River Training: Structural Measures for Flow Guidance - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
River Training: Structural Measures for Flow Guidance
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
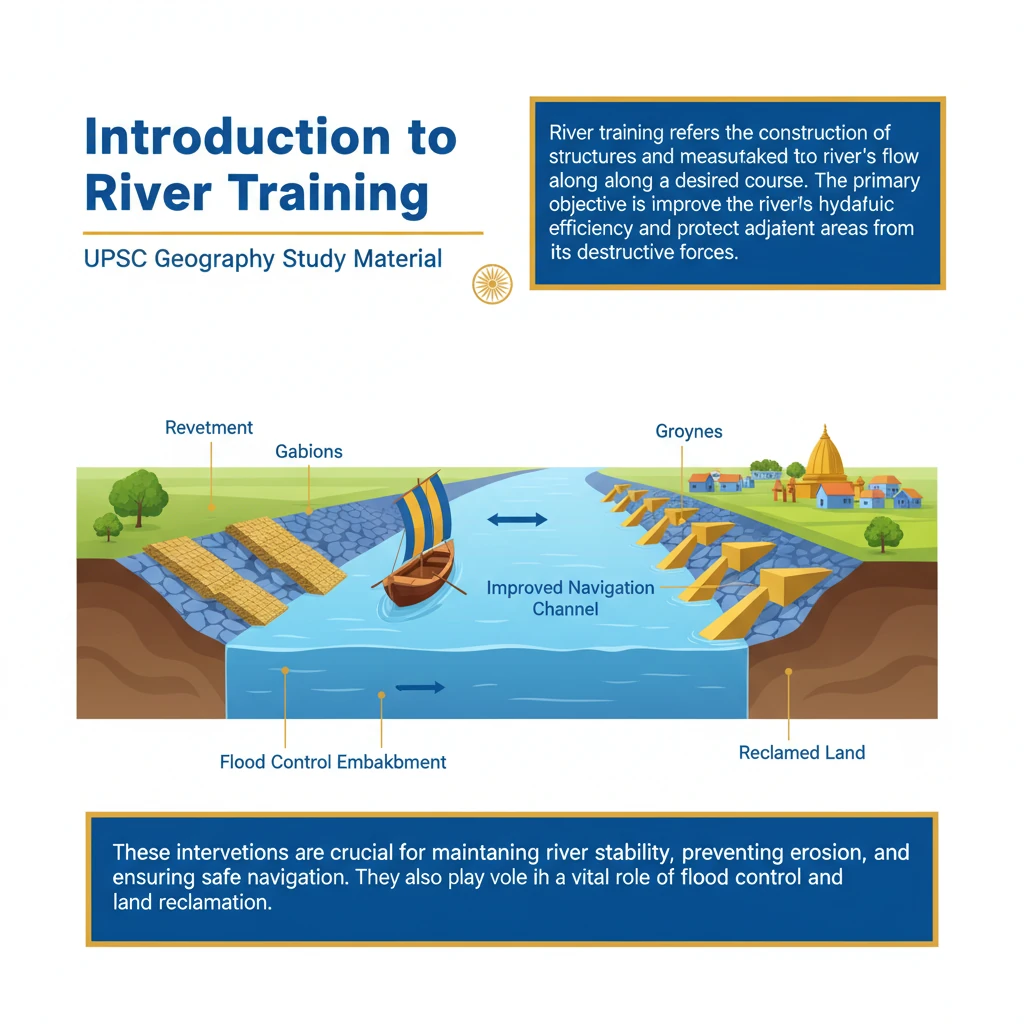
<h4>Introduction to River Training</h4><p><strong>River training</strong> refers to the construction of structures and measures undertaken to guide the river's flow along a desired course. The primary objective is to improve the river's hydraulic efficiency and protect adjacent areas from its destructive forces.</p><p>These interventions are crucial for maintaining river stability, preventing erosion, and ensuring safe navigation. They also play a vital role in flood control and land reclamation efforts.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Concept:</strong> <strong>River training</strong> aims to stabilize river channels, control sediment movement, and protect river banks and infrastructure from damage caused by natural river dynamics.</p></div><h4>Core Components of River Training</h4><p>The source material highlights two fundamental aspects of river training:</p><ul><li><strong>Construction of structures to guide the river’s flow:</strong> This involves engineering works designed to direct the water current, control its velocity, and prevent it from eroding banks or changing its course.</li><li><strong>Providing appropriate support for hanging boulders on the foothills:</strong> This specific measure addresses localized instability, preventing landslides and ensuring the structural integrity of the river system, especially in hilly or mountainous terrains.</li></ul><h4>Objectives of River Training</h4><p>River training projects are typically undertaken with multiple objectives:</p><ul><li><strong>Flood Control:</strong> Guiding the river flow to prevent inundation of adjacent areas.</li><li><strong>Erosion Control:</strong> Protecting river banks and agricultural land from scour and erosion.</li><li><strong>Navigation Improvement:</strong> Maintaining adequate depth and width for safe passage of vessels.</li><li><strong>Sediment Management:</strong> Controlling deposition and scour to prevent silting of channels or reservoirs.</li><li><strong>Land Reclamation:</strong> Stabilizing banks to reclaim land for agriculture or infrastructure.</li></ul><h4>Types of River Training Works</h4><p>River training can be broadly categorized based on its primary purpose:</p><ul><li><strong>High Water Training:</strong> Focuses on controlling floods by confining high flows within a defined channel.</li><li><strong>Low Water Training:</strong> Aims to maintain navigable depths during lean periods, often through dredging or flow concentration.</li><li><strong>Mean Water Training:</strong> Seeks to manage the river's behavior under average flow conditions, balancing flood and navigation needs.</li></ul><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Common River Training Structures:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Guide Banks:</strong> Extend upstream and downstream from a bridge or barrage to guide the river flow smoothly.</li><li><strong>Spurs (Groynes):</strong> Project into the river to deflect currents away from banks or to create deposition.</li><li><strong>Revetments:</strong> Protective coverings on river banks (e.g., stone pitching, concrete blocks) to prevent erosion.</li><li><strong>Embankments/Levees:</strong> Raised structures along river banks to contain floodwaters.</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> River training is a crucial topic for <strong>GS Paper I (Geography)</strong> and <strong>GS Paper III (Disaster Management, Infrastructure)</strong>. Questions often relate to flood control measures, river morphology, and sustainable development practices. Understanding the types of structures and their purposes is key.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •River training involves constructing structures to guide river flow for stability and protection.
- •Key objectives include flood control, erosion prevention, and navigation improvement.
- •Structures like guide banks, spurs, revetments, and embankments are commonly used.
- •Historical context shows ancient roots, with modern engineering bringing systematic approaches.
- •Currently vital for flood management, waterways, and infrastructure, requiring sustainable practices.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•National Water Policy (2012), Government of India
•Drishti IAS Study Material (provided as source)
•Standard textbooks on Fluvial Geomorphology and Hydraulic Engineering
•Reports from Central Water Commission (CWC)