What are the Potential Regional Impacts of La Nina - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are the Potential Regional Impacts of La Nina
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
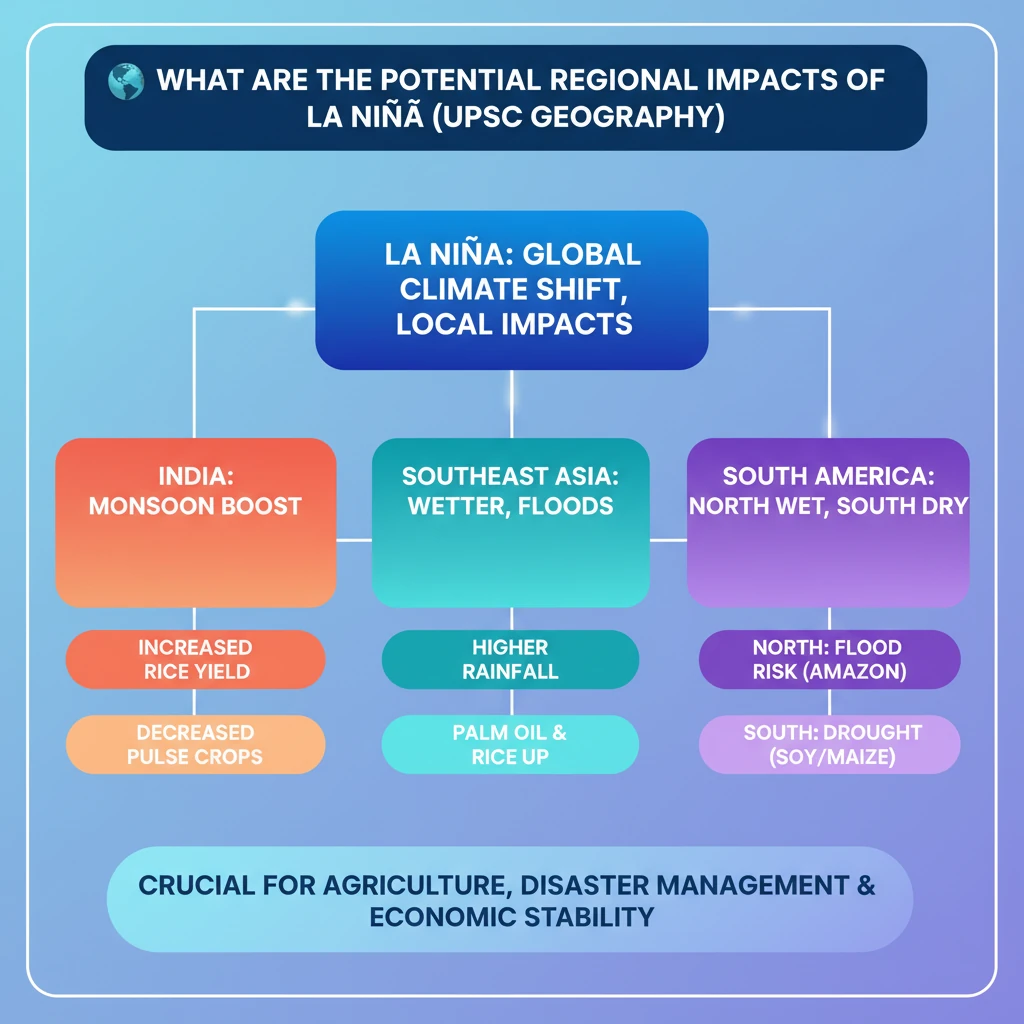
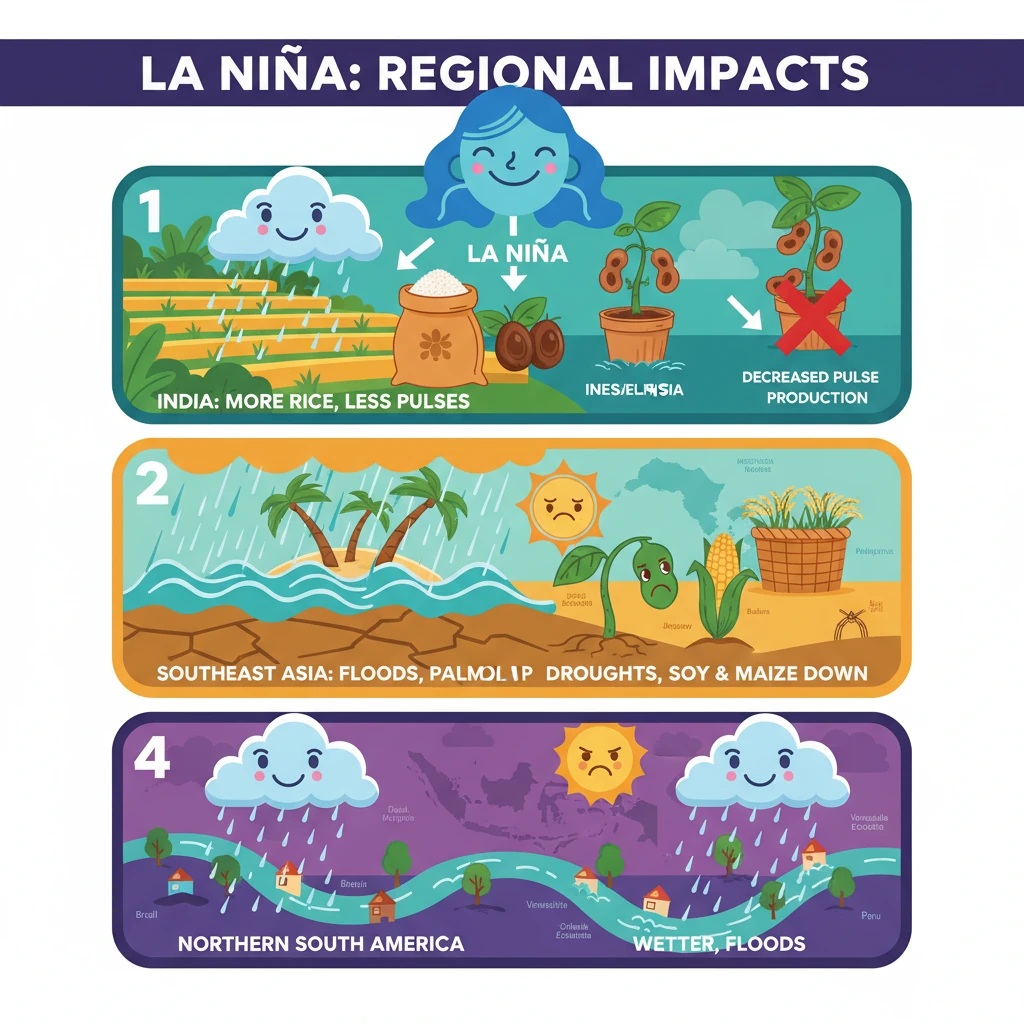
<h4>Understanding La Niña's Regional Impacts</h4><p><strong>La Niña</strong> is a complex climate pattern characterized by the cooling of sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean. This phenomenon significantly alters global weather patterns, leading to varied regional impacts across continents.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Its influence is particularly pronounced in tropical and subtropical regions, affecting rainfall, temperature, and agricultural productivity.</p></div><h4>Impacts in Asia: India</h4><p>In <strong>India</strong>, <strong>La Niña</strong> is typically associated with an enhanced <strong>Southwest Monsoon</strong>. This often translates to above-average rainfall during the crucial <strong>July to September</strong> period.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Expected outcomes in India include:</p><ul><li>A potential <strong>decrease</strong> in the production of <strong>Pulses</strong>, especially in the <strong>Indo-Gangetic Plains</strong>.</li><li>An anticipated <strong>increase</strong> in <strong>rice production</strong>, benefiting from abundant monsoon rains.</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding these specific agricultural impacts is crucial for questions on <strong>Indian agriculture</strong> and <strong>food security</strong> in <strong>UPSC GS-III Economy</strong> and <strong>GS-I Geography</strong>.</p></div><h4>Impacts in Asia: Southeast Asia</h4><p>The <strong>Southeast Asian</strong> region, encompassing countries like <strong>Indonesia</strong>, <strong>Malaysia</strong>, and the <strong>Philippines</strong>, experiences distinct impacts under <strong>La Niña</strong> conditions.</p><p>These nations typically receive above-average rainfall, which can lead to significant flooding events. Despite the challenges posed by floods, the increased moisture generally benefits key agricultural sectors.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Key agricultural outcomes in Southeast Asia include:</p><ul><li>A boost in <strong>rice production</strong>.