Read More: Sikhism - History | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Read More: Sikhism
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
history
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Sikhism</h4><p><strong>Sikhism</strong> is a monotheistic religion that originated in the <strong>Punjab region</strong> of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the youngest major religions in the world.</p><p>The term 'Sikh' means 'disciple' or 'learner'. Adherents of Sikhism are known as <strong>Sikhs</strong>, and they follow the teachings of <strong>Guru Nanak Dev Ji</strong> and his nine successive Sikh Gurus.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Origin:</strong> Punjab, India</p><p><strong>Founder:</strong> Guru Nanak Dev Ji</p><p><strong>Holy Scripture:</strong> Guru Granth Sahib</p></div><h4>Core Principles and Beliefs</h4><p>Sikhism is founded on the belief in <strong>one God</strong> (Ik Onkar), who is the creator and sustainer of the universe. This God is considered formless, eternal, and all-pervading.</p><p>A central tenet is the pursuit of spiritual growth through meditation on God's name (<strong>Naam Simran</strong>) and living an ethical life. Sikhs believe in the equality of all humanity, rejecting discrimination based on caste, creed, gender, or race.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The three pillars of Sikhism are: <strong>Naam Japna</strong> (meditating on God's name), <strong>Kirat Karni</strong> (earning an honest living), and <strong>Vand Chhakna</strong> (sharing earnings with the needy).</p></div><h4>The Ten Gurus and the Guru Granth Sahib</h4><p>The teachings of Sikhism were established by a succession of <strong>ten Gurus</strong>, starting with <strong>Guru Nanak Dev Ji</strong>. Each Guru contributed to the spiritual and social development of the community.</p><p>The tenth Guru, <strong>Guru Gobind Singh Ji</strong>, declared that after him, the <strong>Guru Granth Sahib</strong>, the holy scripture, would be the eternal and living Guru for Sikhs. It contains the teachings of the Gurus and various other saints.</p><h4>The Khalsa Panth</h4><p>In <strong>1699</strong>, <strong>Guru Gobind Singh Ji</strong> formally established the <strong>Khalsa Panth</strong>, a collective body of initiated Sikhs. Members of the Khalsa commit to a strict code of conduct and wear the <strong>Five Ks</strong> (Kakkars).</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>Five Ks</strong> are: <strong>Kesh</strong> (uncut hair), <strong>Kangha</strong> (wooden comb), <strong>Kara</strong> (iron bracelet), <strong>Kachera</strong> (cotton underwear), and <strong>Kirpan</strong> (short sword).</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding the contributions of each Guru and the significance of the <strong>Guru Granth Sahib</strong> and the <strong>Khalsa</strong> is crucial for UPSC. Questions often relate to their social reform aspects and resistance against oppression.</p></div>
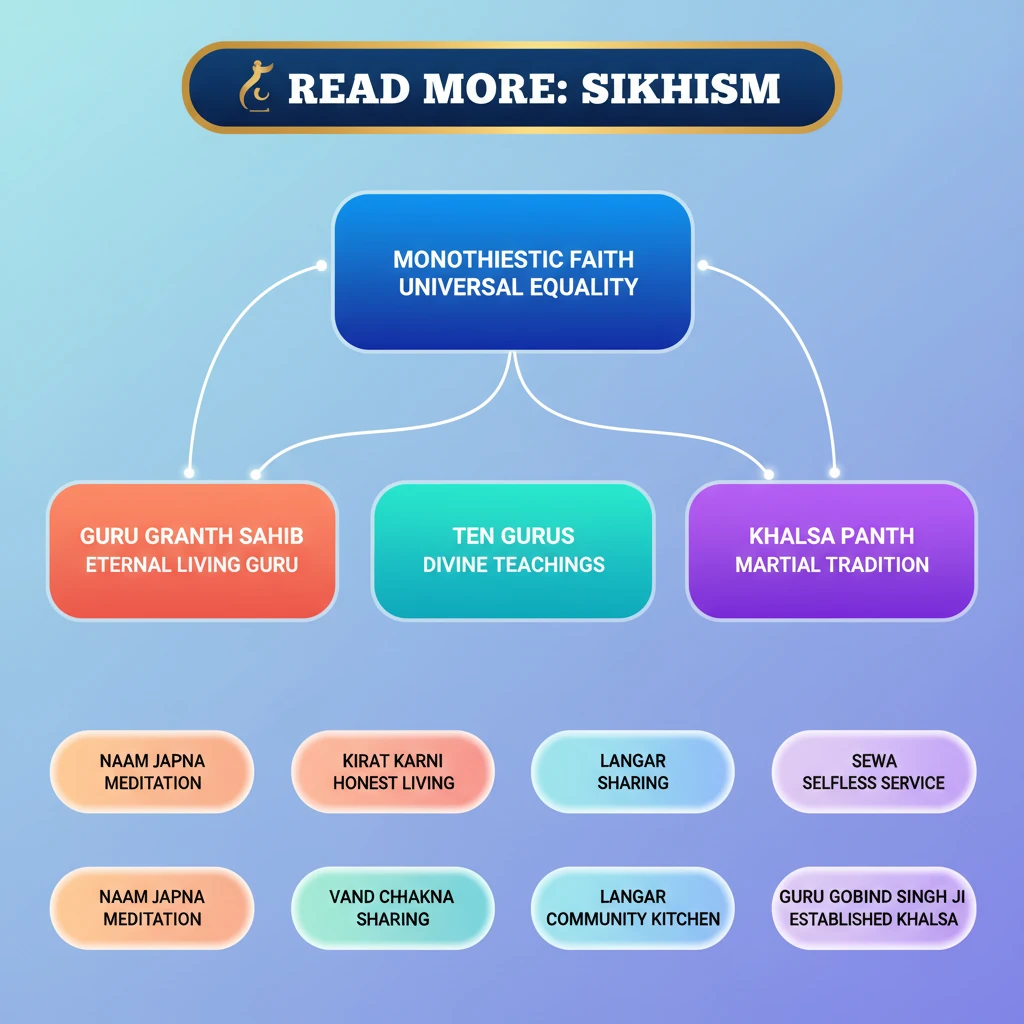
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Sikhism, founded by Guru Nanak Dev Ji, is a monotheistic religion emphasizing one God (Ik Onkar) and universal equality.
- •The teachings are enshrined in the Guru Granth Sahib, the eternal living Guru, and propagated by ten Gurus.
- •Core tenets include Naam Japna (meditation), Kirat Karni (honest living), and Vand Chhakna (sharing).
- •The Khalsa Panth, established by Guru Gobind Singh Ji, created a distinct identity and martial tradition.
- •Key institutions like Langar (community kitchen) promote social equality and selfless service (Sewa).
- •Sikh history includes periods of Mughal persecution, the rise of Misls, and the powerful Sikh Empire under Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•A History of the Sikhs, Vol. 1 & 2 by Khushwant Singh
•Sikhism: A Very Short Introduction by Eleanor Nesbitt
•Drishti IAS study materials on Indian History and Culture