Sant Kabir Das: Life, Philosophy, and the Bhakti Movement - History | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Sant Kabir Das: Life, Philosophy, and the Bhakti Movement
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
history
📖 Introduction
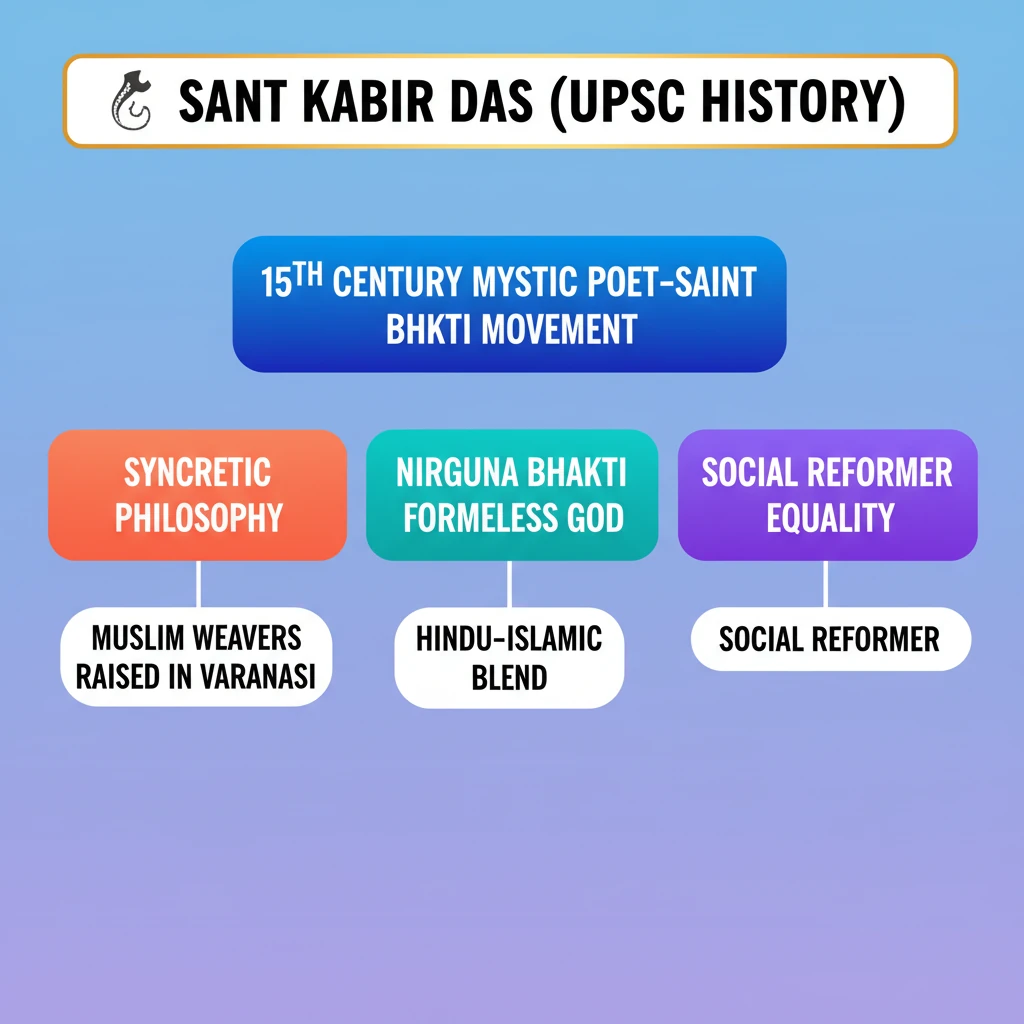
<h4>Introduction to Sant Kabir Das</h4><p>On <strong>June 22, 2024</strong>, the <strong>647th birth anniversary</strong> of <strong>Sant Kabir Das</strong> was observed. He was a pivotal figure in <strong>15th-century Indian spirituality</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Born:</strong> <strong>Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh</strong></p><p><strong>Century:</strong> <strong>15th Century</strong></p><p><strong>Upbringing:</strong> Raised by a <strong>Muslim weaver couple</strong>, though born to a <strong>Hindu family</strong>.</p></div><h4>Kabir and the Bhakti Movement</h4><p><strong>Sant Kabir Das</strong> was a prominent poet-saint of the <strong>Bhakti movement</strong>. This spiritual wave emphasized profound <strong>devotion</strong> and <strong>love for the divine</strong>, transcending ritualistic practices.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>Bhakti movement</strong> originated in <strong>South India</strong> in the <strong>7th century</strong>. It subsequently spread to <strong>North India</strong> during the <strong>14th and 15th centuries</strong>, influencing many regions.</p></div><p>Like other popular poet-saints such as <strong>Ramananda</strong>, <strong>Kabir Das</strong> composed and sang devotional songs in <strong>vernacular languages</strong>. This made spiritual teachings accessible to the common people.</p><h4>Spiritual Guidance and Unique Philosophy</h4><p><strong>Kabir's</strong> spiritual journey was shaped by diverse influences. He sought guidance from teachers including the renowned <strong>Ramananda</strong> and <strong>Sheikh Taqi</strong>.</p><p>This unique blend of influences contributed to his distinctive philosophy, which often bridged the divides between different religious traditions.</p><h4>Legacy and Literary Works</h4><p><strong>Kabir Das</strong> is revered across religious boundaries, held in high esteem by both <strong>Hindus</strong> and <strong>Muslims</strong>. His followers are known as <strong>“Kabir Panthis”</strong>, who continue to propagate his teachings.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> <strong>Kabir's syncretic philosophy</strong> and his role in promoting <strong>Hindu-Muslim unity</strong> are crucial for <strong>GS Paper I (History & Culture)</strong> and <strong>GS Paper IV (Ethics)</strong> discussions.</p></div><p>His profound spiritual insights are captured in his extensive literary works:</p><ul><li><strong>Kabir Bijak:</strong> A collection of his poems and verses, considered his most important work.</li><li><strong>Kabir Parachai:</strong> Biographical accounts and teachings.</li><li><strong>Sakhi Granth:</strong> Another significant compilation of his couplets.</li><li><strong>Adi Granth:</strong> Many of his verses are included in the holy scripture of <strong>Sikhism</strong>.</li><li><strong>Kabir Granthawali:</strong> A collection popular in the <strong>Rajasthan</strong> region.</li></ul>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Sant Kabir Das (15th century) was a mystic poet-saint of the Bhakti movement, born in Varanasi.
- •He was raised by a Muslim weaver couple, fostering a unique syncretic philosophy blending Hindu and Islamic traditions.
- •Kabir advocated Nirguna Bhakti, worshipping a formless God and rejecting idol worship and ritualism.
- •He strongly criticized caste distinctions and religious dogma, promoting universal love and equality.
- •His major literary works include Kabir Bijak, Sakhi Granth, and verses in the Adi Granth.
- •His followers are known as 'Kabir Panthis', continuing his legacy of communal harmony and simple living.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•General knowledge of Indian history and Bhakti movement