How Earthquakes Impact the Course of a River Ganga? - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
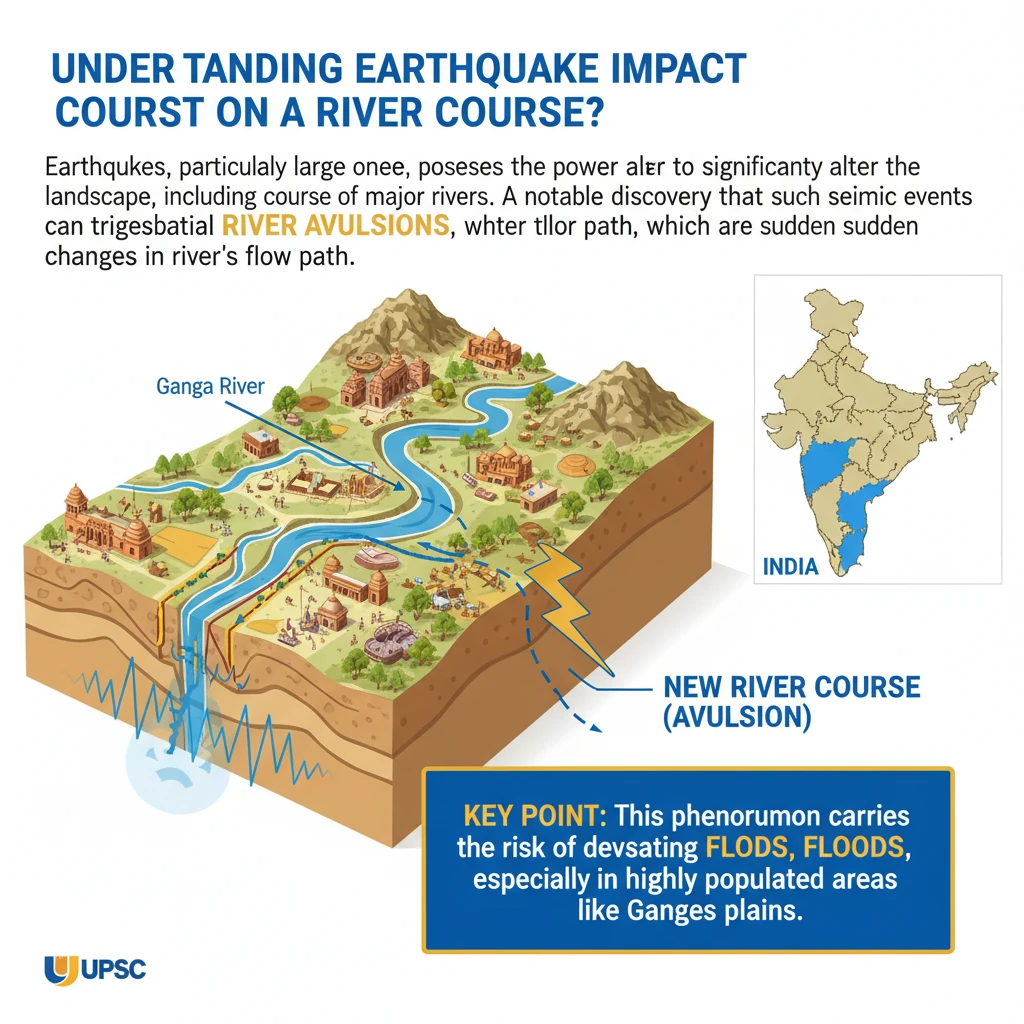
How Earthquakes Impact the Course of a River Ganga?
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
<h4>Understanding Earthquake Impact on River Courses</h4><p>Earthquakes, particularly large ones, possess the power to significantly alter the landscape, including the course of major rivers. A notable discovery highlights that such seismic events can trigger substantial <strong>river avulsions</strong>, which are sudden changes in a river's flow path.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>This phenomenon carries the risk of devastating <strong>floods</strong>, especially in highly populated areas like the <strong>Ganges-Meghna-Brahmaputra delta</strong>, where millions reside.</p></div><h4>Evidence of Earthquake-Induced River Avulsion</h4><p>Researchers have uncovered compelling geological evidence indicating that earthquakes can indeed cause river avulsions. This evidence primarily consists of specific sedimentary formations and dating techniques.</p><h5>Seismite Formation</h5><p><strong>Seismites</strong> are distinctive sedimentary beds that have been deformed by seismic movements. Their formation is a direct indicator of past earthquake activity.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Definition:</strong> <strong>Seismites</strong> are formed when seismic waves pressurize a layer of watery sand, causing it to burst through overlying mud layers, creating characteristic deformation patterns within the sediment.</p></div><h5>Sand Dikes</h5><p>Another crucial piece of evidence found by researchers near a palaeochannel (an ancient river course) were large <strong>sand dikes</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Definition:</strong> <strong>Sand Dikes</strong> are formed when earthquakes disturb the riverbed, leading to the liquefaction of sediments. This process causes sand and water to be injected upwards through overlying layers, forming dike-like structures.</p></div><h5>Dating Techniques: Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL)</h5><p>To establish a timeline for these geological events, researchers employed <strong>Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL) dating</strong>. This technique allows scientists to determine when sediment was last exposed to sunlight.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>OSL Dating Results:</strong> Using <strong>OSL dating</strong>, it was determined that both the river avulsion and the formation of the associated <strong>sand dikes</strong> occurred approximately <strong>2,500 years ago</strong>. This temporal correlation strongly suggests that an earthquake was the causative factor for the river's change in course.</p></div><h4>What are Tectonic Activities?</h4><p>The underlying mechanism for earthquakes and many geological changes is <strong>tectonic activity</strong>. This refers to the dynamic processes occurring within the Earth's lithosphere.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The Earth’s outermost layer, known as the <strong>lithosphere</strong>, is composed of the <strong>crust</strong> and the <strong>upper mantle</strong>. This rigid layer is not a single, continuous shell but is broken into several large, rocky fragments called <strong>tectonic plates</strong>.</p></div><p>These <strong>tectonic plates</strong> do not remain static. They rest upon a partially molten, ductile layer beneath the lithosphere, called the <strong>asthenosphere</strong>.</p><p>The movement of these plates is driven by <strong>convection currents</strong> within the <strong>asthenosphere</strong>. These currents cause the plates to move at varying rates, typically between <strong>2 to 15 centimeters per year</strong>, leading to geological phenomena like earthquakes, volcanic activity, and mountain building.</p>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Large earthquakes can cause significant river avulsions (course changes).
- •Evidence includes seismites and sand dikes, formed by seismic liquefaction.
- •OSL dating confirmed a Ganga River avulsion 2,500 years ago due to an earthquake.
- •Tectonic plates move due to convection currents in the asthenosphere, causing earthquakes.
- •River avulsions pose a major flood risk, especially in densely populated deltas like the Ganges-Meghna-Brahmaputra.
- •This highlights the critical need for integrating geological studies into disaster management and urban planning.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content