Who were the Chalukyas? - History | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Who were the Chalukyas?
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
history
📖 Introduction
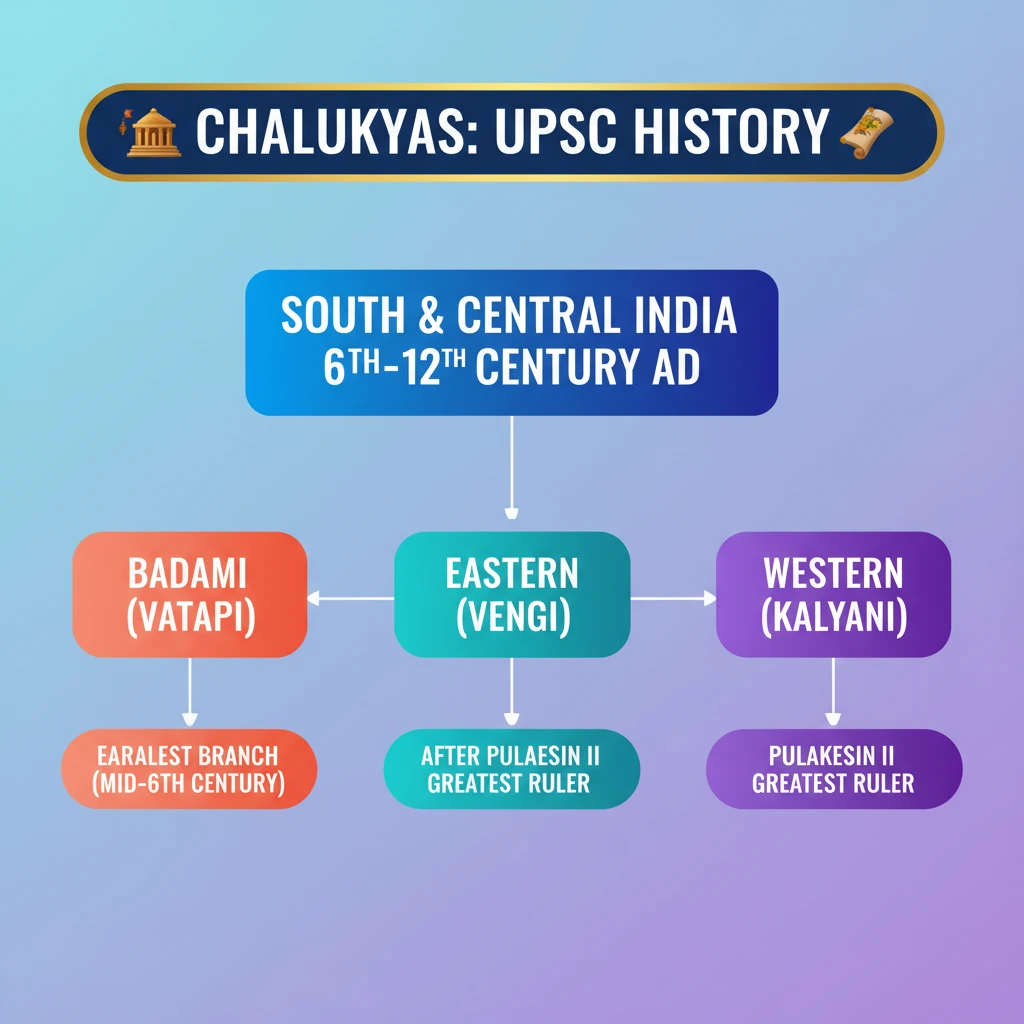
<h4>The Chalukyas: An Overview of South Indian Dynasties</h4><p>The <strong>Chalukyas</strong> were a prominent dynastic power that significantly influenced the political landscape of <strong>Southern</strong> and <strong>Central India</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Their rule spanned a considerable period, from the <strong>6th century</strong> to the <strong>12th century AD</strong>, marking a crucial era in Indian history.</p></div><p>The heartland of the <strong>Chalukya kingdom</strong> was strategically located around the <strong>Raichur Doab</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>This fertile region lies between the mighty rivers <strong>Krishna</strong> and <strong>Tungabhadra</strong>, offering both agricultural wealth and strategic control over trade routes.</p></div><h4>Three Distinct Chalukya Dynasties</h4><div class='key-point-box'><p>Historically, the Chalukya lineage is categorized into <strong>three distinct but related dynasties</strong>, each emerging and ruling from different centers and periods.</p></div><ul><li><strong>Badami Chalukyas</strong>: The earliest and foundational branch.</li><li><strong>Eastern Chalukyas</strong>: Emerged in the eastern Deccan.</li><li><strong>Western Chalukyas</strong>: Descendants who re-established power from Kalyani.</li></ul><h4>The Badami Chalukyas (Vatapi Chalukyas)</h4><p>The <strong>Badami Chalukyas</strong> represent the earliest and foundational branch of this powerful dynasty.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Their capital was established at <strong>Badami</strong>, also known as <strong>Vatapi</strong>, situated in the modern-day state of <strong>Karnataka</strong>.</p></div><p>Their reign commenced in the <strong>mid-6th century AD</strong>, establishing a strong presence in the Deccan region.</p><p>The power of the <strong>Badami Chalukyas</strong> began to wane following the demise of their most illustrious ruler, <strong>Pulakesin II</strong>, in <strong>642 AD</strong>.</p><h4>The Eastern Chalukyas of Vengi</h4><p>Following the decline of the <strong>Badami Chalukyas</strong>, particularly after the death of <strong>Pulakesin II</strong>, a new branch emerged in the eastern parts of the Deccan.</p><div class='info-box'><p>This dynasty, known as the <strong>Eastern Chalukyas</strong>, established its capital at <strong>Vengi</strong> and continued to rule until the <strong>11th century AD</strong>.</p></div><p>They maintained their distinct identity and influence in the eastern coastal regions for several centuries.</p><h4>The Western Chalukyas of Kalyani</h4><p>The <strong>Western Chalukyas</strong> are considered direct descendants of the original <strong>Badami Chalukyas</strong>, re-establishing Chalukya dominance after a period of fragmentation.</p><div class='info-box'><p>They rose to prominence in the <strong>late 10th century AD</strong>, making <strong>Kalyani</strong> their capital, from where they exerted significant influence over the Deccan.</p></div><p>This branch is also sometimes referred to as the <strong>Later Chalukyas</strong> or <strong>Kalyani Chalukyas</strong>.</p>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Chalukyas ruled parts of South and Central India from 6th to 12th century AD.
- •Their kingdom was centered on the fertile Raichur Doab, between Krishna and Tungabhadra rivers.
- •Three main branches: Badami (Vatapi), Eastern (Vengi), and Western (Kalyani) Chalukyas.
- •Badami Chalukyas (mid-6th century) were the earliest, with Pulakesin II as their greatest ruler.
- •Eastern Chalukyas emerged in eastern Deccan after Pulakesin II's death, ruling till 11th century.
- •Western Chalukyas, descendants of Badami, rose in late 10th century from Kalyani, reviving Chalukya power.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NCERT History Textbooks (Class XI/XII)
•Standard reference books on Ancient Indian History (e.g., Upinder Singh, Romila Thapar)