Imposition of Restrictions on Heavy Construction - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Imposition of Restrictions on Heavy Construction
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Construction Restrictions</h4><p>The principle of imposing <strong>restrictions on heavy construction</strong> is crucial for ensuring public safety and environmental protection. It mandates a thorough assessment of geological and topographical factors before any significant building activity commences.</p><p>This approach prevents potential disasters and ensures the long-term stability of structures and the surrounding environment.</p><h4>Assessing Site Suitability</h4><p>Before allowing any construction, it is imperative to examine the <strong>load-bearing capacity of the soil</strong>. This refers to the maximum pressure the soil can withstand without undergoing excessive settlement or shear failure.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Load-bearing capacity</strong> is a critical geotechnical parameter, often determined through soil tests like Standard Penetration Test (SPT) or Cone Penetration Test (CPT).</p></div><p>Equally important is evaluating the <strong>stability of the site</strong>. This includes assessing factors like seismic activity, susceptibility to landslides, erosion, and groundwater levels.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>A <strong>stable site</strong> minimizes risks of structural failure, especially in regions prone to natural hazards like earthquakes or heavy rainfall.</p></div><h4>Restrictions on Slope Excavation</h4><p>Beyond foundation assessment, strict <strong>restrictions should be imposed on the excavation of slopes</strong>. Uncontrolled cutting of hillsides can destabilize the natural gradient.</p><p>This destabilization often leads to increased risks of <strong>landslides</strong>, <strong>rockfalls</strong>, and <strong>soil erosion</strong>, particularly during heavy rainfall or seismic events.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>UPSC often asks about disaster management strategies. Understanding these restrictions is vital for answering questions on <strong>landslide mitigation</strong> and <strong>sustainable urban planning</strong> in hilly areas (<strong>GS Paper I & III</strong>).</p></div>
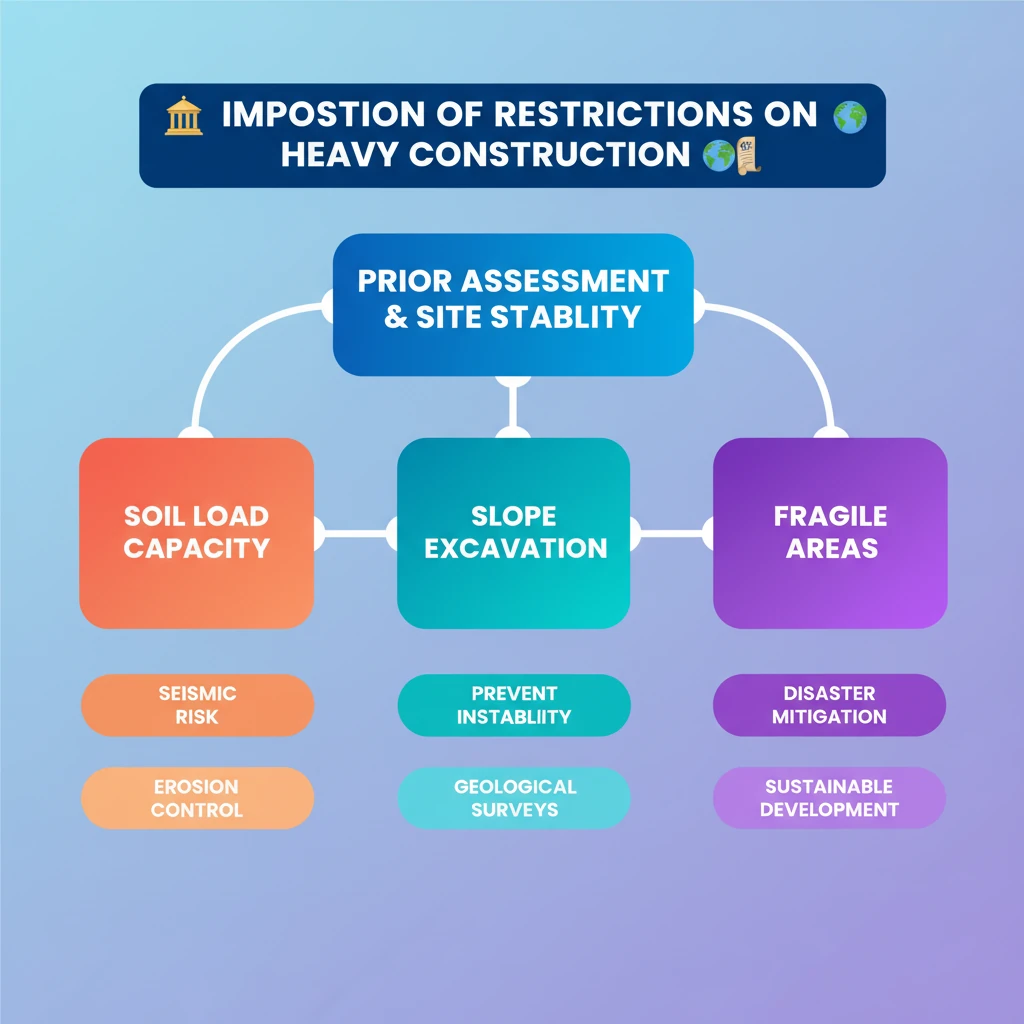
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Heavy construction requires prior assessment of soil's load-bearing capacity.
- •Site stability (seismic, landslide risk, erosion) is crucial before construction.
- •Strict restrictions on slope excavation are vital to prevent geological instability.
- •Unregulated construction in fragile areas can lead to major disasters like land subsidence and landslides.
- •Implementing these restrictions is key for sustainable development and effective disaster risk reduction.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) Guidelines
•Geological Survey of India (GSI) Reports on Landslides
•Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) Codes for Construction
•Reports on Joshimath Land Subsidence (e.g., Mishra Committee Report)