Ken-Betwa Link Project - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
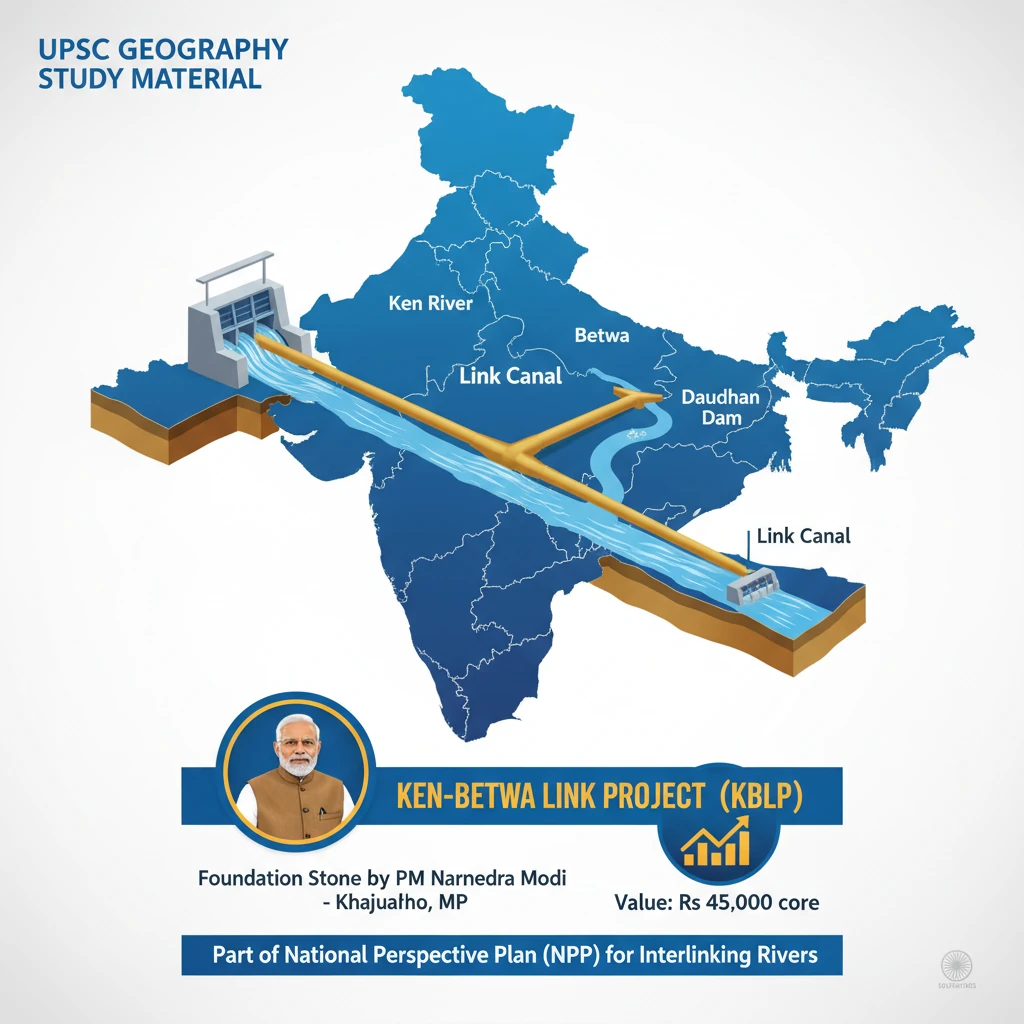
Ken-Betwa Link Project
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
<h4>Context and Recent Developments</h4><p>Recently, Prime Minister <strong>Narendra Modi</strong> laid the foundation stone for the ambitious <strong>Ken-Betwa Link Project (KBLP)</strong> in <strong>Khajuraho, Madhya Pradesh</strong>. This significant event marks a crucial step in India's efforts to address water scarcity.</p><p>The project, valued at approximately <strong>Rs 45,000 crore</strong>, is a key component of the <strong>National Perspective Plan (NPP)</strong> for interlinking rivers. Its primary goal is to alleviate water shortages, particularly in the drought-prone <strong>Bundelkhand</strong> region.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Alongside the <strong>KBLP</strong>, the Prime Minister also initiated the foundation for <strong>five major Dam Irrigation Projects</strong>. These projects are designed to provide irrigation to an estimated <strong>11 lakh hectares</strong> of agricultural land in the region.</p><p>Furthermore, <strong>Madhya Pradesh's first floating solar energy project</strong> was inaugurated at <strong>Omkareshwar</strong>, highlighting a commitment to renewable energy adoption.</p></div><h4>About the Ken-Betwa Link Project (KBLP)</h4><p>The <strong>KBLP</strong> stands as India's <strong>first river interlinking project</strong> under the <strong>National Perspective Plan (NPP)</strong>, which was formulated in <strong>1980</strong>. It is being implemented by the <strong>Ken-Betwa Link Project Authority</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The core objective of the project is to transfer surplus water from the <strong>Ken River</strong> in <strong>Madhya Pradesh</strong> to the water-deficit <strong>Betwa River</strong> in <strong>Uttar Pradesh</strong>. Both <strong>Ken</strong> and <strong>Betwa</strong> are vital tributaries of the <strong>Yamuna River</strong>.