Eruptions in Kilauea Volcano - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Eruptions in Kilauea Volcano
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
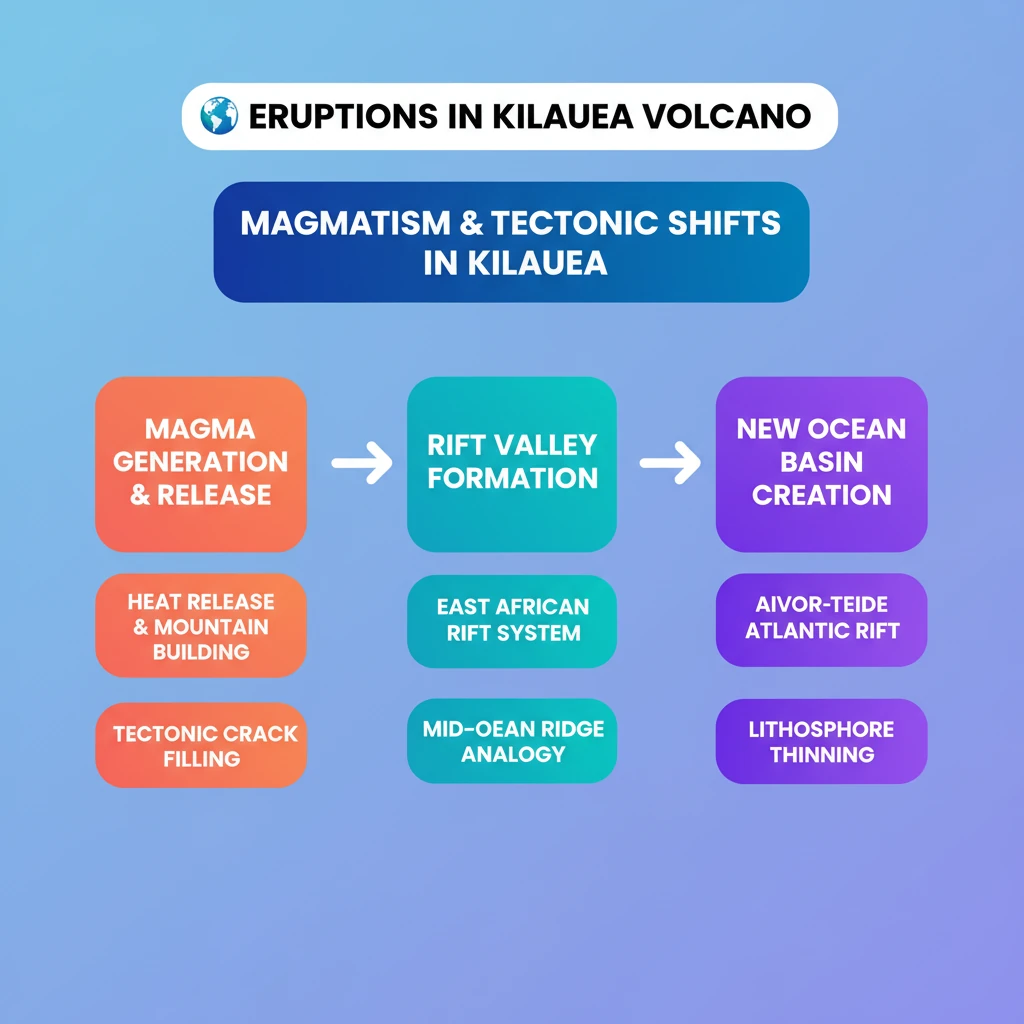
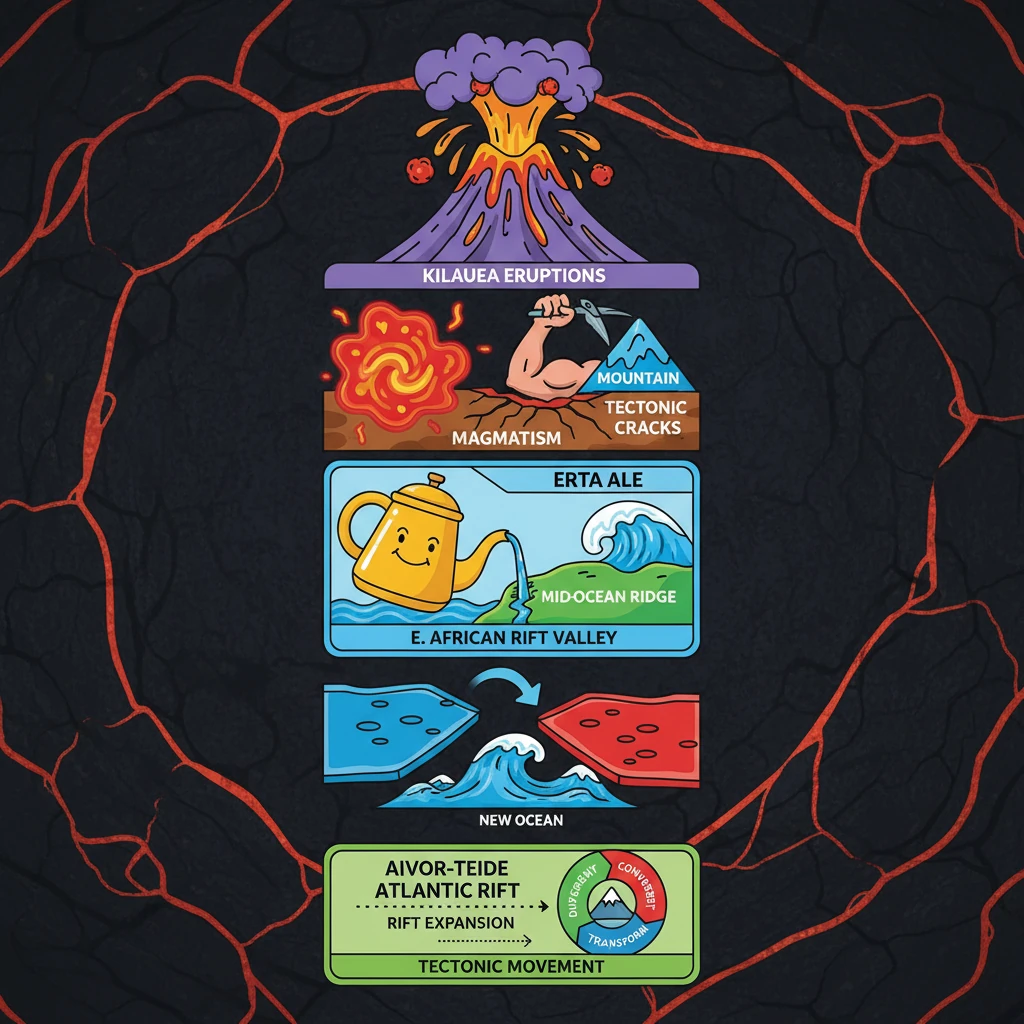
<h4>Understanding Magmatism and Tectonic Transitions</h4><p>The study of volcanic activity, particularly at the <strong>Erta Ale volcano</strong>, provides crucial insights into <strong>tectonic transitions</strong>. This region exhibits characteristics that closely mimic those of a <strong>mid-ocean ridge</strong>, offering a natural laboratory for geological processes.</p><div class="key-point-box"><p>The <strong>magmatism</strong> observed at <strong>Erta Ale</strong> is a key indicator of ongoing geological shifts, reflecting processes typically associated with the formation of new oceanic crust.</p></div><h4>What is Magmatism?</h4><p><strong>Magmatism</strong> refers to the complex process involving the formation and subsequent movement of <strong>magma</strong> beneath the Earth's surface. This fundamental geological phenomenon plays a vital role in shaping our planet.</p><div class="info-box"><p><strong>Magmatism's Contributions:</strong></p><ul><li>Fills <strong>tectonic cracks</strong> within the Earth's crust.</li><li>Contributes to the formation of <strong>mountains</strong>.</li><li>Aids in the efficient release of internal <strong>heat from the Earth’s core</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Potential Formation of a New Ocean</h4><p>The ongoing <strong>rift expansion</strong> in the East African Rift Valley region holds significant implications for future global geography. Scientists hypothesize that this process could eventually lead to the formation of an entirely new ocean basin.</p><p>This nascent ocean has been tentatively named the <strong>“Aivor-Teide Atlantic Rift”</strong>. Its formation would involve the eventual flooding of the <strong>Afar region</strong> and the <strong>East African Rift Valley</strong> by waters from the <strong>Red Sea</strong> and the <strong>Gulf of Aden</strong>.</p><div class="exam-tip-box"><p>Understanding the concept of <strong>rift expansion</strong> and its potential to form new oceans is crucial for UPSC Geography, especially for topics related to <strong>Plate Tectonics</strong> and <strong>Geomorphology</strong>.</p></div><h4>Key Tectonic Concepts Explained</h4><div class="info-box"><p><strong>Tectonic Movement:</strong></p><p>This describes the large-scale motion of the Earth’s <strong>lithosphere</strong>, driven by the dynamic interactions of various <strong>tectonic plates</strong>. These movements are responsible for most major geological features.