Gulf of Aden and Red Sea - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Gulf of Aden and Red Sea
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction: Strategic Waterways Under Threat</h4><p>India's Defence Minister recently highlighted increasing threats in the <strong>Gulf of Aden</strong>, <strong>Red Sea</strong>, and adjacent East African waters. These threats include <strong>maritime piracy</strong>, <strong>terrorism</strong>, and <strong>regional conflicts</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>This statement underscores the growing geopolitical significance of these regions for <strong>India's maritime security</strong> and trade, a crucial topic for <strong>UPSC Mains GS-II (International Relations)</strong> and <strong>GS-III (Internal Security)</strong>.</p></div><h4>The 'Year of Naval Civilians'</h4><p>The year <strong>2024</strong> was designated as the <strong>'Year of Naval Civilians'</strong>. These individuals constitute approximately <strong>one-third</strong> of the <strong>Indian Navy's workforce</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Naval Civilians</strong> are essential personnel, often working without uniforms, who provide critical <strong>technical assistance</strong>, <strong>administrative management</strong>, and <strong>logistics support</strong>, significantly bolstering the operational strength of uniformed troops.</p></div><h4>📍 Gulf of Aden: An Overview</h4><p>The <strong>Gulf of Aden</strong> is a vital extension of the <strong>Indian Ocean</strong>. It is strategically positioned between the <strong>Arabian Peninsula</strong> to its north and the <strong>African continent</strong> to its south.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Location Boundaries:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>South:</strong> <strong>Somalia</strong> and the <strong>Socotra Islands</strong></li><li><strong>North:</strong> <strong>Yemen</strong></li><li><strong>East:</strong> <strong>Arabian Sea</strong></li><li><strong>West:</strong> <strong>Djibouti</strong></li></ul></div><p>It forms a crucial link, connecting to the <strong>Somali Sea</strong> via the <strong>Guardafui Channel</strong> and to the <strong>Red Sea</strong> through the narrow <strong>Strait of Bab el Mandeb</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Economic Importance:</strong> The Gulf of Aden is a major global maritime artery. Approximately <strong>10% of global seaborne petroleum</strong> transits through this gulf. Furthermore, over <strong>USD 110 billion</strong> of <strong>India’s trade</strong> relies on this passage.