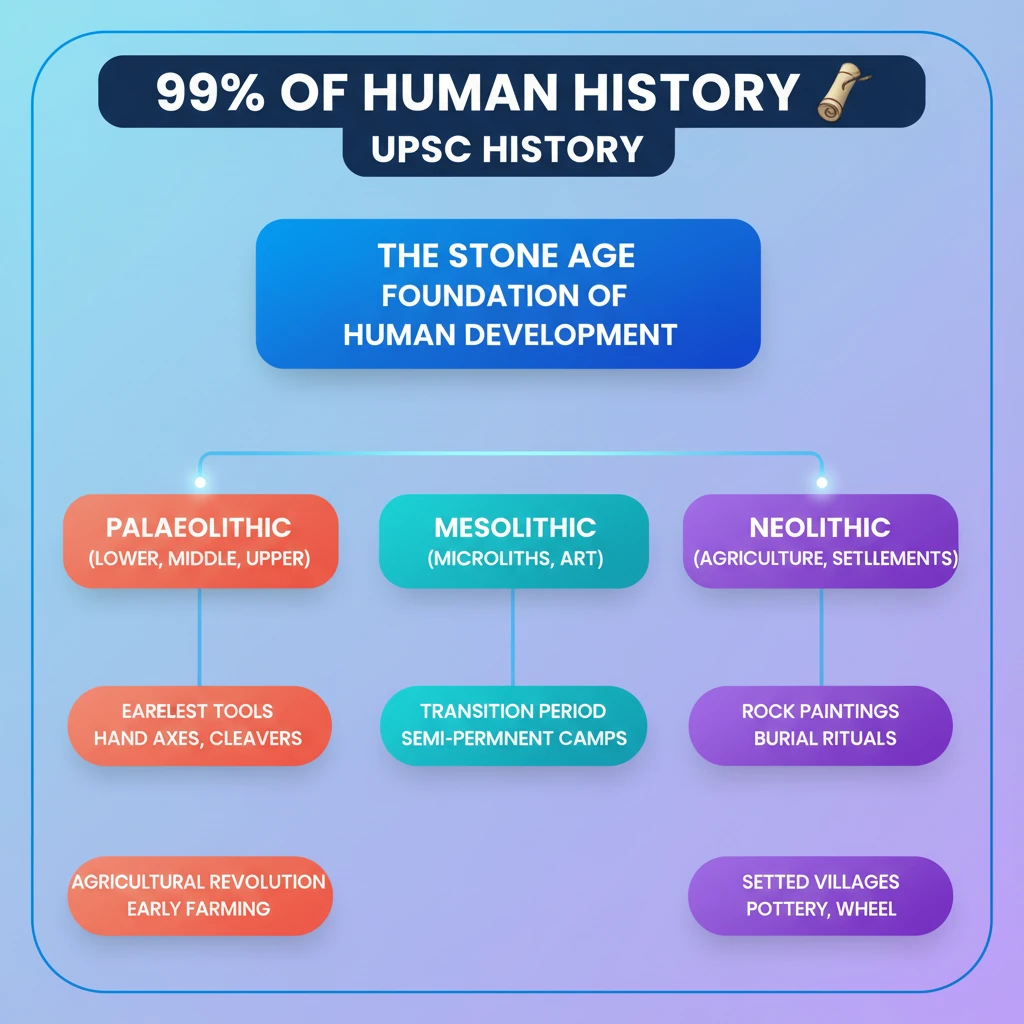
<h4>Introduction to Human History: The Stone Age</h4><p>The vast majority, approximately <strong>99%</strong>, of all <strong>human history</strong> is encompassed within the <strong>Stone Age</strong>. This period is crucial for understanding the foundational developments of human civilization.</p><p>In <strong>India</strong>, the diverse geographical features including varied landforms, abundant water sources, diverse plant life, and a rich animal population, facilitated human habitation across most regions. Exceptions were primarily the high <strong>Himalayas</strong> and the heavily riverine <strong>Indo-Gangetic plains</strong> during certain early phases of the Stone Age.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>Stone Age</strong> is broadly categorized into three principal periods based on technological advancements and cultural characteristics:</p><ul><li><strong>Paleolithic Period</strong> (Old Stone Age)</li><li><strong>Mesolithic Period</strong> (Middle Stone Age)</li><li><strong>Neolithic Period</strong> (New Stone Age)</li></ul></div><h4>The Paleolithic Period in India</h4><p>The <strong>Indian Paleolithic</strong> era itself is further subdivided into three distinct developmental stages, reflecting progressive changes in tool-making techniques and human adaptation.</p><h5>Lower Paleolithic (600,000 BP to 150,000 BP)</h5><p>This earliest phase of the Paleolithic period is characterized by the use of relatively large and crude tools. Early humans primarily utilized <strong>large pebbles</strong> or <strong>flakes</strong> to craft their implements.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Tools:</strong> <strong>Choppers</strong>, <strong>chopping tools</strong>, <strong>hand axes</strong>, <strong>cleavers</strong>, and <strong>knives</strong> were common during this period.</p></div><p>The <strong>Lower Paleolithic</strong> in India is distinguished by two prominent cultural traditions:</p><ul><li>The <strong>Soanian pebble-tool tradition</strong>, primarily found in the north-west.</li><li>The <strong>Peninsular Indian handaxe-cleaver tradition</strong>, widespread across the Indian subcontinent.</li></ul><h5>Middle Paleolithic (165,000 BP to 31,000 BP)</h5><p>This phase represents a refinement in tool-making. It is marked by a shift towards tools made from a variety of <strong>flakes</strong>, which were carefully struck from stone cores.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Tools:</strong> Common tools included <strong>scrapers</strong>, <strong>points</strong>, and <strong>borers</strong>, indicating more specialized functions compared to the Lower Paleolithic.</p></div><h5>Upper Paleolithic (40,000 BP to 12,000 BP)</h5><p>The <strong>Upper Paleolithic</strong> period witnessed significant improvements in tool technology and diversity. Humans began creating more sophisticated and specialized tools.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Advanced Techniques:</strong> This phase saw the development of the <strong>punch technique</strong>, allowing for the creation of long, parallel-sided blades.</p><p><strong>Key Tools:</strong> Tools such as <strong>blunted blades</strong>, <strong>penknife blades</strong>, <strong>blades with serrated edges</strong>, and <strong>arrow points</strong> became prevalent, suggesting advancements in hunting and processing.