</p><ul><li><strong>Divergent Boundaries:</strong> Plates move apart.</li><li><strong>Convergent Boundaries:</strong> Plates move towards each other.</li><li><strong>Transform Boundaries:</strong> Plates slide past each other horizontally.</li></ul></div><div class="info-box"><p><strong>Rifting:</strong></p><p><strong>Rifting</strong> is a geological process where the Earth's <strong>lithosphere</strong>, its outermost rigid layer, undergoes stretching and thinning. This process ultimately leads to the creation of characteristic <strong>rift valleys</strong> or <strong>basins</strong>.</p><p>As <strong>tectonic plates</strong> move apart, powerful <strong>tensional forces</strong> cause the lithosphere to fracture and break, defining these active <strong>rift zones</strong>.</p></div><div class="info-box"><p><strong>Mid-Oceanic Ridge:</strong></p><p>A <strong>mid-oceanic ridge</strong> is an extensive underwater mountain range that develops along <strong>divergent boundaries</strong> between tectonic plates, specifically within the <strong>oceanic crust</strong>. These are some of the most prominent features on Earth's surface.</p><p>These ridges are distinguished by intense <strong>volcanic activity</strong> and the continuous upwelling of <strong>magma</strong> from the Earth's mantle. This magma solidifies upon reaching the surface, forming new <strong>oceanic crust</strong>.</p><div class="key-point-box"><p><strong>Mid-oceanic ridges</strong> are central to the concept of <strong>seafloor spreading</strong>, a process where new crust is perpetually generated as tectonic plates diverge.</p></div></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Magmatism is the formation and movement of magma, contributing to heat release, mountain building, and tectonic crack filling.
- •The Erta Ale volcano in the East African Rift Valley provides clues to tectonic transitions, mimicking mid-ocean ridge characteristics.
- •Ongoing rift expansion in the East African Rift Valley could lead to a new ocean, the "Aivor-Teide Atlantic Rift."
- •Tectonic movement involves the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere, forming divergent, convergent, and transform boundaries.
- •Rifting is the stretching and thinning of the lithosphere, creating rift valleys or basins.
- •Mid-oceanic ridges are underwater mountain ranges at divergent boundaries, characterized by volcanic activity and new oceanic crust formation (seafloor spreading).
🧠 Memory Techniques
90% Verified Content