What are UNESCO Global Geoparks (Geo Heritage Sites)? - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are UNESCO Global Geoparks (Geo Heritage Sites)?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
<h4>Understanding UNESCO Global Geoparks</h4><p><strong>UNESCO Global Geoparks</strong> are distinct, unified geographical areas. They are recognized for their <strong>internationally significant geological sites</strong> and landscapes.</p><p>These areas are managed with a <strong>holistic approach</strong>. This approach integrates <strong>protection</strong>, <strong>education</strong>, and <strong>sustainable development</strong> for the benefit of local communities.</p><h4>Defining Geo Heritage Sites</h4><p><strong>Geo Heritage Sites</strong> are specific locations within these geoparks. Their significance stems from unique geological features.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Geo Heritage Sites</strong> can include:</p><ul><li>Distinctive <strong>rock formations</strong></li><li>Rich <strong>fossil deposits</strong></li><li>Valuable <strong>mineral deposits</strong></li><li>Remarkable <strong>landforms</strong> created by natural processes</li></ul></div><h4>Designation and Revalidation Process</h4><p>The designation as a <strong>UNESCO Global Geopark</strong> is not permanent. It is initially granted for a period of <strong>four years</strong>.</p><p>After this initial period, each geopark undergoes a rigorous <strong>revalidation process</strong> to ensure it continues to meet the stringent criteria set by UNESCO.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Revalidation Outcomes:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Green Card:</strong> Awarded if the geopark fully meets all criteria.</li><li><strong>Yellow Card:</strong> Issued if the geopark shows deficiencies, allowing <strong>two years</strong> for improvements.</li><li><strong>Red Card:</strong> Issued if the geopark fails to meet criteria after a yellow card period, leading to the <strong>loss of its status</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Global Presence and India's Status</h4><p>Globally, the network of <strong>UNESCO Global Geoparks</strong> is expanding. As of the latest figures, there are <strong>213 Geoparks</strong> spread across <strong>48 countries</strong> worldwide.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Despite India's rich geological diversity, it currently <strong>does not have any UNESCO Global Geoparks</strong>. This is a crucial point for UPSC aspirants, especially for questions related to heritage and conservation.</p></div><h4>Diversity of Geo Heritage Sites</h4><p>The geological features protected within these sites are incredibly diverse. They represent a wide spectrum of Earth's natural history and processes.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Examples of <strong>Geo Heritage Site</strong> types include:</p><ul><li>Active or ancient <strong>volcanic formations</strong></li><li>Areas rich in <strong>fossils</strong>, offering insights into past life</li><li>Intricate <strong>cave systems</strong> and karst landscapes</li><li>Majestic <strong>mountain ranges</strong> and their associated geological structures</li><li>Features carved by <strong>glacial activity</strong>, such as U-shaped valleys</li><li>Regions abundant in specific <strong>mineral deposits</strong></li></ul></div>
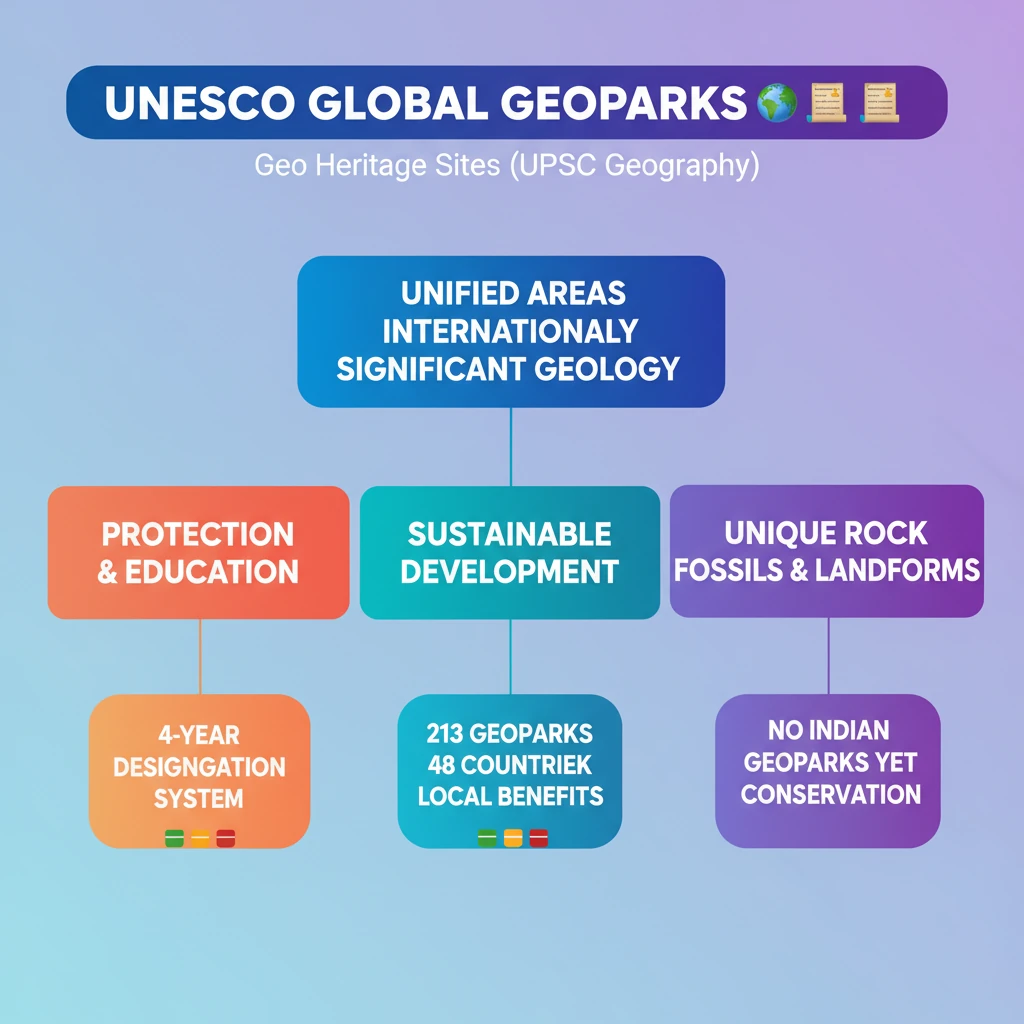
💡 Key Takeaways
- •UNESCO Global Geoparks are unified areas with internationally significant geological sites.
- •They are managed for protection, education, and sustainable development.
- •Geo Heritage Sites are locations with unique rock formations, fossils, minerals, or landforms.
- •Designation is for four years, followed by revalidation (Green, Yellow, Red Card system).
- •There are 213 Geoparks in 48 countries; India currently has none.
- •Sites exhibit diverse geology: volcanic, fossil-rich, caves, mountains, glacial, mineral regions.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Official UNESCO Global Geoparks website (for program launch year and global statistics)