Rapid Expansion of Himalayan Glacial Lakes - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Rapid Expansion of Himalayan Glacial Lakes
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
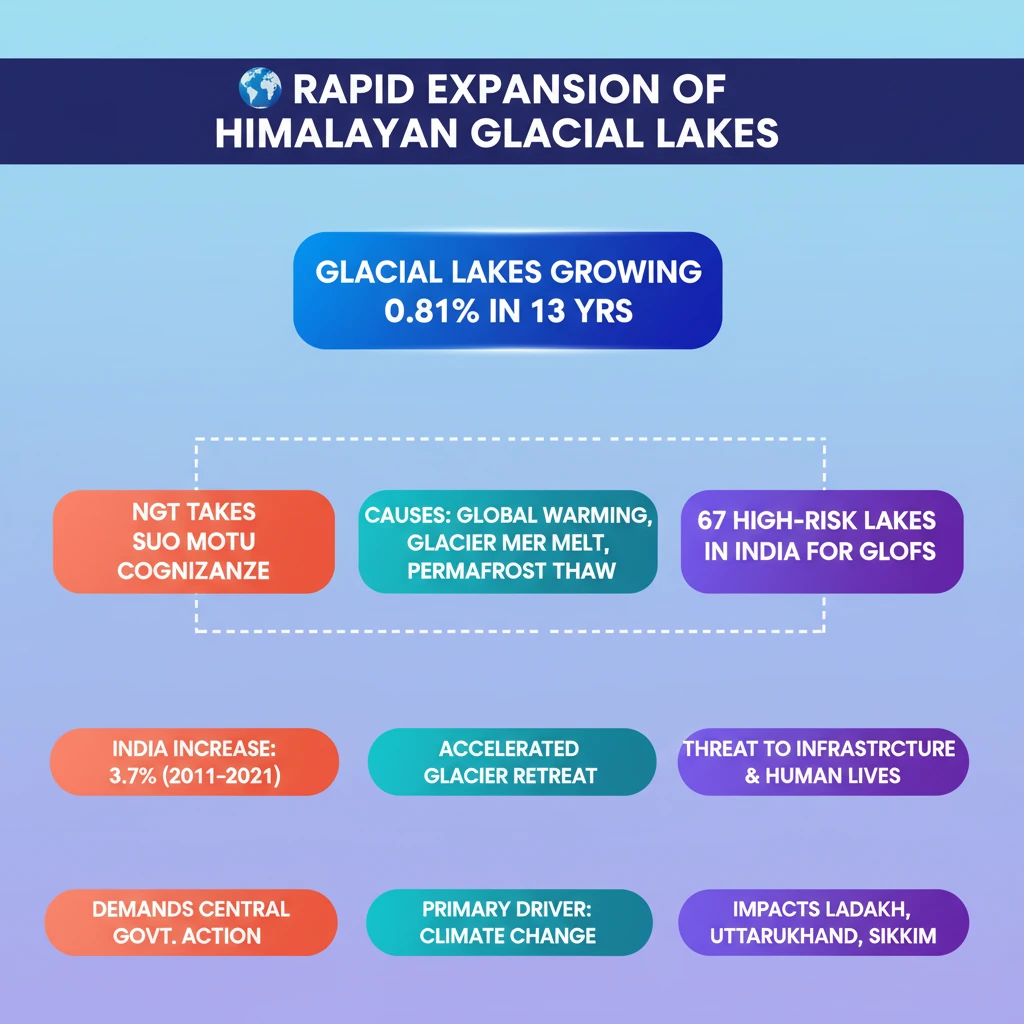
<h4>Introduction to Glacial Lake Expansion</h4><p>The <strong>National Green Tribunal (NGT)</strong> recently took <strong>suo motu cognizance</strong> of a news report. This action highlighted the alarming increase in the size of <strong>Himalayan glacial lakes</strong>.</p><p>The NGT has issued a notice to the central government, emphasizing the significant environmental concern. This rapid expansion is primarily attributed to rising temperatures across the Himalayan region.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Statistic:</strong> Himalayan glacial lakes have expanded by approximately <strong>0.81%</strong> over the past <strong>13 years</strong>. This growth is a direct consequence of global warming accelerating glacier melt.</p></div><h4>What are Glacial Lakes?</h4><p>A <strong>glacial lake</strong> is a body of water that forms in connection with a <strong>glacier</strong>. These lakes are typically found at the base of a glacier, but can also develop on, within, or beneath the ice mass.</p><p>Their formation is a natural geological process, intricately linked to the dynamics of glacial movement and retreat.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Definition:</strong> A <strong>glacial lake</strong> is a water body formed when a glacier erodes the land, creating depressions that subsequently fill with <strong>meltwater</strong> as the glacier retreats.</p></div><h4>Formation of Glacial Lakes</h4><p><strong>Glacial lakes</strong> primarily form in depressions carved out by advancing glaciers. As these glaciers retreat, the meltwater accumulates in these newly exposed basins.</p><p>Natural dams, often composed of <strong>ice</strong> or <strong>moraines</strong> (accumulations of glacial debris), can also impound water, leading to the formation of these lakes. However, these natural dams are often unstable.</p><p>The instability of these dams makes them prone to bursting, which can lead to catastrophic events known as <strong>Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs)</strong>.</p><h4>Alarming Expansion in India</h4><p>The NGT's notice underscored a critical finding regarding glacial lake expansion specifically within India. The surface area of these lakes has shown a substantial increase in recent years.</p><p>This expansion poses a severe threat to both human settlements and critical infrastructure located downstream in vulnerable regions.