What was Harappan Civilization? - History | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
What was Harappan Civilization?
Easy⏱️ 4 min read
history
📖 Introduction
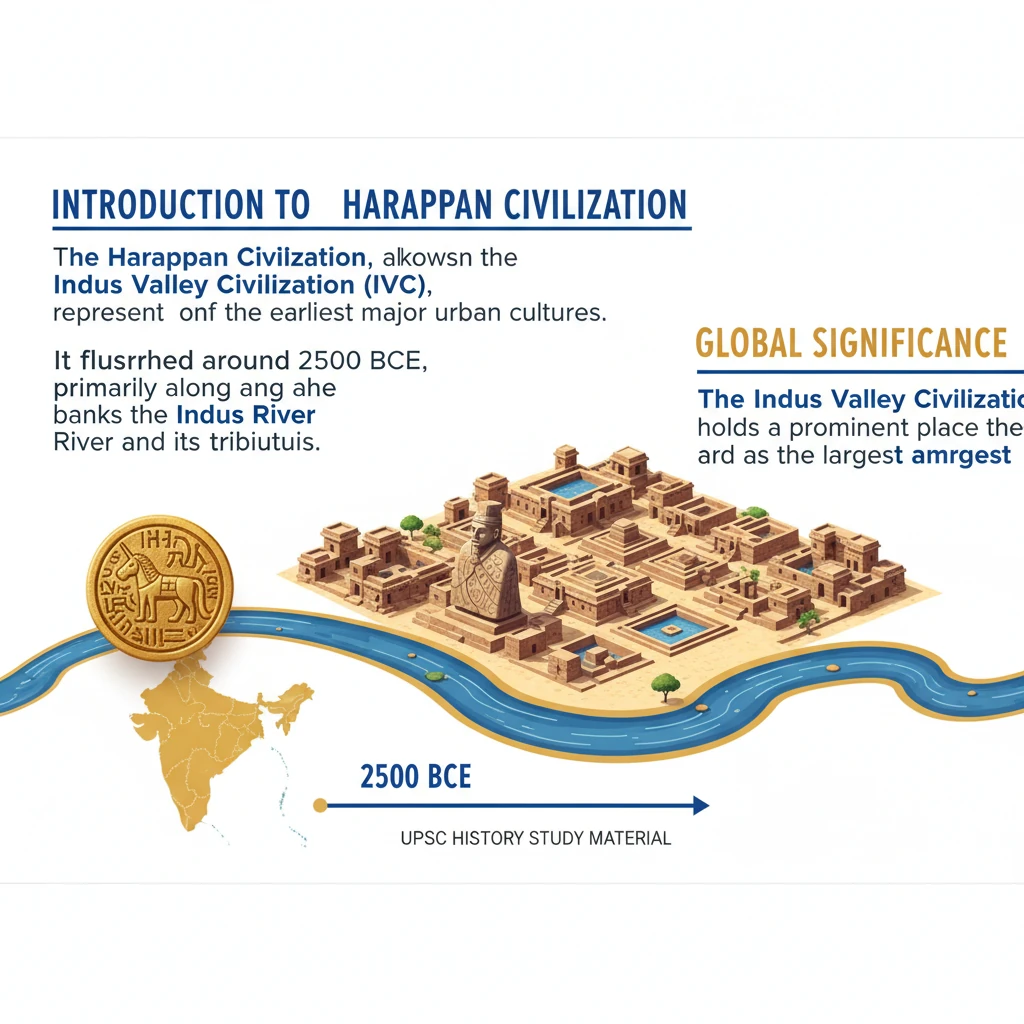
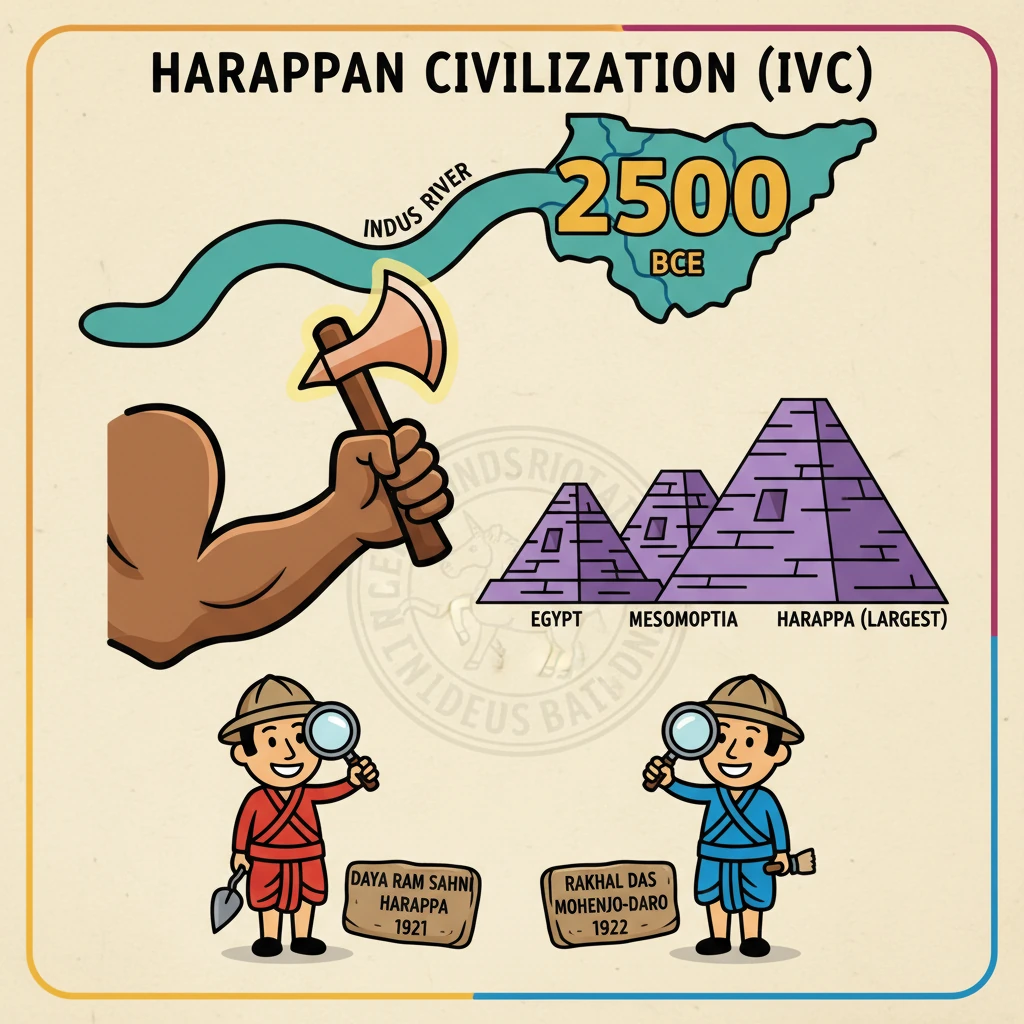
<h4>Introduction to Harappan Civilization</h4><p>The <strong>Harappan Civilization</strong>, also known as the <strong>Indus Valley Civilization (IVC)</strong>, represents one of the earliest major urban cultures.</p><p>It flourished around <strong>2500 BCE</strong>, primarily along the fertile banks of the <strong>Indus River</strong> and its tributaries.</p><h4>Global Significance</h4><p>The <strong>Indus Valley Civilization</strong> holds a prominent place as the <strong>largest</strong> among the four ancient urban civilizations known to history.</p><p>It was a contemporary of other great civilizations such as <strong>Egypt</strong>, <strong>Mesopotamia</strong>, and <strong>China</strong>, showcasing a parallel development of complex societies.</p><h4>Bronze Age Classification</h4><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>IVC</strong> is unequivocally classified as a <strong>Bronze-age civilization</strong>.</p></div><p>This classification is derived from the extensive discovery of numerous <strong>artefacts</strong> crafted from <strong>copper-based alloys</strong> throughout its various sites.</p><h4>Key Discoveries and Excavators</h4><p>The unearthing of the <strong>Harappan Civilization</strong> was a monumental achievement in archaeology, significantly reshaping the understanding of ancient Indian history.</p><ul><li><strong>Daya Ram Sahni</strong> conducted the first excavations at <strong>Harappa</strong> during <strong>1921-22</strong>.</li><li><strong>Rakhal Das Banerji</strong> initiated the excavation of <strong>Mohenjo-daro</strong> in <strong>1922</strong>.</li><li><strong>Sir John Marshall</strong>, serving as the <strong>Director-General of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI)</strong>, played a pivotal role in overseeing these crucial discoveries.