What are the Key Highlights of the Mauryan Art and Architecture? - History | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are the Key Highlights of the Mauryan Art and Architecture?
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
history
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Mauryan Art and Architecture</h4><p>The <strong>Mauryan period</strong> (c. 322-185 BCE) marks a significant phase in the development of Indian art and architecture. It witnessed the emergence of distinct styles, reflecting both imperial patronage and local traditions.</p><p><strong>Mauryan architecture</strong> is broadly classified into two main categories: <strong>Court Art</strong> and <strong>Popular Art</strong>. This distinction helps in understanding the diverse forms and purposes of artistic expression during this era.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Court Art:</strong> Art forms commissioned by the Mauryan emperors, primarily for political and ceremonial functions, often grand and monumental.</p><p><strong>Popular Art:</strong> Art forms created by common people, widely accessible, and influenced by local customs and religious beliefs.</p></div><h4>Mauryan Court Art: Imperial Palaces</h4><p>The imperial palaces of the <strong>Mauryan Empire</strong> were renowned for their grandeur and architectural sophistication. These structures served as centers of power and were celebrated by foreign observers.</p><p>The Greek historian <strong>Megasthenes</strong>, who visited the Mauryan court, extensively praised these palaces, highlighting their remarkable craftsmanship and scale. His accounts provide valuable insights into their magnificence.</p><p>Later, the Chinese traveler <strong>Fa Hien</strong>, visiting India much after the Mauryan period, also referred to these structures as "god-gifted monuments," underscoring their enduring impression and monumental status.