Land Subsidence: Examples from Jakarta & Netherlands - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Land Subsidence: Examples from Jakarta & Netherlands
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
<h4>Understanding Land Subsidence</h4><p><strong>Land subsidence</strong> refers to the gradual sinking or settling of the Earth's surface. This phenomenon can occur over large areas and is often caused by a variety of natural and anthropogenic factors.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>It is a significant geological hazard that can lead to severe consequences, including increased flood risk, damage to infrastructure, and altered hydrological systems.</p></div><h4>Case Study 1: Jakarta, Indonesia</h4><p><strong>Jakarta</strong>, the capital city of <strong>Indonesia</strong>, is experiencing one of the most severe rates of <strong>land subsidence</strong> globally. This critical issue poses an existential threat to the sprawling metropolis.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Data:</strong> Jakarta's land is subsiding at an alarming rate of up to <strong>25 cm per year</strong> in some areas. This makes it one of the fastest-sinking cities in the world.</p></div><p>The primary driver behind Jakarta's rapid subsidence is the excessive <strong>groundwater extraction</strong>. As the city's population and industrial activities grow, the demand for fresh water escalates, leading to unsustainable pumping from underground aquifers.</p><h4>Case Study 2: The Netherlands</h4><p>The <strong>Netherlands</strong>, much of which lies below sea level, has historically grappled with issues of land management and water control. <strong>Land subsidence</strong> has been a persistent and significant problem in various parts of the country.