</li><li>An increase in <strong>palm oil production</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Impacts in South America: Southern Regions</h4><p>In the southern parts of <strong>South America</strong>, <strong>La Niña</strong> often brings contrasting conditions compared to Asia. Regions such as <strong>Southern Brazil</strong>, <strong>Uruguay</strong>, <strong>Northern Argentina</strong>, and <strong>Southern Bolivia</strong> face drier weather.</p><p>This reduction in rainfall frequently results in prolonged droughts, severely impacting agricultural output in these vital farming areas.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Agricultural sectors significantly affected by droughts in these regions include:</p><ul><li><strong>Soybeans</strong> production.</li><li><strong>Maize (corn)</strong> production.</li></ul></div><h4>Impacts in South America: Northern Regions</h4><p>Conversely, the northern parts of <strong>South America</strong> experience different climatic shifts during <strong>La Niña</strong>. Countries like <strong>Northern Brazil</strong>, <strong>Colombia</strong>, <strong>Venezuela</strong>, and parts of <strong>Ecuador</strong> and <strong>Peru</strong> tend to receive increased rainfall.</p><p>These wetter conditions elevate the risk of potential flooding, posing challenges for infrastructure and communities in these areas.</p>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •La Niña typically brings above-average monsoon rainfall to India, potentially increasing rice but decreasing pulse production.
- •Southeast Asian nations (Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines) experience increased rainfall and flooding, boosting rice and palm oil output.
- •Southern South America (Brazil, Uruguay, Argentina, Bolivia) faces droughts, impacting soybean and maize crops.
- •Northern South America (Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru) sees wetter conditions and increased flood risk.
- •Understanding these regional impacts is vital for agricultural planning, disaster management, and economic stability globally.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) – Climate Prediction Center
•India Meteorological Department (IMD)
•World Meteorological Organization (WMO)
•NASA Earth Observatory