2024 Arctic Report Card - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

2024 Arctic Report Card
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
<h4>Understanding the 2024 Arctic Report Card</h4><p>The <strong>2024 Arctic Report Card</strong>, released by the <strong>National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)</strong>, presents critical insights into the rapidly changing Arctic region. This annual report highlights significant environmental shifts impacting global climate patterns.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>Arctic Report Card</strong> has been issued annually since <strong>2006</strong>. It provides reliable and concise environmental information on the Arctic’s current state, comparing it against historical records to identify trends.</p></div><div class='info-box'><p><strong>NOAA</strong> is a federal agency of the <strong>United States</strong>. Its primary mission is to understand and predict environmental changes, manage coastal and marine resources, and support informed decision-making.</p></div><h4>Key Findings: Accelerated Arctic Warming</h4><p>The Arctic is experiencing warming at an unprecedented and accelerated rate. The year <strong>2024</strong> has been recorded as the <strong>second-warmest year</strong> since comprehensive records began in <strong>1900</strong>.</p><p>The summer of <strong>2024</strong> was particularly notable, ranking as the <strong>third warmest on record</strong> for the Arctic. Regions such as <strong>Alaska</strong> and <strong>Canada</strong> witnessed severe and prolonged <strong>extreme heat waves</strong> during this period.</p><h4>Arctic Tundra: From Carbon Sink to Carbon Source</h4><div class='key-point-box'><p>A critical finding is the transformation of the <strong>Arctic tundra</strong> from a traditional <strong>carbon sink</strong> to an active <strong>carbon source</strong>. This shift is primarily driven by extensive <strong>permafrost thaw</strong> across the region.</p></div><p>The decomposition of organic matter within the thawing <strong>permafrost</strong> releases significant quantities of greenhouse gases. These include both <strong>carbon dioxide (CO2)</strong> and <strong>methane (CH4)</strong>, further accelerating the process of <strong>global warming</strong>.</p><p>Furthermore, the frequency and intensity of <strong>wildfires</strong> in the Arctic are increasing. These fires release substantial amounts of stored carbon, contributing to atmospheric carbon load and extending the overall <strong>wildfire season</strong>.