Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) - History | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Archaeological Survey of India (ASI)
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
history
📖 Introduction
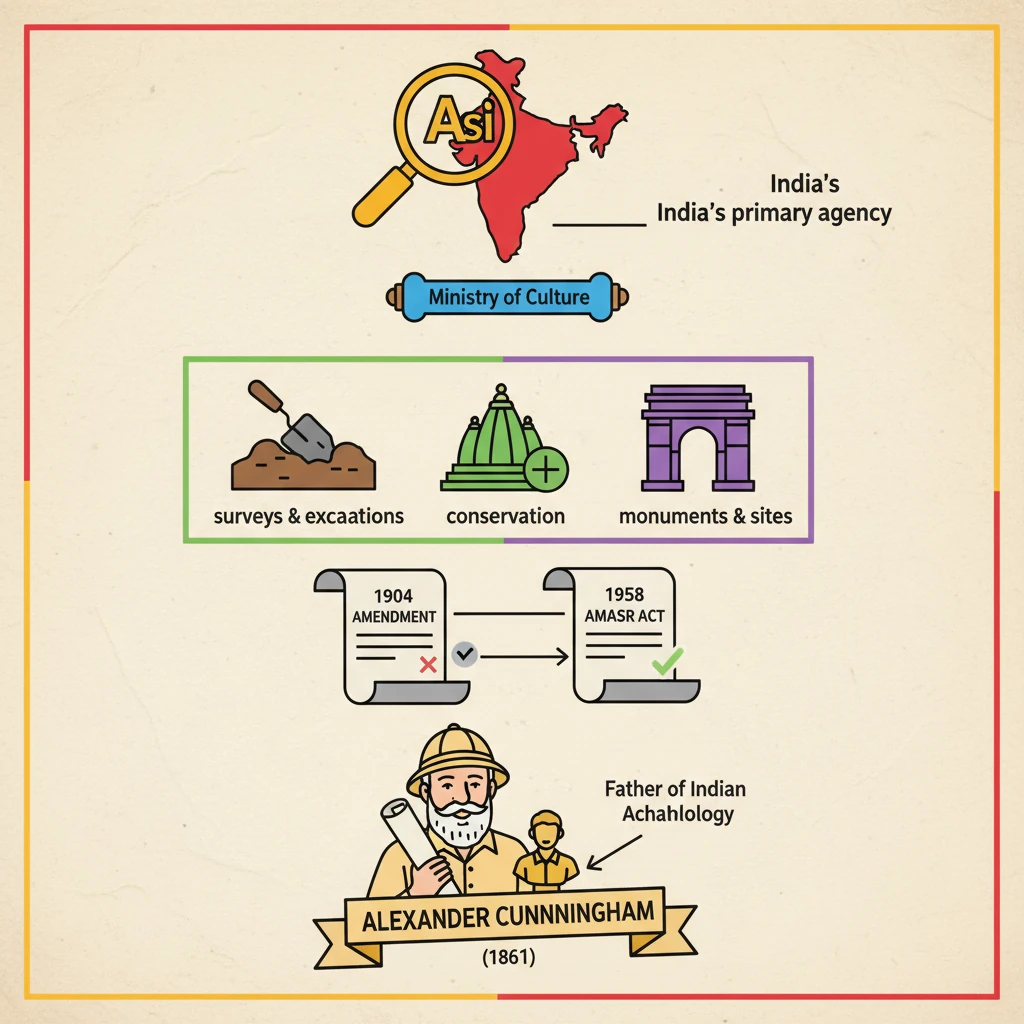
<h4>Introduction to the Archaeological Survey of India</h4><p>The <strong>Archaeological Survey of India (ASI)</strong> is a premier Indian government agency responsible for archaeological research and the protection of cultural heritage. It operates under the <strong>Union Ministry of Culture</strong>.</p><h4>Mandate and Core Functions</h4><p>The primary mandate of <strong>ASI</strong> is to protect and maintain <strong>monuments</strong> and <strong>archaeological sites of national importance</strong> across India.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Key functions include:</p><ul><li>Conducting <strong>surveys</strong> to identify new sites.</li><li>Undertaking <strong>excavations</strong> to unearth historical artifacts and structures.</li><li>Ensuring <strong>conservation</strong> and preservation of protected monuments and sites.</li></ul></div><h4>Legislative Framework</h4><p><strong>ASI</strong> derives its authority and responsibilities from specific parliamentary acts. These acts provide the legal framework for its operations.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Ancient Monuments Preservation Act, 1904</strong>: An early legislation focused on the preservation of ancient monuments.</li><li><strong>The Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958 (AMASR Act)</strong>: This is the principal act governing the protection, preservation, and maintenance of ancient monuments and archaeological sites.