What was SC Bose Role in India’s Freedom Movement? - History | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What was SC Bose Role in India’s Freedom Movement?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
history
📖 Introduction
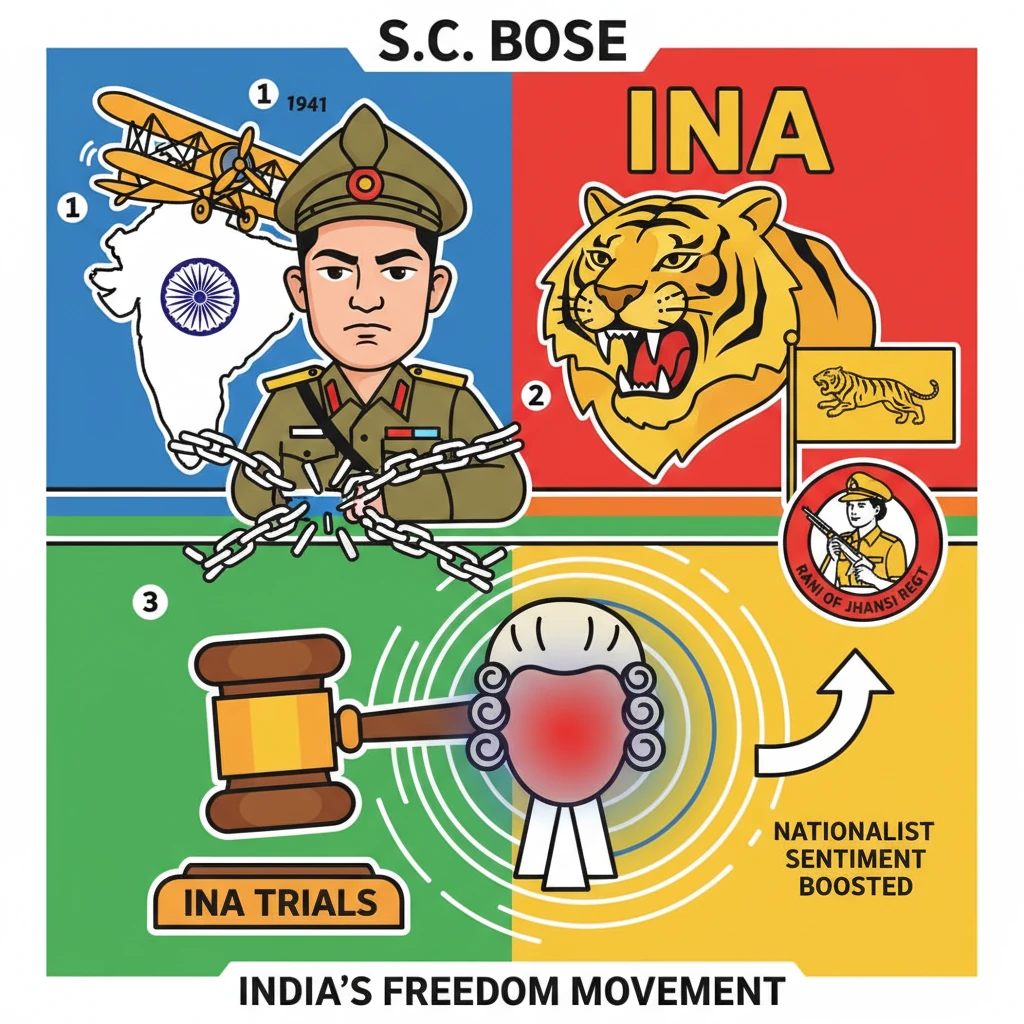
<h4>Dramatic Escape and Early Actions</h4><p><strong>Subhas Chandra Bose</strong> was arrested in <strong>1940</strong> before he could campaign against the monument dedicated to the <strong>Black Hole tragedy of Calcutta</strong>. This incident, where <strong>123 Europeans</strong> died on <strong>June 20, 1756</strong>, occurred a year before the <strong>Battle of Plassey</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>His dramatic escape from India in <strong>1941</strong>, traveling under various disguises, showcased his relentless pursuit of independence. This act demonstrated his resolve even in the face of stringent British surveillance.</p></div><h4>International Alliances During World War II</h4><p>After reaching Europe, <strong>Bose</strong> strategically sought support from powers interested in defeating Britain during <strong>World War II</strong>. He approached <strong>Nazi Germany</strong>, the <strong>Soviet Union</strong>, and later <strong>Imperial Japan</strong> in Asia.</p><div class='info-box'><p>These alliances allowed <strong>Bose</strong> to establish the <strong>Azad Hind Radio</strong>. He was also provided with several thousand <strong>Indian prisoners of war (POWs)</strong> captured by the <strong>Axis powers</strong> during the war.</p></div><h4>Perilous Journey to Southeast Asia</h4><p>In <strong>February 1943</strong>, <strong>Bose</strong> and his aide, <strong>Abid Hasan</strong>, embarked on an arduous journey. They traveled from <strong>Germany</strong> in a submarine, crossing the <strong>Atlantic Ocean</strong>, the <strong>Cape of Good Hope</strong>, and the <strong>Indian Ocean</strong>.</p><p>The journey culminated with them reaching <strong>Tokyo</strong> by air, completing a <strong>90-day, perilous voyage</strong>. This demonstrated his commitment to securing international backing for India's freedom.</p><h4>Formation of the Indian National Army (INA)</h4><p>The <strong>Indian National Army (INA)</strong> was formed in <strong>1942</strong>. It comprised thousands of <strong>Indian prisoners of war</strong> who had been captured by the <strong>Japanese</strong>, receiving support from <strong>Japanese troops</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Initially, <strong>Captain Mohan Singh</strong> was appointed as the commander of the <strong>INA</strong>. Later, <strong>Subhas Chandra Bose</strong> took over its leadership, galvanizing its forces for the independence struggle.