Preventing Water Seepage - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Preventing Water Seepage
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
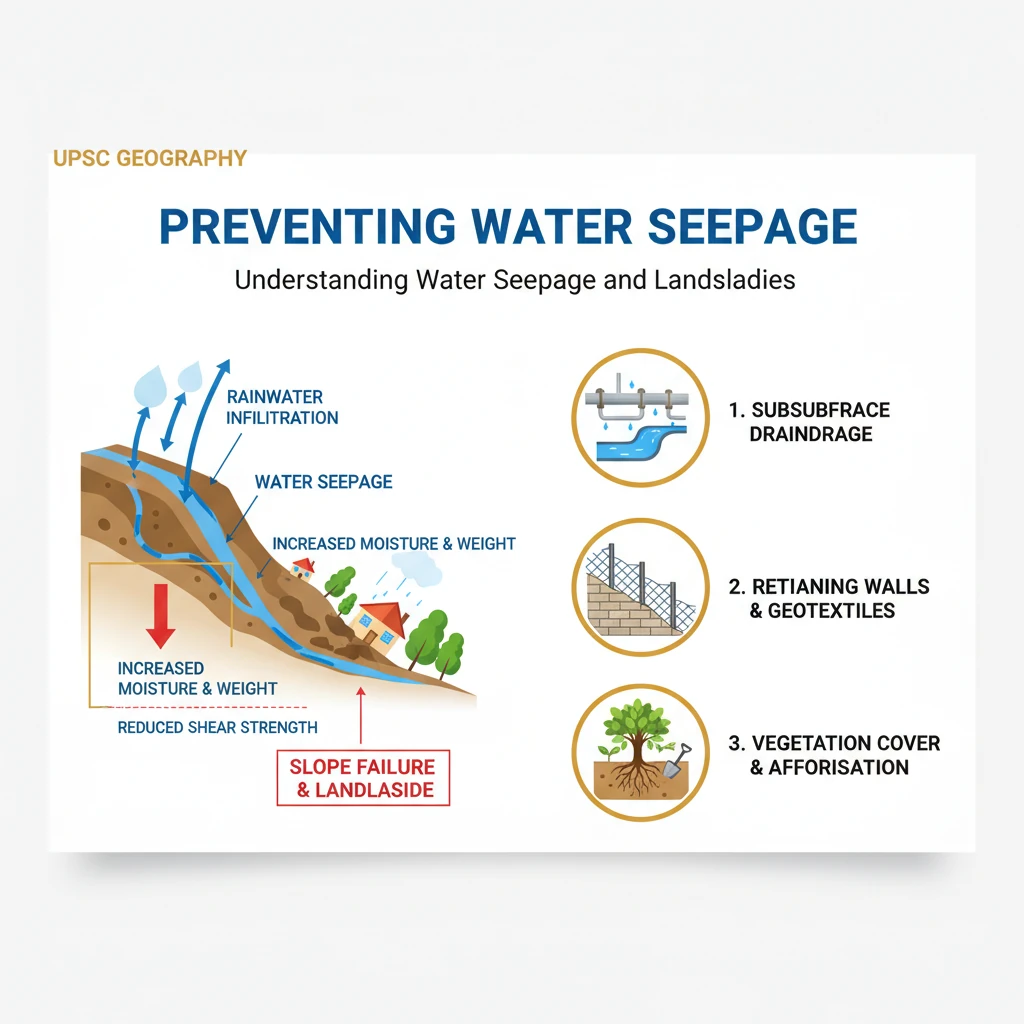
<h4>Understanding Water Seepage and Landslides</h4><p><strong>Water seepage</strong> refers to the slow movement of water through the pores and cracks within soil and rock masses. When <strong>rainwater</strong> infiltrates the ground, it can accumulate, increasing the moisture content and weight of the soil.</p><p>This increased moisture reduces the <strong>shear strength</strong> of the soil, making it less stable. The added weight and reduced cohesion can lead to slope failure, resulting in devastating <strong>landslides</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Definition:</strong> <strong>Landslides</strong> are the movement of a mass of rock, debris, or earth down a slope. They are a type of 'mass wasting' which denotes any down-slope movement of soil and rock under the direct influence of gravity.</p></div><h4>The Critical Role of Drainage Systems</h4><p>To effectively prevent future <strong>landslides</strong>, it is crucial to manage and control the flow of surface and subsurface water. The primary strategy involves stopping the <strong>seepage of open rainwater</strong> into vulnerable slopes.</p><p>This is achieved through the construction of a robust and well-designed <strong>pucca drainage system</strong>. A 'pucca' system implies a permanent, durable, and engineered solution, typically involving concrete or masonry channels.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Concept:</strong> A <strong>pucca drainage system</strong> diverts rainwater away from slopes, preventing it from infiltrating the soil and increasing <strong>pore water pressure</strong>, which is a major destabilizing factor for slopes.