Surge in Demand of Copper - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Surge in Demand of Copper
Medium⏱️ 12 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
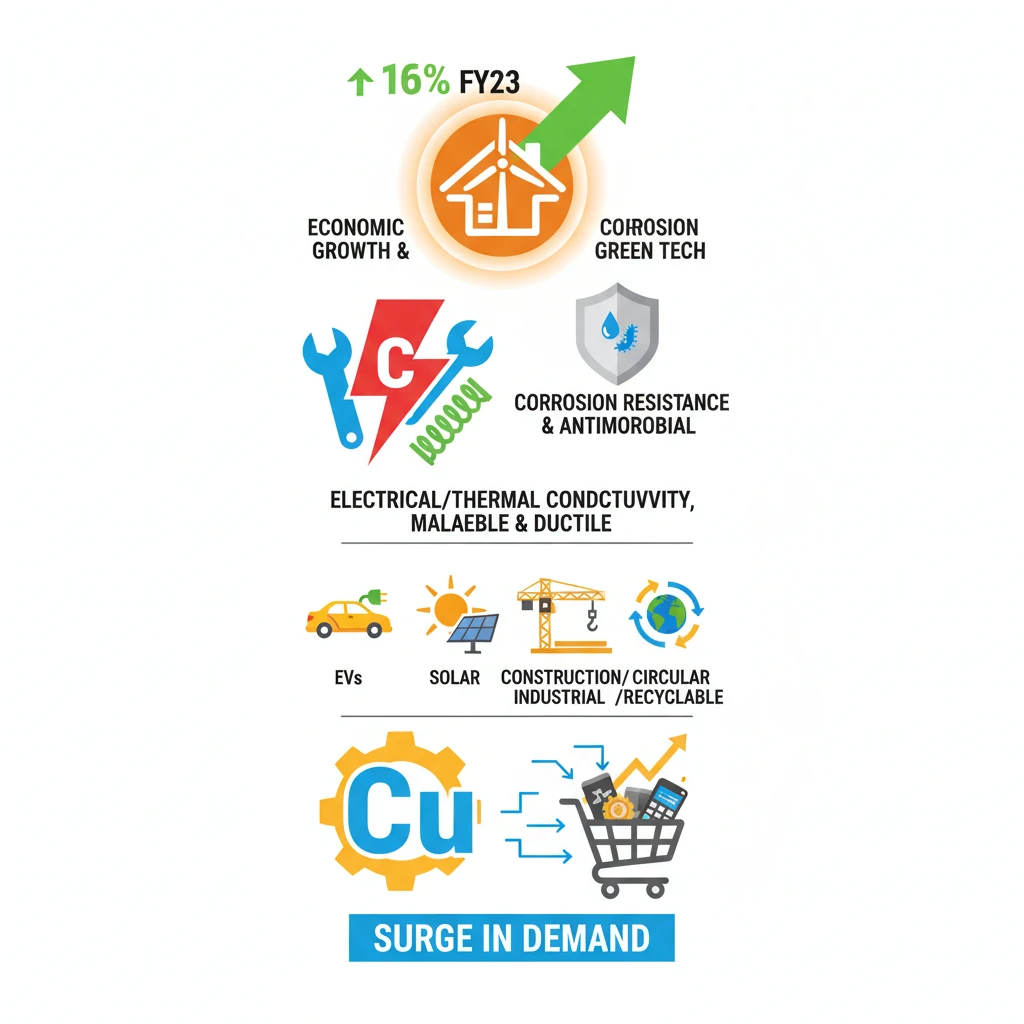
<h4>Context of Copper Demand Surge</h4><p>The demand for <strong>copper</strong> has experienced a significant surge, growing by <strong>16% year-on-year in FY23</strong>. This escalating demand has drawn the attention of <strong>policymakers</strong> and <strong>corporations</strong>, highlighting copper's increasingly critical role in driving <strong>economic growth</strong> globally.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Relevance:</strong> The surge in demand for critical minerals like <strong>copper</strong> is a recurring theme in <strong>GS Paper 1 (Geography)</strong> and <strong>GS Paper 3 (Economy, Environment)</strong>, especially concerning <strong>resource geopolitics</strong> and <strong>sustainable development</strong>.</p></div><h4>About Copper: Key Properties</h4><p><strong>Copper</strong> is a highly valued metal known for its distinctive properties. It is a <strong>malleable</strong> and <strong>ductile metal</strong>, making it versatile for various industrial applications. Its exceptional <strong>heat and electricity conductivity</strong> are paramount to its widespread use.</p><p>Furthermore, copper exhibits strong <strong>corrosion resistance</strong> and possesses inherent <strong>antimicrobial properties</strong>, adding to its utility in diverse environments.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Malleability:</strong> The ability of a material to be pressed or rolled into <strong>thin sheets</strong> without breaking or cracking.</p><p><strong>Ductility:</strong> The property of a material that allows it to be stretched or drawn out into a <strong>thin wire</strong> without losing its strength or breaking.</p></div><h4>Applications of Copper</h4><p>Copper's versatility leads to its extensive use across numerous sectors:</p><ul><li><strong>Construction:</strong> Integral for wiring, plumbing, and roofing.</li><li><strong>Consumer Durables:</strong> Found in electronics, appliances, and household items.</li><li><strong>Transportation:</strong> Essential for wiring harnesses and components in vehicles.</li><li><strong>Industrial Manufacturing:</strong> Used in machinery, heat exchangers, and electrical equipment.</li></ul><p>Critically, copper is also a foundational material for <strong>clean energy technologies</strong>. This includes components in <strong>solar panels</strong>, wiring in <strong>electric vehicles (EVs)</strong>, and efficient motors for various applications.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Circular Economy:</strong> Copper is a <strong>100% recyclable metal</strong>, which significantly contributes to the principles of a <strong>circular economy</strong> by reducing the need for virgin material extraction and minimizing waste.</p></div><h4>Occurrence and Composition of Copper</h4><p><strong>Copper</strong> occurs naturally in various forms within the <strong>Earth’s crust</strong>. Its presence is typically found in different types of mineral deposits.