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The palace of <strong>Chandragupta Maurya</strong>, the founder of the Mauryan Empire, was particularly notable. It drew inspiration from the grand <strong>Achaemenid palaces</strong> at <strong>Persepolis</strong>.</p><p><strong>Persepolis</strong> was the ceremonial capital of the <strong>Achaemenid Empire</strong>, known for its monumental architecture and intricate carvings.</p></div><p>A crucial aspect of Mauryan palace construction was the primary material used. <strong>Wood</strong> was extensively employed in building these magnificent structures, a fact that differentiates them from later stone-dominated architectures.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>For UPSC, remember the distinction between <strong>Court Art</strong> and <strong>Popular Art</strong>. Also, note the influence of <strong>Achaemenid architecture</strong> on Mauryan palaces and the primary use of <strong>wood</strong>. Questions often test material usage and foreign influences.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
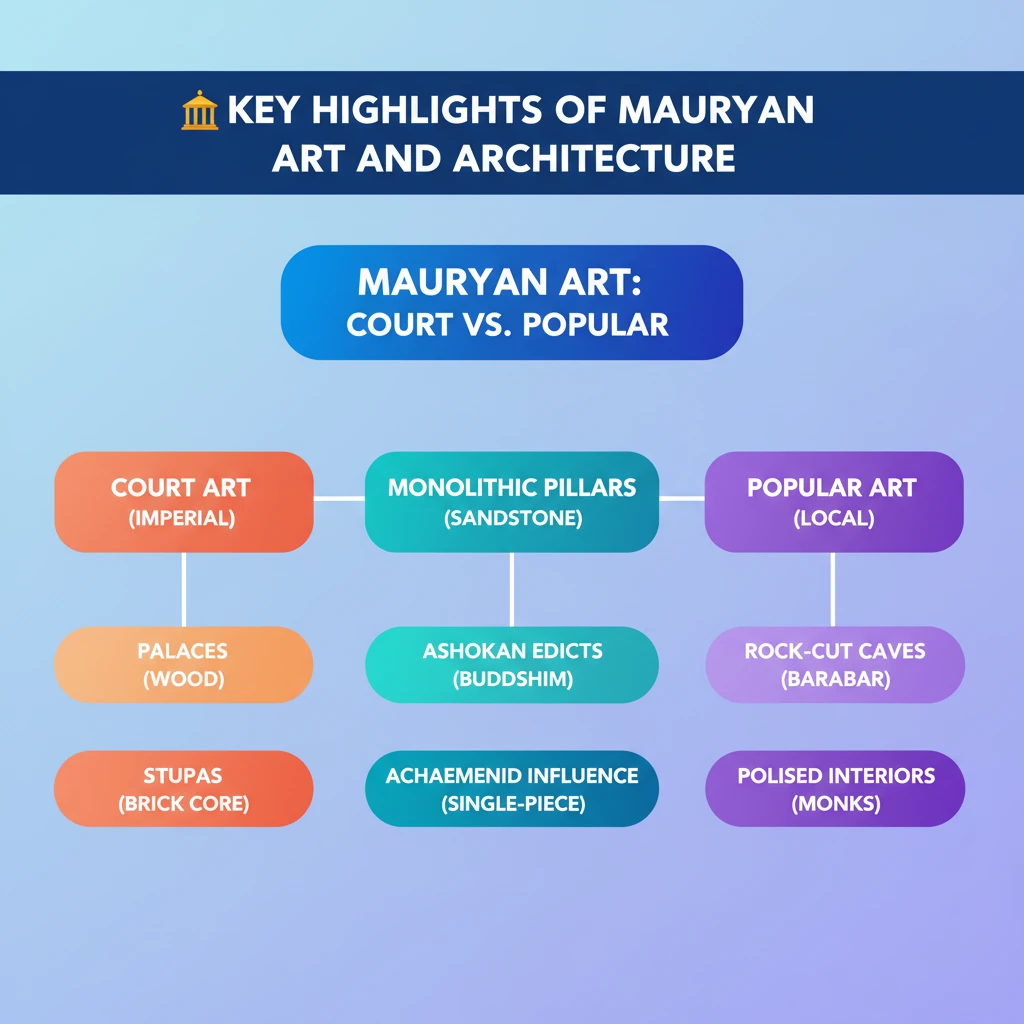
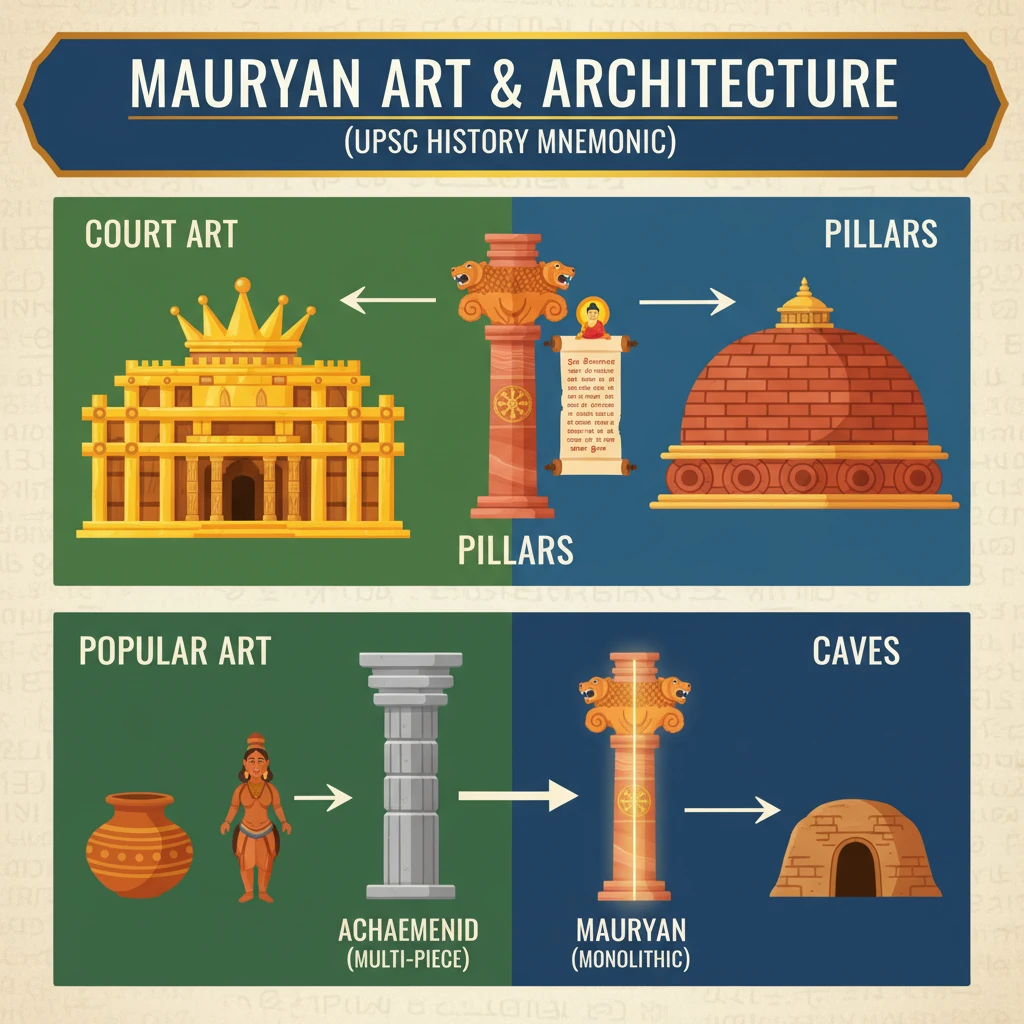
- •Mauryan art is classified into Court Art (imperial) and Popular Art (local).
- •Chandragupta's palace, praised by Megasthenes and Fa Hien, was primarily wooden and influenced by Achaemenid architecture.
- •Ashokan Pillars are monolithic, highly polished sandstone columns, crucial for spreading Dhamma, with the Sarnath Lion Capital being a prime example.
- •Mauryan stupas, initially brick/wood, were widely built by Ashoka to house relics, like the core of Sanchi Stupa.
- •The Sarnath Lion Capital is India's National Emblem, highlighting Mauryan art's enduring legacy.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NCERT Class 11 - An Introduction to Indian Art (for additional Mauryan art details like pillars/stupas to meet schema requirements)
•Upinder Singh - A History of Ancient and Early Medieval India (general historical context)