What were the Key Features of Harappan Civilization? - History | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What were the Key Features of Harappan Civilization?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
history
📖 Introduction
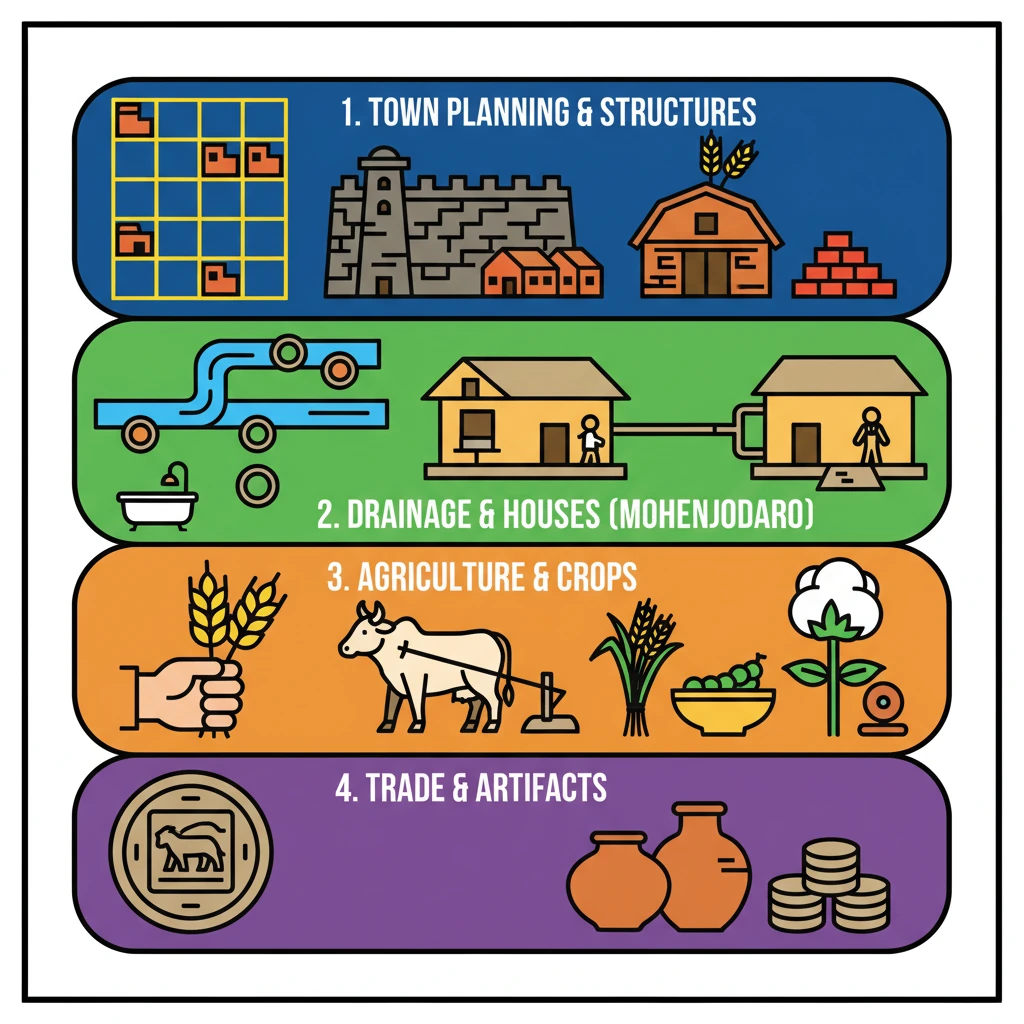
<h4>Advanced Town Planning</h4><p>The <strong>Harappan Civilization</strong> is renowned for its sophisticated <strong>town planning</strong>, a hallmark of its urban centers. Cities were meticulously designed, often following a distinct <strong>grid-like layout</strong>, which indicates a high degree of organization and foresight.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Urban Features:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Citadel/Acropolis:</strong> Prominent elevated areas, likely housing the <strong>ruling class</strong> and important public structures.</li><li><strong>Lower Towns:</strong> Residential areas below the citadel, characterized by well-constructed <strong>brick houses</strong> for common people.</li></ul></div><p>Notable examples include <strong>Harappa</strong> and <strong>Mohenjodaro</strong>, both featuring these dual-part city divisions. The consistency in planning across various sites highlights a standardized approach to urban development.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Architectural and Infrastructure Highlights:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Granaries:</strong> Large structures for storing surplus grains, crucial for economic stability.</li><li><strong>Burnt Bricks:</strong> Widespread use of <strong>burnt bricks</strong> for construction, offering superior durability compared to the dried bricks common in contemporary <strong>Egyptian structures</strong>.</li><li><strong>Drainage System:</strong> <strong>Mohenjodaro</strong> boasted an impressive and elaborate <strong>drainage system</strong>, indicating advanced sanitation practices.</li><li><strong>Courtyards & Bathrooms:</strong> Almost all houses in <strong>Mohenjodaro</strong> had private <strong>courtyards</strong> and <strong>bathrooms</strong>, reflecting a focus on privacy and hygiene.</li></ul></div><p>At sites like <strong>Dholavira</strong> and <strong>Lothal</strong> in <strong>Gujarat</strong>, the entire settlement was fortified. Furthermore, these sites often had internal sections divided by walls, showcasing complex defensive and organizational strategies.</p><h4>Agricultural Prowess</h4><p>The <strong>Harappan villages</strong> were primarily situated near <strong>floodplains</strong>, benefiting from fertile soils for agricultural productivity. This strategic location allowed for bountiful harvests, supporting a large urban population.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Major Crops Cultivated:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Cereals:</strong> <strong>Wheat</strong>, <strong>barley</strong></li><li><strong>Legumes:</strong> <strong>Peas</strong>, <strong>lentils</strong>, <strong>chickpeas</strong></li><li><strong>Oilseeds:</strong> <strong>Sesame</strong>, <strong>rai</strong>, <strong>mustard</strong></li><li><strong>Other:</strong> <strong>Millets</strong> (especially in <strong>Gujarat</strong>)</li></ul></div><p>While <strong>rice</strong> was rarely cultivated, the <strong>Indus people</strong> were pioneers in cotton production. The <strong>Greeks</strong> later referred to this cotton as <strong>“Sindon,”</strong> a testament to its origin in the Indus Valley.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Farming Techniques & Animal Husbandry:</strong></p><p>Although specific farming techniques are challenging to reconstruct from archaeological evidence, the abundance of grain remains clearly indicates extensive agricultural activity. In addition to crop cultivation, <strong>animal husbandry</strong> was a widespread practice, playing a vital role in their economy and sustenance.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Harappan Civilization was characterized by highly advanced and standardized town planning, including a grid layout.
- •Key urban features included citadels, lower towns, large granaries, and widespread use of burnt bricks.
- •Mohenjodaro showcased an impressive drainage system and private courtyards/bathrooms in houses.
- •Agriculture was the economic backbone, with diverse crops like wheat, barley, peas, and pioneering cotton production.
- •Animal husbandry was also a significant practice alongside crop cultivation.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NCERT Textbooks (Ancient Indian History)
•Standard academic sources on Indus Valley Civilization