</p></div><h4>The Mesolithic Culture</h4><p>The <strong>Mesolithic era</strong>, or Middle Stone Age, served as a transitional period between the Paleolithic and Neolithic. It is characterized by significant changes in human lifestyle and technology.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Features of Mesolithic Culture:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Settlements:</strong> People inhabited both <strong>semi-permanent</strong> and <strong>temporary settlements</strong>.</li><li><strong>Habitats:</strong> They utilized natural shelters like <strong>caves</strong> as well as <strong>open areas</strong> for living.</li><li><strong>Rituals:</strong> Evidence of <strong>burial rituals</strong> indicates developing social structures and beliefs.</li><li><strong>Art:</strong> Demonstrated significant <strong>artistic abilities</strong>, often seen in cave paintings.</li><li><strong>Continuity:</strong> Maintained a strong sense of <strong>cultural continuity</strong> from previous periods.</li><li><strong>Tools:</strong> The defining characteristic was the use of <strong>microlithic tools</strong> (small, geometric stone tools), ideal for hunting smaller prey.</li></ul></div><h4>The Neolithic Period</h4><p>The <strong>Neolithic period</strong>, or New Stone Age, marks one of the most transformative phases in human history, often referred to as the <strong>Neolithic Revolution</strong>.</p><div class='highlight-box'><p>This period fundamentally changed human society by marking the definitive <strong>beginning of agriculture</strong> and the widespread practice of <strong>animal domestication</strong>.</p></div><p>Early evidence for the development of <strong>Neolithic culture</strong> is found in several key regions globally. These areas became cradles of early agricultural societies.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Early Neolithic Evidence Locations:</strong></p><ul><li>The <strong>Fertile Crescent region</strong> of <strong>Egypt</strong> and <strong>Mesopotamia</strong>.</li><li>The <strong>Indus region</strong> of present-day India and Pakistan.</li><li>The <strong>Ganges Valley</strong> of India.</li><li>Various sites across <strong>China</strong>.</li></ul></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The Stone Age constitutes 99% of human history, laying the foundation for all subsequent development.
- •It is divided into Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic periods, reflecting technological and cultural evolution.
- •Indian geography played a crucial role in early human settlement patterns during the Stone Age.
- •The Paleolithic period in India had three phases (Lower, Middle, Upper) with distinct tool types (e.g., hand axes, scrapers, blades).
- •The Mesolithic period is characterized by microlithic tools, semi-permanent settlements, and early art/burial rituals.
- •The Neolithic period marked the revolutionary shift to agriculture and animal domestication, leading to settled life.
- •Early evidence of Neolithic culture is found in the Fertile Crescent, Indus region, Ganges Valley, and China.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content