What is the Stone Age? - History | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
What is the Stone Age?
Easy⏱️ 8 min read
history
📖 Introduction
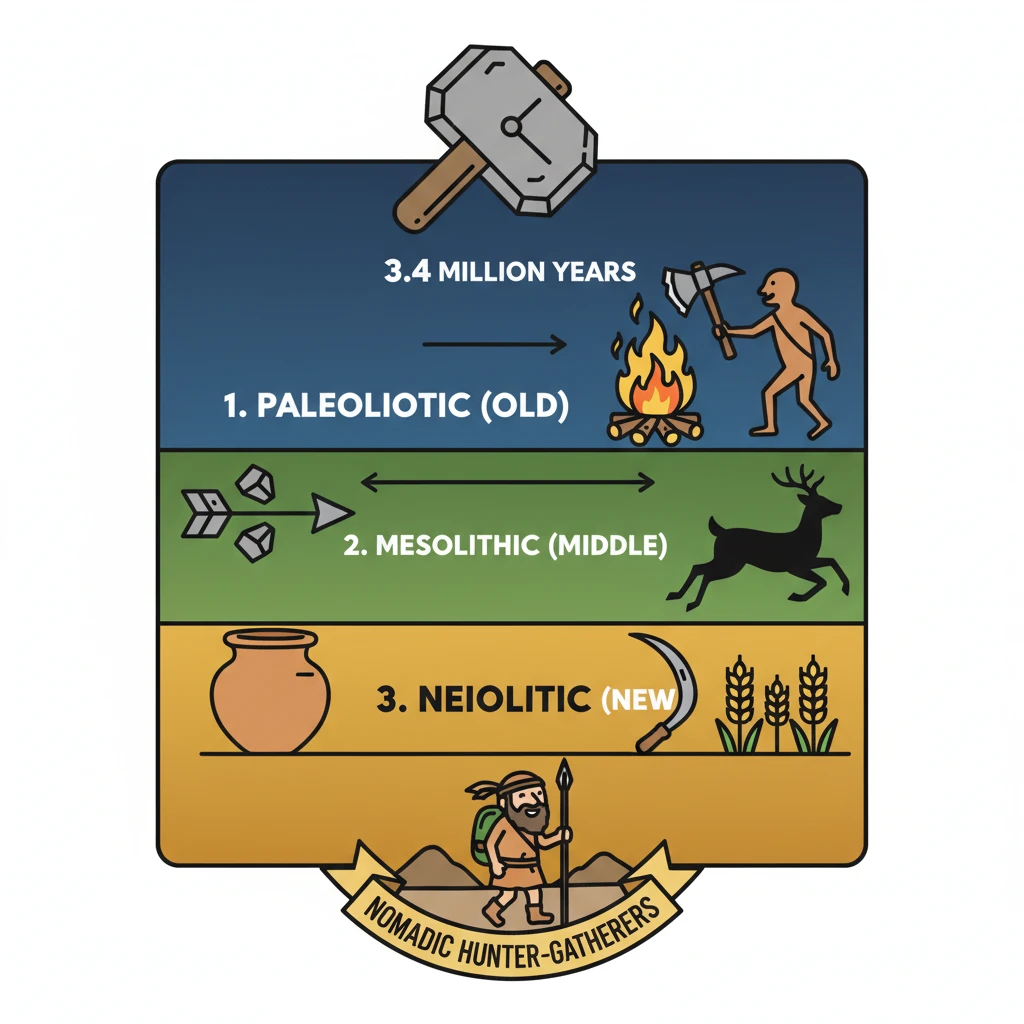
<h4>Introduction to the Stone Age</h4><p>The <strong>Stone Age</strong> represents the earliest and longest period of human prehistory. It is fundamentally defined by the widespread use of <strong>stone tools</strong> by early hominids.</p><p>This era began approximately <strong>3.4 million years ago (mya)</strong> when our ancestors first started fashioning and utilizing rudimentary stone implements for various tasks.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Definition:</strong> The <strong>Stone Age</strong> is a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make implements with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface.</p></div><h4>Key Characteristics of the Stone Age</h4><p>Life during the Stone Age was characterized by a <strong>nomadic hunting-gathering lifestyle</strong>. Early humans relied entirely on their environment for sustenance, moving frequently to find food and resources.</p><p>The development of <strong>stone tool technology</strong> was a pivotal aspect, evolving from simple choppers to more refined blades and projectile points over millennia. This technological progression enabled better hunting, processing of food, and defense.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Primary Occupation:</strong> Hunting, fishing, and gathering wild plants were the main methods of acquiring food. There was no agriculture or domestication of animals in the early phases.</p></div><h4>Phases of the Stone Age</h4><p>The Stone Age is typically divided into three main periods, each marked by distinct technological advancements and societal structures.</p><ul><li><strong>Paleolithic Age (Old Stone Age):</strong> The longest period, characterized by crude stone tools, nomadic hunter-gatherers, and the discovery of fire.</li><li><strong>Mesolithic Age (Middle Stone Age):</strong> A transitional period featuring smaller, more refined microlithic tools, incipient animal domestication, and settled communities.</li><li><strong>Neolithic Age (New Stone Age):</strong> Marked by polished stone tools, the advent of agriculture, animal husbandry, pottery, and permanent settlements, leading to the formation of villages.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the characteristics and transitions between these phases is crucial for questions on prehistoric India, often appearing in <strong>GS Paper 1 (History)</strong>.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •The Stone Age began approximately 3.4 million years ago with the first use of stone tools by hominids.
- •It is divided into Paleolithic (Old), Mesolithic (Middle), and Neolithic (New) ages, marked by tool advancements.
- •Early humans were primarily nomadic hunter-gatherers, adapting to diverse environments.
- •Key innovations include fire control (Paleolithic), microliths (Mesolithic), and agriculture/pottery (Neolithic).
- •Archaeological sites like Olduvai Gorge, Bhimbetka, and Mehrgarh provide crucial evidence of Stone Age life and transitions.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NCERT Class VI - Our Pasts – I
•Upinder Singh - A History of Ancient and Early Medieval India
•D.N. Jha - Ancient India: An Introductory Outline