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>India-Specific Data:</strong> The surface area of glacial lakes in India increased by <strong>3.7%</strong> from <strong>2011 to 2021</strong>. A total of <strong>67 lakes</strong> have been identified as having a <strong>high risk</strong> for <strong>GLOFs</strong>.</p><p><strong>Vulnerable Regions:</strong> This significant threat impacts states and union territories such as <strong>Ladakh</strong>, <strong>Himachal Pradesh</strong>, <strong>Uttarakhand</strong>, <strong>Sikkim</strong>, and <strong>Arunachal Pradesh</strong>.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> The <strong>NGT's suo motu cognizance</strong> highlights the role of judicial activism in environmental protection. Questions may arise on its powers, functions, and specific cases related to climate change impacts or disaster management.</p></div><h4>Drivers of Expansion</h4><p>The rapid expansion of <strong>Himalayan glacial lakes</strong> is driven by a combination of climate-related factors. These factors accelerate both the formation of new lakes and the growth of existing ones.</p><ul><li><strong>Global Warming:</strong> Rising global temperatures lead to accelerated <strong>glacier melting</strong> in the Himalayas, directly contributing more water to glacial lakes.</li><li><strong>Glacier Retreat:</strong> As glaciers retreat, they expose new land surfaces. This creates new depressions and allows existing lakes to expand into the newly uncovered terrain.</li><li><strong>Thawing Permafrost:</strong> The thawing of <strong>permafrost</strong> (permanently frozen ground) creates depressions where water can collect. As permafrost thaws, it loses its natural drainage barrier, further expanding glacial lakes.</li></ul>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Himalayan glacial lakes are rapidly expanding, increasing by 0.81% over 13 years and 3.7% in India (2011-2021).
- •NGT has taken suo motu cognizance, highlighting the urgency and demanding central government action.
- •Expansion is primarily driven by global warming, accelerating glacier melt, glacier retreat, and thawing permafrost.
- •67 lakes in India are identified as high-risk for Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs).
- •GLOFs pose significant threats to infrastructure and human lives in states like Ladakh, Uttarakhand, and Sikkim.
- •Proactive monitoring, early warning systems, and integrated disaster management strategies are crucial for mitigation.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•News reports cited by National Green Tribunal (NGT)
•General scientific literature on Himalayan glacier dynamics and climate change impacts