Antarctica’s Deep Winter Heatwaves - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Antarctica’s Deep Winter Heatwaves
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
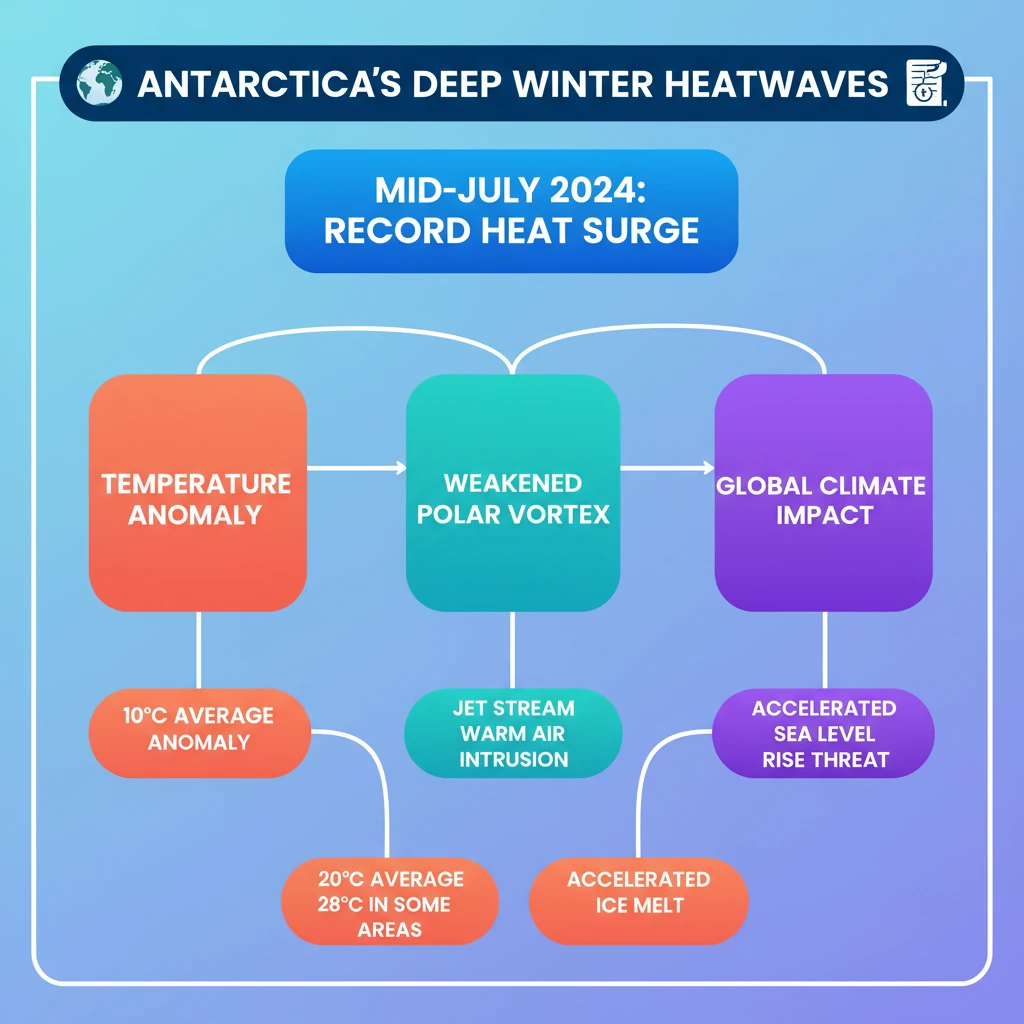
<h4>Recent Antarctic Deep-Winter Heatwave</h4><p><strong>Antarctica</strong> has recently experienced a significant <strong>deep-winter heatwave</strong>, marking the second such instance of record-breaking temperatures in just two years.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Ground temperatures have risen by an average of <strong>10 degrees Celsius</strong> above normal since mid-July 2024. Some areas have witnessed increases of up to <strong>28 degrees Celsius</strong>.</p></div><h4>Causes of Deep-Winter Heatwaves</h4><p>Several interconnected factors contribute to these extreme temperature anomalies in <strong>Antarctica</strong>.</p><h4>Weakening of the Polar Vortex</h4><p>The <strong>polar vortex</strong> is a crucial atmospheric phenomenon. It refers to the counterclockwise flow of air that typically keeps colder air confined near the <strong>Earth's poles</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>polar vortex</strong> naturally weakens in summer and strengthens in winter, but its recent disruption is a key concern.</p></div><p>Higher temperatures and powerful <strong>atmospheric waves</strong> (periodic disturbances in atmospheric variables) have disrupted the stability of the <strong>polar vortex</strong>.</p><p>This disruption allows <strong>cold air</strong> to escape from the pole and facilitates the descent of <strong>warm air</strong> from higher altitudes. The arrival of this warmer air leads to a sharp increase in regional temperatures.</p><h4>Reduction of Antarctic Sea Ice</h4><p><strong>Antarctic sea ice</strong> has reached historically low levels, significantly diminishing its capacity to reflect solar energy back into space.</p><p>Sea ice also acts as a vital barrier, insulating the cold polar air from warmer ocean waters. Its reduction exposes more ocean surface to the atmosphere.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The loss of <strong>sea ice</strong> reduces the <strong>albedo effect</strong>, contributing to increased absorption of solar radiation and accelerating global warming.</p></div><h4>High Rate of Global Warming</h4><p><strong>Antarctica</strong> is warming at an alarming rate, nearly double the global average. This accelerated warming is a primary driver of extreme weather events.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The continent is warming at an estimated rate of <strong>0.22 to 0.32 degrees Celsius per decade</strong>, compared to the Earth's overall warming rate of <strong>0.14-0.18 degrees Celsius per decade</strong> (as per <strong>IPCC estimates</strong>).</p></div><p>This rapid warming is predominantly driven by <strong>anthropogenic climate change</strong>, which intensifies the effects of natural climate variability.</p><h4>Impact of the Southern Ocean</h4><p>The <strong>Southern Ocean</strong> plays a critical role. With reduced <strong>sea ice</strong>, it absorbs more heat from the atmosphere and sunlight.</p><p>This increased heat absorption by the ocean creates a dangerous <strong>feedback loop</strong>, further raising air temperatures over <strong>Antarctica</strong> and escalating the risk of extreme weather events like heatwaves.</p>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Antarctica is experiencing unprecedented deep-winter heatwaves, with temperatures up to 28°C above normal.
- •Key causes include a weakened polar vortex, record low Antarctic sea ice, and rapid global warming.
- •Antarctica warms at nearly double the global average, driven by anthropogenic climate change.
- •The warming Southern Ocean creates a feedback loop, exacerbating air temperature increases.
- •These events have critical implications for global climate, sea level, and polar ecosystems.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content