</p><ul><li><strong>Sulphide Deposits:</strong> Commonly found as <strong>chalcopyrite</strong>, <strong>bornite</strong>, and <strong>chalcocite</strong>.</li><li><strong>Carbonate Deposits:</strong> Occurs as minerals like <strong>azurite</strong> and <strong>malachite</strong>.</li><li><strong>Silicate Deposits:</strong> Present in minerals such as <strong>chrysocolla</strong> and <strong>dioptase</strong>.</li><li><strong>Native Copper:</strong> Can also be found in its pure, uncombined metallic form.</li></ul><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Ore Grade:</strong> Most <strong>commercial copper ore deposits</strong> contain an average grade of <strong>0.8% copper</strong>. In contrast, <strong>copper ore in India</strong> typically has a slightly higher average copper content of around <strong>1%</strong>.</p></div><h4>Copper Mining Methods</h4><p>There are two primary methods employed for extracting copper from the Earth:</p><ul><li><strong>Open-pit Mining:</strong> This method involves excavating large, open pits from the surface.</li><li><strong>Underground Mining:</strong> This technique involves creating tunnels and shafts to access deeper ore bodies.</li></ul><p><strong>Open-pit mining</strong> is the dominant method globally, accounting for approximately <strong>80%</strong> of all copper mining operations due to its efficiency for large, shallow deposits.</p><h4>Copper Deposits in India</h4><p>Significant <strong>copper deposits</strong> in India are primarily located in specific districts across a few states:</p><ul><li><strong>Singhbhum</strong> district in <strong>Jharkhand</strong>.</li><li><strong>Balaghat</strong> district in <strong>Madhya Pradesh</strong>.</li><li><strong>Jhunjhunu</strong> and <strong>Alwar</strong> districts in <strong>Rajasthan</strong>.</li></ul>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Copper demand surged 16% in FY23, driven by economic growth and green technologies.
- •It is a malleable, ductile metal with excellent electrical/thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and antimicrobial properties.
- •Key applications include construction, consumer durables, transportation, industrial manufacturing, and crucial clean energy technologies (EVs, solar).
- •Copper is 100% recyclable, supporting a circular economy.
- •Found in sulphide, carbonate, silicate deposits, and as native copper; India's ore grade is ~1%.
- •Open-pit mining dominates (80%); major Indian deposits are in Jharkhand, MP, and Rajasthan.
- •Its historical use from the Copper Age to the Electrical Age underscores its enduring importance.
- •Copper is a critical mineral for global energy transition, economic growth, and has significant geopolitical implications.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Geological Survey of India (GSI) reports on mineral resources
•International Copper Association (ICA) publications
•Ministry of Mines, Government of India reports
•General knowledge on critical minerals and energy transition