</p></div><h4>Phases of the Project</h4><p>The <strong>Ken-Betwa Link Project</strong> is structured into two distinct phases to ensure systematic development and implementation:</p><ul><li><strong>Phase I:</strong> Involves the construction of the <strong>Daudhan Dam complex</strong>, along with low-level and high-level tunnels. This phase also includes the development of the <strong>Ken-Betwa link canal</strong> and associated powerhouses.</li><li><strong>Phase II:</strong> Focuses on the development of the <strong>Lower Orr Dam</strong>, situated across the <strong>Orr River</strong> (a tributary of the <strong>Betwa</strong>). Additionally, this phase encompasses the <strong>Bina Complex Project</strong> and the construction of the <strong>Kotha Barrage</strong>.</li></ul><h4>Key Benefits of KBLP</h4><p>The project is envisioned to bring about multifaceted benefits to the region:</p><ul><li><strong>Irrigation:</strong> It will provide annual irrigation for approximately <strong>6.3 lakh hectares</strong> of agricultural land, significantly boosting agricultural productivity.</li><li><strong>Drinking Water:</strong> The project aims to ensure a stable supply of drinking water for about <strong>62 lakh people</strong>, addressing a critical need in the region.</li><li><strong>Power Generation:</strong> Provisions are included for generating <strong>100 Megawatts (MW) of hydropower</strong> and an additional <strong>27 MW of solar energy</strong>, contributing to the region's energy security.</li></ul><h4>Importance for the Bundelkhand Region</h4><p><strong>Bundelkhand</strong> is a geographically distinct region that encompasses <strong>13 districts</strong> spread across both <strong>Uttar Pradesh</strong> and <strong>Madhya Pradesh</strong>. This area has historically been plagued by severe droughts and chronic water shortages.