</p><div class='info-box'><p>In the Netherlands, a major cause of subsidence is the extraction of <strong>natural gas</strong> from underground reservoirs. The removal of these subsurface fluids reduces pore pressure, leading to the compaction of overlying sediment layers.</p></div><p>This anthropogenic subsidence, combined with natural processes like peat oxidation, exacerbates the challenges of maintaining flood defenses and protecting infrastructure in a low-lying nation.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding specific examples like <strong>Jakarta</strong> and the <strong>Netherlands</strong> helps illustrate the diverse causes (<strong>groundwater extraction</strong> vs. <strong>natural gas extraction</strong>) and global prevalence of <strong>land subsidence</strong>, crucial for answers in <strong>Geography (GS Paper I)</strong> and <strong>Environment (GS Paper III)</strong>.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
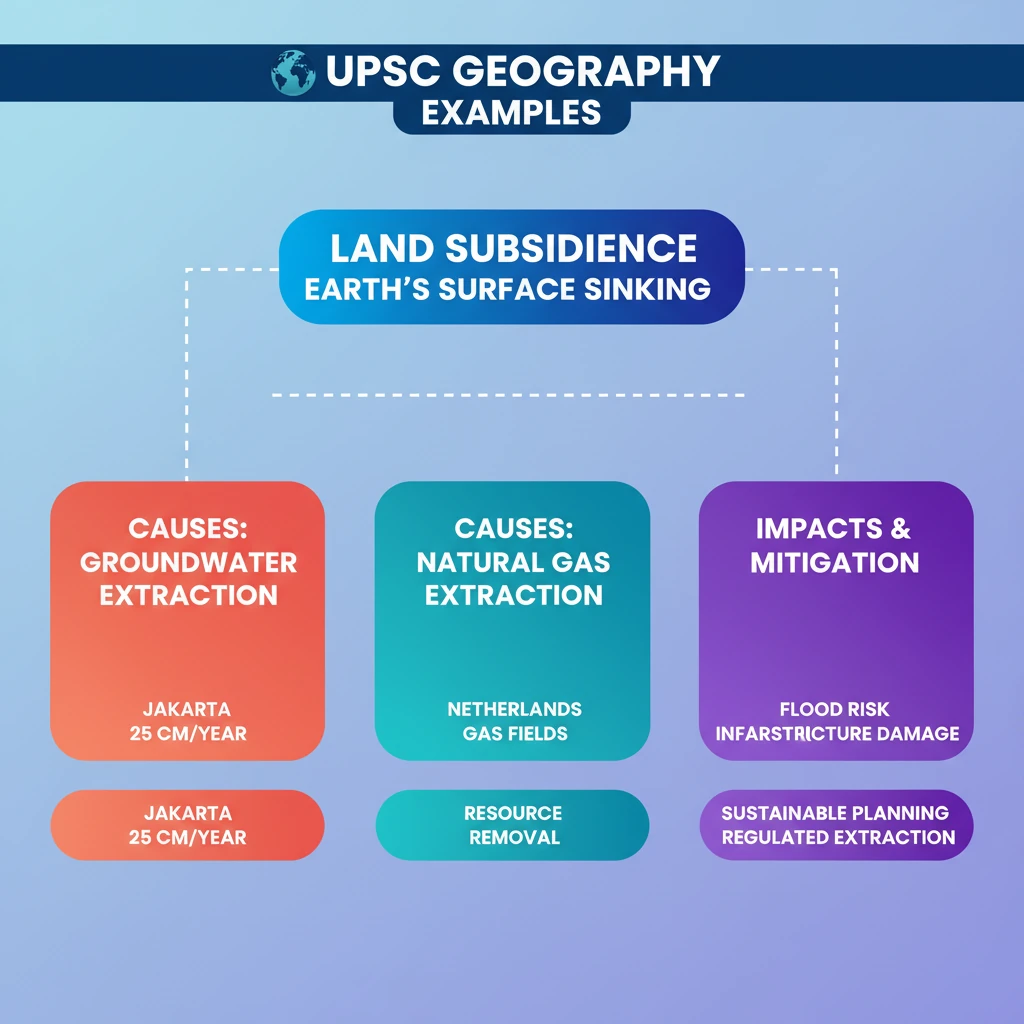
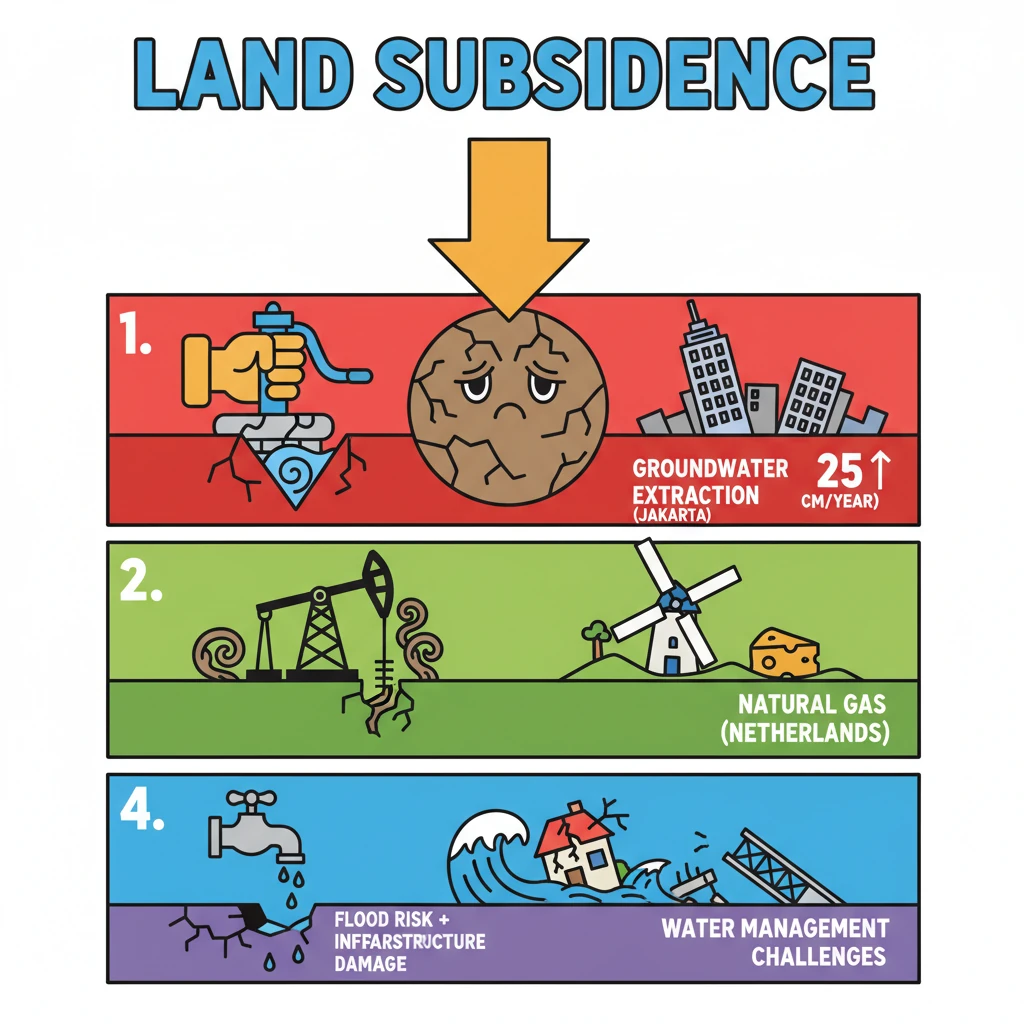
- •Land subsidence is the sinking of Earth's surface, caused by natural and anthropogenic factors.
- •Excessive groundwater extraction is a major cause, exemplified by Jakarta (25 cm/year subsidence).
- •Extraction of natural gas also causes subsidence, as seen in the Netherlands.
- •Subsidence leads to increased flood risk, infrastructure damage, and challenges in water management.
- •Sustainable urban planning and regulated resource extraction are crucial for mitigation.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) reports on urban subsidence
•Scientific articles on land subsidence in Jakarta and the Netherlands
•Geological Survey of the Netherlands (TNO) publications