</li></ul><h4>Phases of Harappan Civilization</h4><p>The development and eventual decline of the <strong>Harappan Civilization</strong> can be understood through three distinct chronological phases:</p><ol><li><strong>Early Phase (3200 BCE to 2600 BCE)</strong>:<ul><li>This period is strongly associated with the <strong>Hakra Phase</strong>, which was identified in the <strong>Ghaggar-Hakra River Valley</strong>.</li><li>The earliest known examples of the <strong>Indus script</strong> date back to approximately <strong>3000 BCE</strong> within this phase.</li></ul></li><li><strong>Mature Period (2600 BCE to 1900 BCE)</strong>:<ul><li>By <strong>2600 BCE</strong>, the <strong>IVC</strong> had reached its peak, exhibiting advanced urbanization and sophisticated planning.</li><li>Early Harappan towns, including major centers like <strong>Harappa</strong> and <strong>Mohenjo-daro</strong> (in modern-day Pakistan) and <strong>Lothal</strong> (in India), evolved into significant urban hubs.</li></ul></li><li><strong>Late Phase (1900 BCE to 1500 BCE)</strong>:<ul><li>This final phase is characterized by the gradual <strong>decay and eventual collapse</strong> of the once-flourishing <strong>Harappan Civilization</strong>.</li></ul></li></ol>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •The Harappan Civilization (IVC) flourished around 2500 BCE along the Indus River.
- •It was the largest of the four ancient urban civilizations, alongside Egypt, Mesopotamia, and China.
- •Classified as a Bronze-age civilization due to extensive use of copper-based alloys.
- •Key excavators: Daya Ram Sahni (Harappa, 1921-22) and Rakhal Das Banerji (Mohenjo-daro, 1922).
- •Sir John Marshall, DG of ASI, was responsible for coordinating and announcing these discoveries.
- •The civilization progressed through Early (3200-2600 BCE), Mature (2600-1900 BCE), and Late (1900-1500 BCE) phases.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content