</p><p>The persistent water crisis in <strong>Bundelkhand</strong> has often led to forced migration of its inhabitants in search of employment and better living conditions.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>The <strong>KBLP</strong> is critical for <strong>Bundelkhand</strong> as it promises enhanced access to drinking water, stable irrigation for agriculture, and overall regional development. These benefits are expected to significantly reduce migration pressures and foster economic growth.</p></div><h4>Environmental Concerns and Criticisms</h4><p>Despite its developmental potential, the <strong>Ken-Betwa Link Project</strong> has faced considerable opposition due to environmental concerns.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Critics have specifically highlighted the potential adverse impact on the <strong>Panna Tiger Reserve</strong>. It is estimated that over <strong>10% of the core area</strong> of this vital tiger habitat could be submerged due to the project, raising serious conservation issues.</p></div>
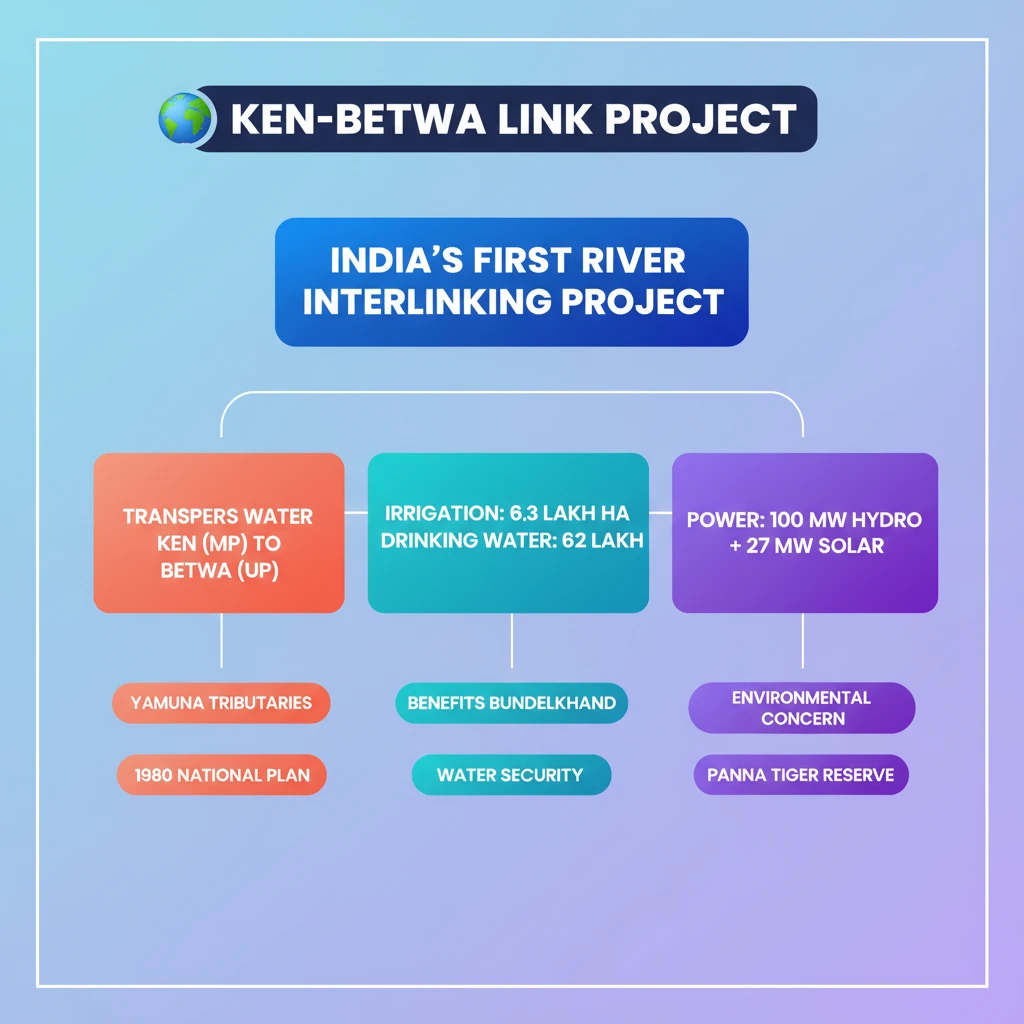
💡 Key Takeaways
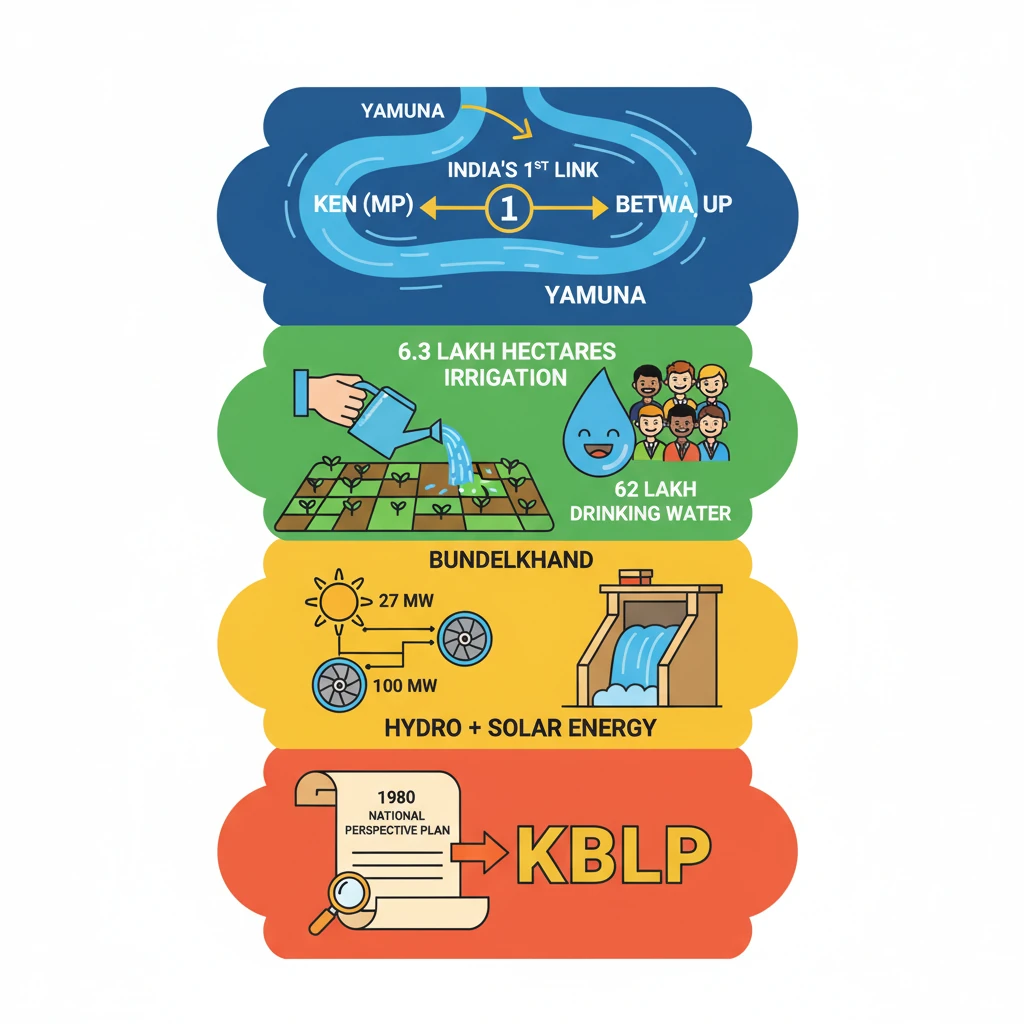
- •KBLP is India's first river interlinking project under the 1980 National Perspective Plan.
- •It transfers surplus water from Ken River (MP) to Betwa River (UP), both Yamuna tributaries.
- •Aims to provide irrigation for 6.3 lakh hectares and drinking water for 62 lakh people in Bundelkhand.
- •Includes 100 MW hydropower and 27 MW solar energy generation.
- •Faces environmental concerns, notably submergence of over 10% of Panna Tiger Reserve's core area.
- •Crucial for addressing water scarcity and reducing migration in the drought-prone Bundelkhand region.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content