</p></div><h4>The 'Chalo Delhi' Campaign</h4><p>Under <strong>SC Bose's</strong> leadership, the <strong>INA</strong> launched the <strong>'Chalo Delhi' campaign</strong>. In <strong>March 1944</strong>, they crossed the <strong>Indo-Burma border</strong> and marched towards <strong>Imphal</strong> and <strong>Kohima</strong>.</p><p>However, the campaign ultimately ended in <strong>Imphal</strong> with the defeat of <strong>Japan</strong> in <strong>World War II</strong>, significantly impacting the INA's advance.</p><h4>The Provisional Government of Azad Hind</h4><p>In <strong>October 1943</strong>, <strong>Bose</strong> established the <strong>Provisional Government of Azad Hind</strong> in <strong>Singapore</strong>. This government was a symbolic assertion of India's independence from British rule.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The headquarters of the <strong>Azad Hind Government</strong> were subsequently moved to <strong>Rangoon</strong> in <strong>January 1944</strong>, further consolidating its operational base in Southeast Asia.</p></div><h4>The Mysterious Demise of SC Bose</h4><p><strong>Subhas Chandra Bose's</strong> fate remains a subject of historical debate. He allegedly boarded a <strong>Japanese plane</strong> headed towards <strong>China</strong>, which reportedly crashed.</p><p>According to some accounts, <strong>SC Bose</strong> was badly burned but still alive after the alleged crash. The exact circumstances of his death continue to be a mystery.</p><h4>Legacy of Subhas Chandra Bose</h4><p><strong>Bose’s</strong> leadership, his strong ideology, and his unwavering call for <strong>complete independence</strong> made him one of the most influential figures in India’s freedom struggle. His radical approach inspired many.</p><div class='highlight-box'><p>His slogan, <strong>'Give me blood, and I shall give you freedom!'</strong>, continues to resonate as a powerful symbol of his revolutionary spirit and dedication to the nation.</p></div><h4>Rani of Jhansi Regiment</h4><p>A testament to his progressive vision, <strong>Bose</strong> also created the <strong>Rani of Jhansi Regiment</strong>. This was a unique military unit composed entirely of <strong>women</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>These women fought alongside men in the struggle for independence, marking a significant and pioneering step for women's participation in armed resistance.