</p></div><h4>Mechanism of Seepage Prevention</h4><p>A <strong>pucca drainage system</strong> works by collecting surface runoff efficiently and channeling it safely away from the slope. This prevents water from pooling and gradually seeping into the ground.</p><p>Such systems often include features like lined surface drains, catchwater drains, and subsurface drains. These components ensure that both direct rainfall and runoff from higher areas are managed.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the mechanics of <strong>water seepage</strong> and the role of <strong>drainage systems</strong> is vital for questions on <strong>disaster management</strong> (GS-III) and <strong>physical geography</strong> (GS-I), particularly in the context of mountainous regions like the Himalayas.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
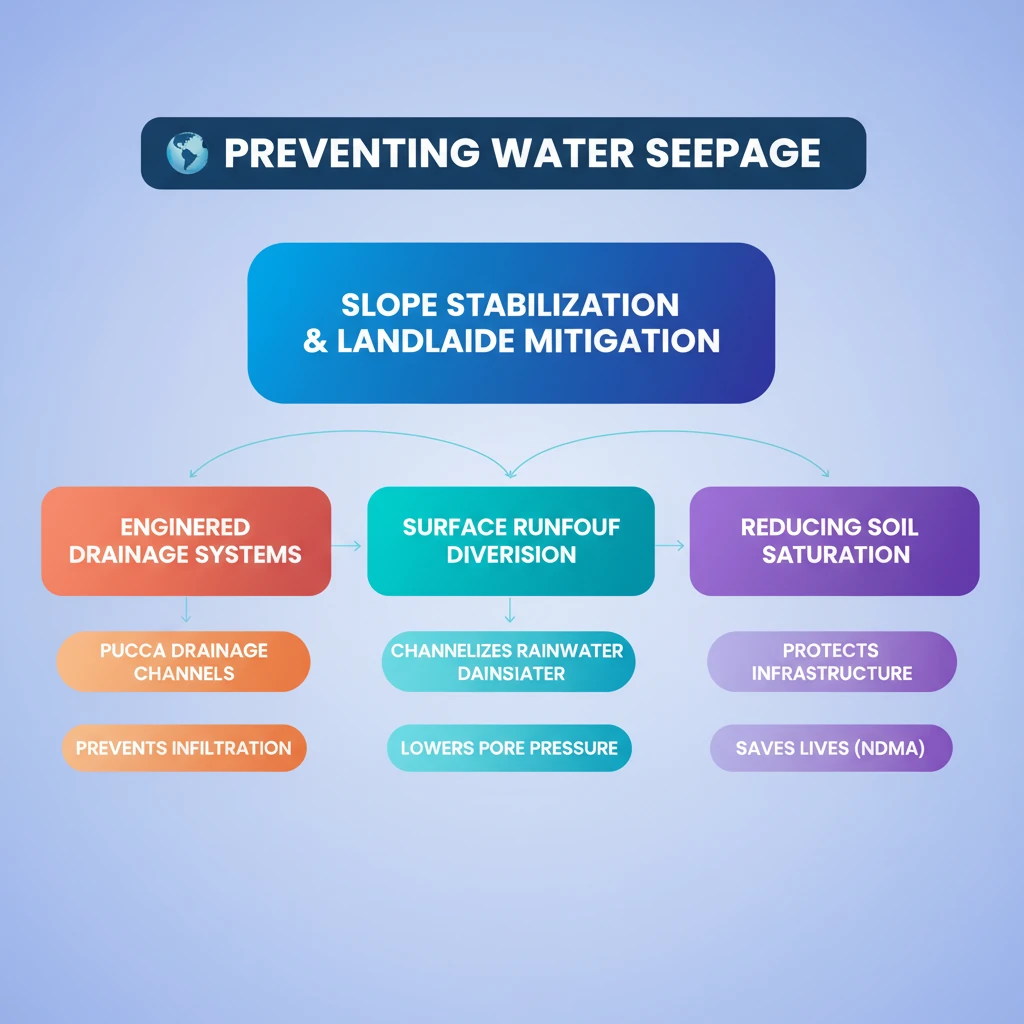
- •Water seepage, primarily from rainwater, significantly destabilizes slopes and causes landslides.
- •Construction of a 'pucca' (permanent, engineered) drainage system is essential to prevent water infiltration.
- •Effective drainage diverts surface runoff, reducing soil saturation and pore water pressure.
- •This mitigation strategy is crucial for protecting infrastructure and lives in landslide-prone areas.
- •Modern approaches integrate engineering solutions with bio-engineering and policy frameworks like NDMA's NLRMS.
- •Understanding seepage prevention is vital for UPSC topics like disaster management and physical geography.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Geological Survey of India (GSI) Publications on Landslides
•Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) Codes for Hill Area Development
•Textbooks on Geotechnical Engineering and Soil Mechanics
•Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) Manuals for Hill Road Construction