</p></div><h4>📍 Red Sea: A Tropical Rift Sea</h4><p>The <strong>Red Sea</strong> holds the distinction of being the <strong>world’s northernmost tropical sea</strong>. It is geologically unique, underlain by the <strong>Red Sea Rift</strong>, making it an integral part of the larger <strong>Great Rift Valley</strong> system.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The distinctive name <strong>Red Sea</strong> is believed to originate from the seasonal proliferation of a specific red-colored <strong>cyanobacteria</strong>, scientifically known as <strong><em>Trichodesmium erythraeum</em></strong>.</p></div><p>The <strong>Red Sea Rift</strong> represents a <strong>divergent plate boundary</strong>, where the <strong>African Plate</strong> and the <strong>Arabian Plate</strong> are moving apart. This geological feature extends from <strong>East Africa</strong> into the <strong>Middle East</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Location and Connections:</strong></p><ul><li>The <strong>Red Sea</strong> is a <strong>semi-enclosed extension</strong> of the <strong>Indian Ocean</strong>, situated between the continents of <strong>Africa</strong> and <strong>Asia</strong>.</li><li>In the <strong>south</strong>, it connects to the <strong>Indian Ocean</strong> and <strong>Arabian Sea</strong> via the <strong>Bab el Mandeb Strait</strong> and the <strong>Gulf of Aden</strong>.</li><li>In the <strong>north</strong>, it branches into two gulfs at the <strong>Sinai Peninsula</strong>: the <strong>Gulf of Aqaba</strong> and the <strong>Gulf of Suez</strong>. The <strong>Gulf of Suez</strong> further connects to the <strong>Mediterranean Sea</strong> through the strategically important <strong>Suez Canal</strong>.</li></ul></div>
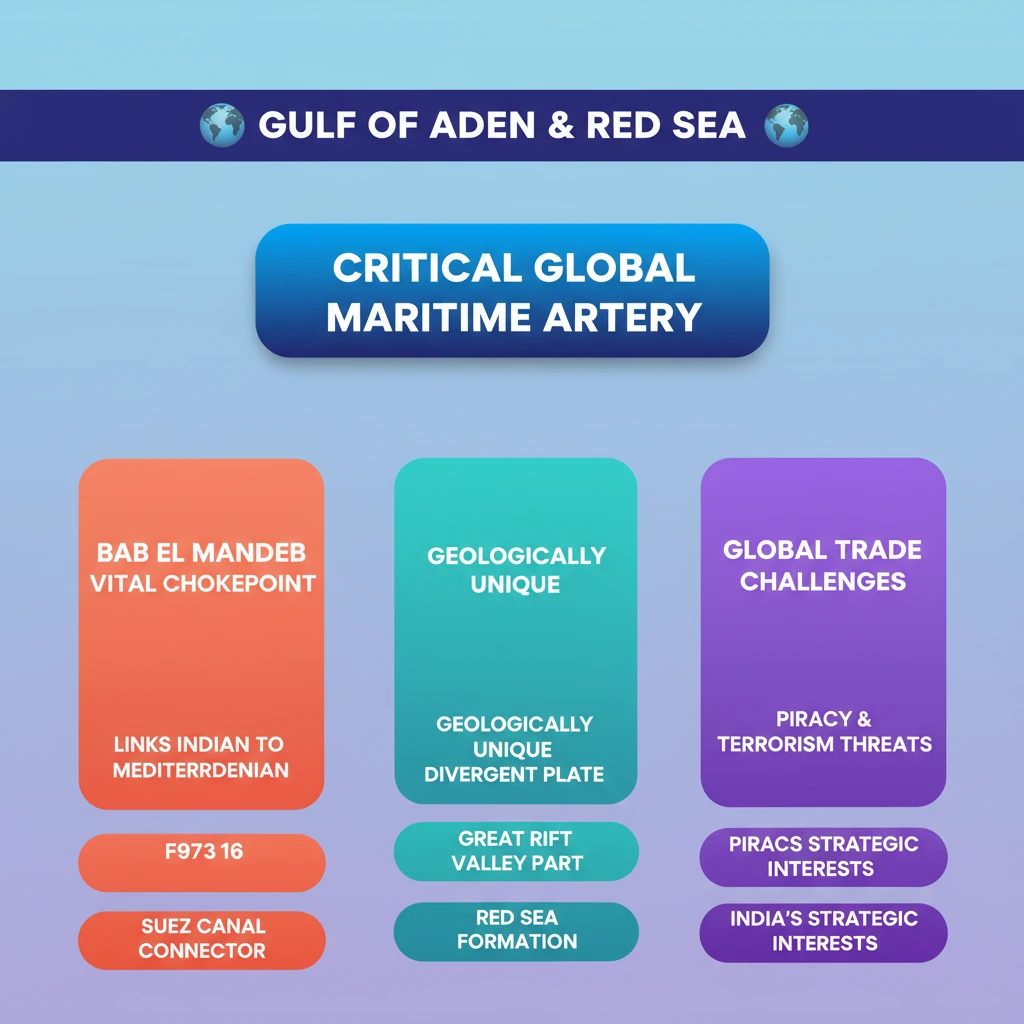
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Gulf of Aden and Red Sea are critical global maritime arteries, linking the Indian Ocean to the Mediterranean via the Suez Canal.
- •Bab el Mandeb Strait is a vital choke point connecting the Gulf of Aden and Red Sea.
- •The Red Sea is geologically unique, part of the Great Rift Valley, formed by a divergent plate boundary.
- •Region faces threats from piracy, terrorism, and regional conflicts, impacting global trade and energy security.
- •India has significant economic and strategic interests, leading to active naval presence and diplomatic engagements.
- •Naval Civilians are crucial non-uniformed personnel supporting the Navy's operational capabilities.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Defence, Government of India (for 'Year of Naval Civilians')
•UNCLOS (United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea)
•International Maritime Organization (IMO) reports on piracy