</p><h4>Declining Sea Ice and Melting Glaciers</h4><p>The <strong>extent and thickness of Arctic sea ice</strong> have significantly reduced over recent decades. This reduction leads to a shorter <strong>sea ice season</strong> each year.</p><p>A shorter sea ice season means more dark ocean surfaces are exposed to solar radiation for longer periods. These dark surfaces absorb more heat, creating a feedback loop that further contributes to <strong>Arctic warming</strong>.</p><p>Arctic glaciers and the massive <strong>Greenland Ice Sheet</strong> continue to melt at an alarming rate. The meltwater from these ice bodies directly contributes to rising global <strong>sea levels</strong>, posing a threat to coastal communities worldwide.</p><h4>Global Implications of Arctic Changes</h4><p>The profound environmental changes occurring in the Arctic have far-reaching implications that extend beyond the polar region. These changes contribute to several significant global challenges.</p><ul><li><strong>Coastal Flooding:</strong> Rising sea levels, driven by melting ice, exacerbate coastal flooding in low-lying areas globally.</li><li><strong>Extreme Weather Events:</strong> Alterations in Arctic climate patterns can influence atmospheric circulation, potentially leading to more frequent and intense extreme weather events in mid-latitudes.</li><li><strong>Wildfires:</strong> Increased Arctic wildfires contribute to global air pollution and carbon emissions, impacting climate and ecosystems worldwide.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding the <strong>Arctic Report Card's findings</strong> is crucial for UPSC. It connects directly to topics like <strong>Climate Change (GS-III)</strong>, <strong>Physical Geography (GS-I)</strong>, and <strong>Environmental Degradation (GS-III)</strong>. Be prepared to discuss feedback loops and global impacts.</p></div>
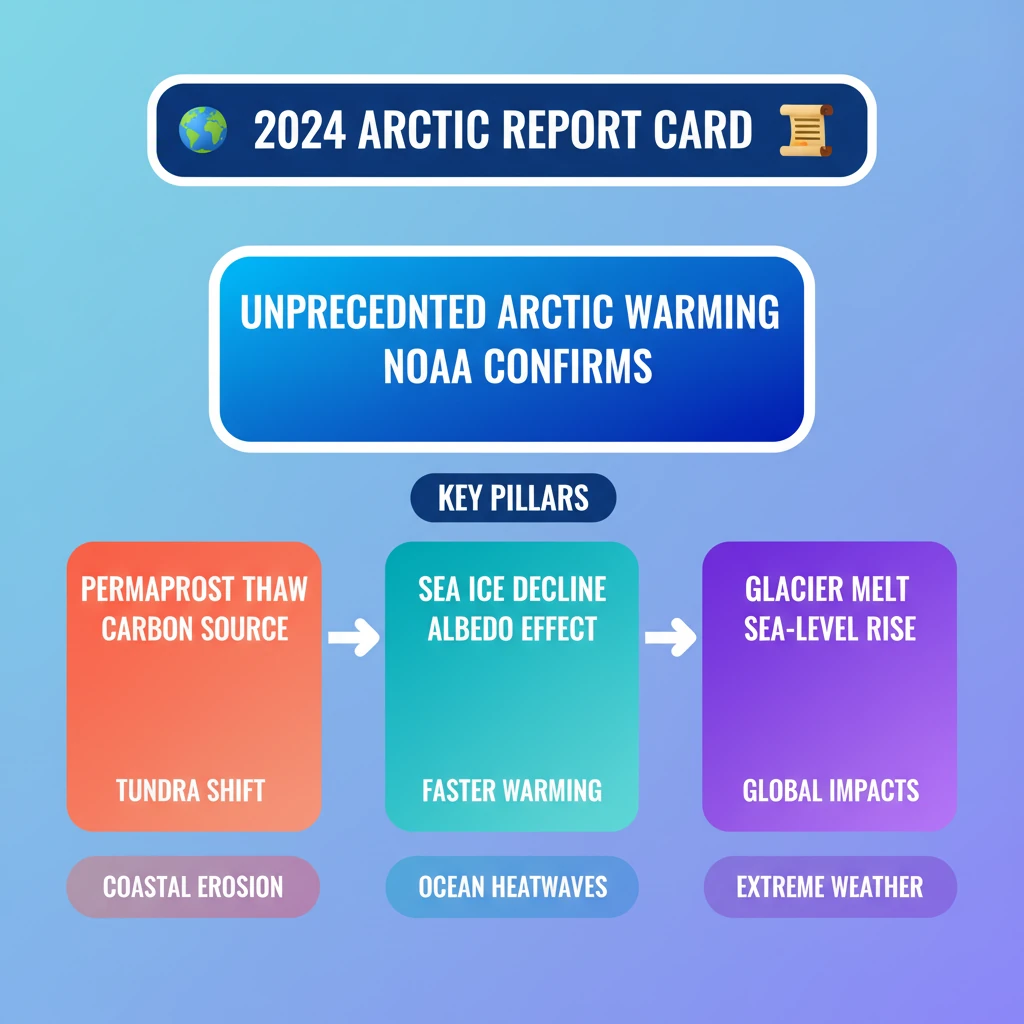
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The 2024 Arctic Report Card by NOAA confirms unprecedented Arctic warming.
- •Arctic tundra is transitioning from a carbon sink to a carbon source due to permafrost thaw.
- •Significant decline in sea ice extent and thickness accelerates warming via the albedo effect.
- •Melting glaciers and the Greenland Ice Sheet contribute to global sea-level rise.
- •Arctic changes have severe global implications, including extreme weather and coastal flooding.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Drishti IAS Summary on 2024 Arctic Report Card