</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight</strong>: Understanding the evolution of these acts (<strong>1904</strong> to <strong>1958 AMASR Act</strong>) is crucial for questions on heritage legislation and governance (<strong>GS-I, GS-II</strong>).</p></div><h4>Founding and Key Figure</h4><p>The <strong>Archaeological Survey of India</strong> was formally established in <strong>1861</strong>, marking a significant step in organized archaeological research in India.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Founder and First Director-General</strong>: <strong>Alexander Cunningham</strong></p><p><strong>Alexander Cunningham</strong> is widely recognized as the <strong>“Father of Indian Archaeology”</strong> for his pioneering work and contributions to the field.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight</strong>: Remember <strong>Alexander Cunningham</strong> and the founding year <strong>1861</strong> as frequently asked factual points in prelims (<strong>GS-I History</strong>).</p></div>
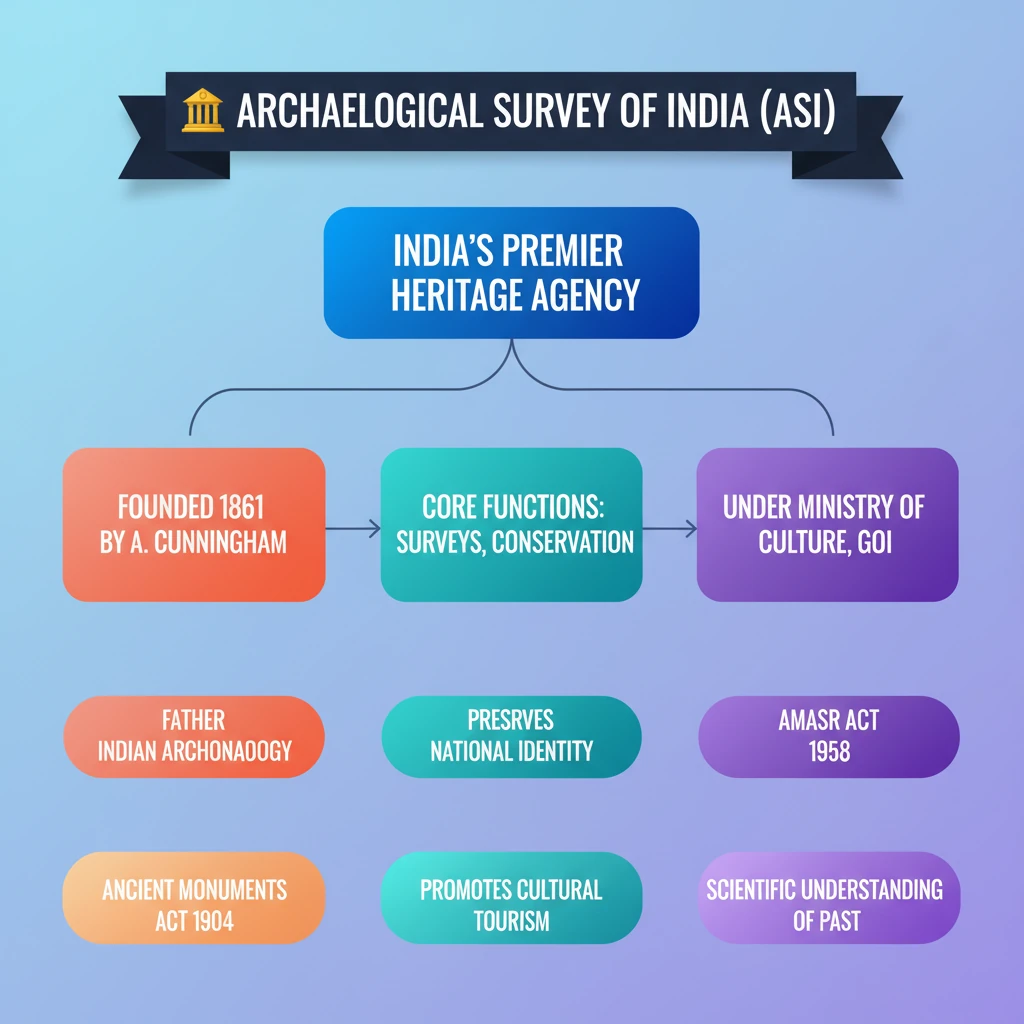
💡 Key Takeaways
- •ASI is India's primary agency for archaeological research and heritage protection, under the Ministry of Culture.
- •Its core functions include surveys, excavations, and conservation of nationally important monuments and sites.
- •Governed by the Ancient Monuments Preservation Act, 1904, and the more comprehensive AMASR Act, 1958.
- •Founded in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham, known as the 'Father of Indian Archaeology'.
- •Crucial for preserving national identity, promoting cultural tourism, and scientific understanding of India's past.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Official ASI Website (general knowledge)
•NCERT History Textbooks (general knowledge)