Economic Significance of Deccan Volcanism - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Economic Significance of Deccan Volcanism
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Deccan Volcanism's Economic Impact</h4><p>The <strong>Deccan Volcanism</strong>, primarily forming the <strong>Deccan Traps</strong>, has profoundly shaped the economic landscape of peninsular India. Its geological characteristics contribute significantly to both mineral wealth and agricultural productivity.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>Deccan Traps</strong> are a large igneous province located on the <strong>Deccan Plateau</strong> of west-central India. They are one of the largest volcanic features on Earth.</p></div><h4>Major Rock Formations</h4><p>The predominant rock type found in the <strong>Deccan Traps</strong> is <strong>Basalt</strong>. This igneous rock is crucial to the region's unique geological and soil characteristics.</p><p>Beyond the volcanic regions, other significant rock types like <strong>granite</strong> and <strong>gneiss</strong> are common in southern India, particularly in states such as <strong>Karnataka</strong> and <strong>Tamil Nadu</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Basalt</strong>: Dominant in <strong>Deccan Traps</strong>, formed from rapidly cooling lava.</li><li><strong>Granite & Gneiss</strong>: Prevalent in southern India, especially <strong>Karnataka</strong> and <strong>Tamil Nadu</strong>, representing older crystalline rocks.</li></ul></div><h4>Rich Mineral Resources</h4><p>The geological formations resulting from <strong>Deccan Volcanism</strong> and associated processes have led to significant mineral deposits. These are vital for India's industrial sector.</p><p><strong>Iron ore</strong> is found in abundance, particularly in the state of <strong>Karnataka</strong>, making it a key contributor to the national steel industry.</p><p>Furthermore, significant deposits of <strong>bauxite</strong>, the primary ore for aluminum, are located in the <strong>Eastern Ghats</strong> region.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Iron Ore</strong>: Abundant in <strong>Karnataka</strong>.</li><li><strong>Bauxite</strong>: Found in the <strong>Eastern Ghats</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Agricultural Significance: Black Soil</h4><p>One of the most significant economic contributions of <strong>Deccan Volcanism</strong> is the formation of <strong>Black soil</strong>, also known as <strong>Regur soil</strong>. This soil type is highly fertile and supports specific cash crops.</p><p>The presence of <strong>Black soil</strong> makes the region ideal for cultivating crops such as <strong>cotton</strong> and <strong>tobacco</strong>, which are economically important.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Black soil</strong> is renowned for its high moisture retention capacity, making it suitable for rain-fed agriculture, especially for crops like <strong>cotton</strong>.</p></div><h4>Formation and Composition of Black Soil</h4><p><strong>Black soil</strong> originates from the <strong>weathering</strong> of <strong>volcanic rocks</strong>, primarily <strong>basalt</strong>. This process releases a rich array of minerals into the soil.</p><p>The soil is particularly rich in essential minerals like <strong>iron</strong>, <strong>magnesium</strong>, <strong>calcium</strong>, and <strong>potassium</strong>, which contribute to its fertility and dark color.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Key minerals in <strong>Black soil</strong>: <strong>Iron</strong>, <strong>Magnesium</strong>, <strong>Calcium</strong>, <strong>Potassium</strong>. These elements are crucial for plant growth and agricultural productivity.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding the link between <strong>Deccan Volcanism</strong>, <strong>Basalt</strong>, and <strong>Black soil</strong> formation is crucial for questions on Indian physical geography and agriculture in <strong>UPSC Prelims</strong> and <strong>Mains (GS Paper I)</strong>.</p></div>
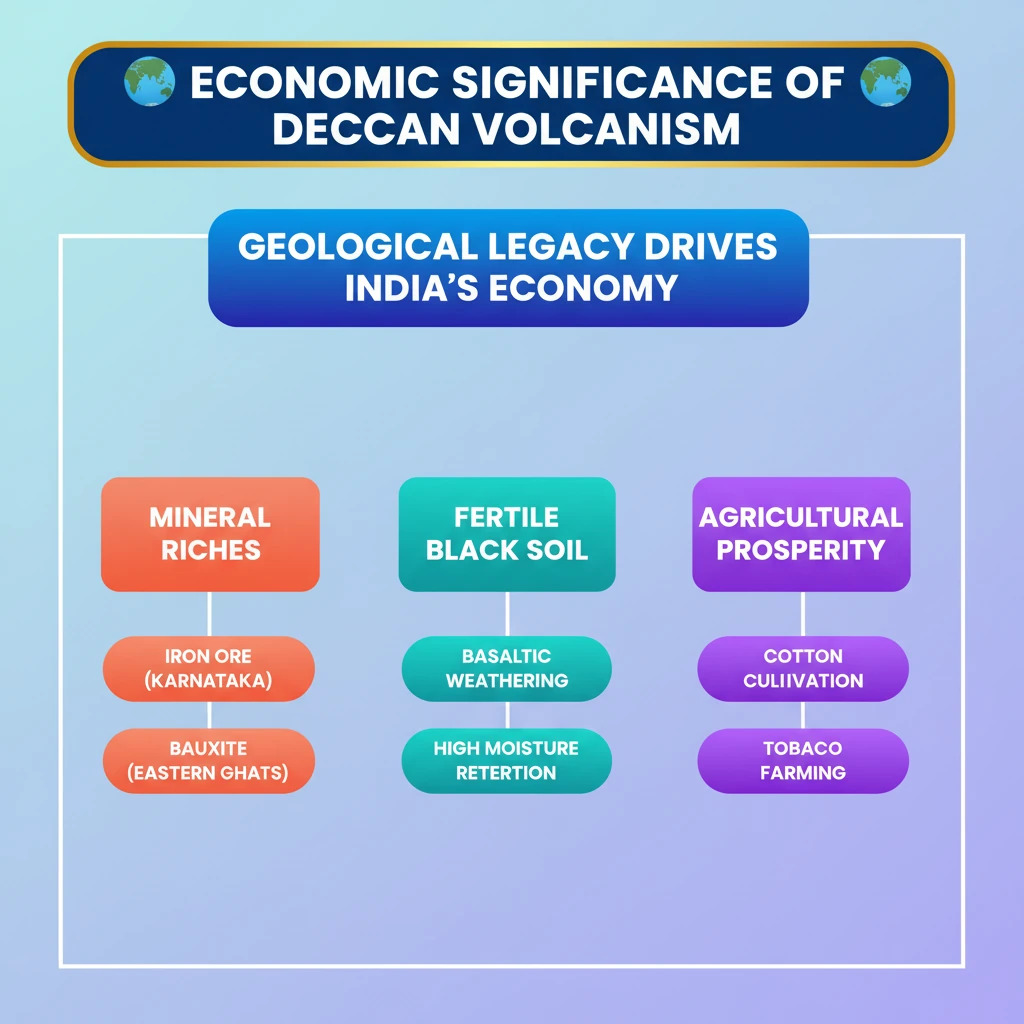
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Deccan Volcanism primarily formed Basaltic rocks, leading to the Deccan Traps.
- •The region is rich in mineral resources like Iron ore (Karnataka) and Bauxite (Eastern Ghats).
- •Weathering of Basalt forms fertile Black soil, ideal for cotton and tobacco cultivation.
- •Black soil is rich in iron, magnesium, calcium, and potassium, known for high moisture retention.
- •The geological legacy profoundly impacts India's agricultural and industrial economy.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NCERT Geography Textbooks (Class XI, 'Fundamentals of Physical Geography' & 'India: Physical Environment')
•Geological Survey of India (GSI) Publications
•Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) data on soils