</p></div><h4>The INA Trials (Red Fort Trials)</h4><p>The <strong>INA Trials</strong> were a series of military tribunals held by the <strong>British colonial government</strong> in <strong>1945-46</strong>. They were conducted to try <strong>INA officers and soldiers</strong> for treason.</p><p>The trials of prominent officers like <strong>Shah Nawaz Khan</strong>, <strong>Prem Kumar Sehgal</strong>, and <strong>Gurbaksh Singh Dhillon</strong> ignited a powerful wave of nationalist sentiment. This led to widespread violent confrontations against the <strong>British Raj</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>The <strong>INA Trials</strong> are crucial for <strong>UPSC Mains (GS Paper I - Modern History)</strong>. They represent a pivotal moment where public sympathy for the INA significantly weakened British authority and bolstered the independence movement.</p></div><h4>Subhas Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar</h4><p>The <strong>Subhas Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar</strong> was instituted in <strong>2018</strong>. This annual award recognizes and honors the invaluable contribution and selfless service rendered in the field of <strong>disaster management</strong> in India.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The award is announced every year on <strong>January 23rd</strong>, <strong>Bose's birth anniversary</strong>. It carries a cash prize of <strong>Rs 51 lakh</strong> and a certificate for an institution, and <strong>Rs 5 lakh</strong> and a certificate for an individual.</p></div>
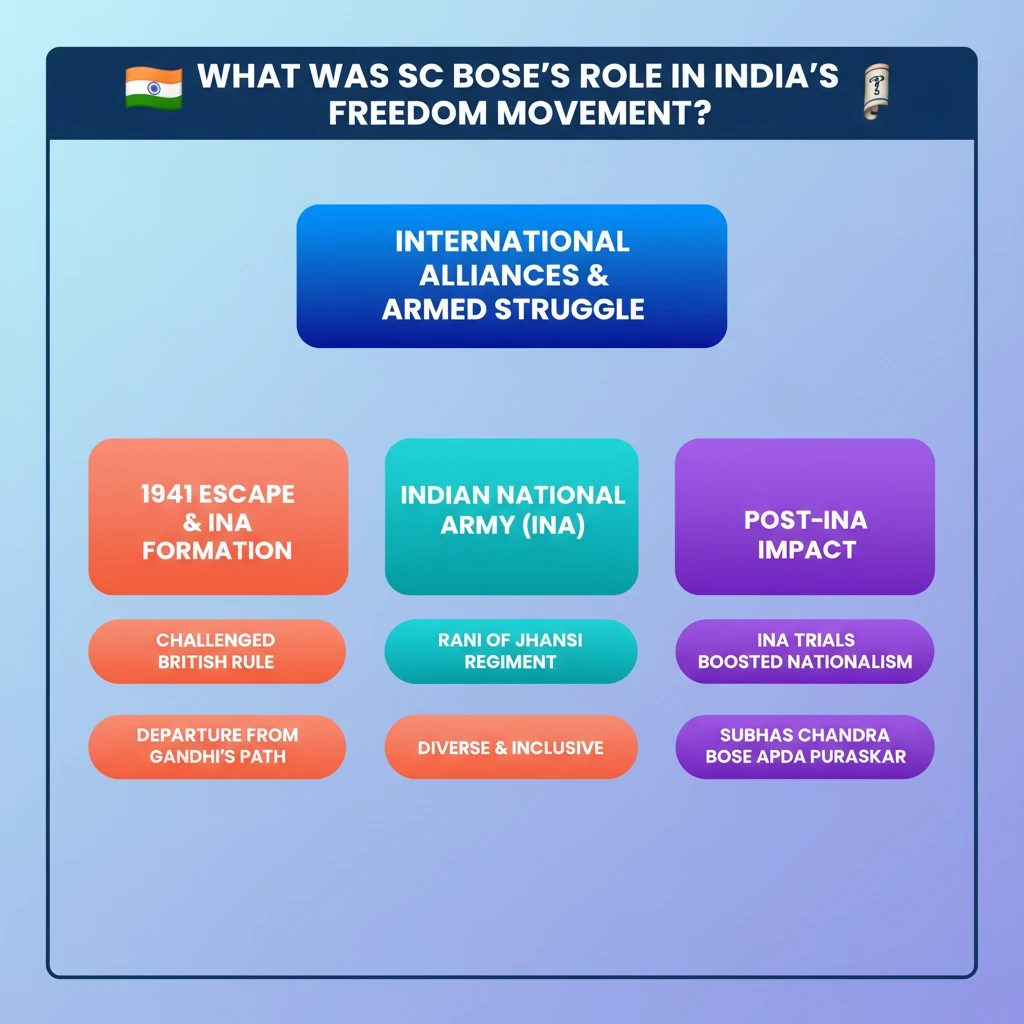
💡 Key Takeaways
- •SC Bose pursued independence through international alliances and armed struggle, a departure from Gandhi's non-violence.
- •His escape in 1941 and formation of the INA were pivotal in challenging British rule.
- •The INA, including the Rani of Jhansi Regiment, demonstrated a diverse and inclusive approach to warfare.
- •The INA Trials significantly boosted nationalist sentiment across India.
- •Bose's legacy is honored through the Subhas Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar for disaster management.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NCERT History Textbooks (Class XII)
•Spectrum's 'A Brief History of Modern India'