Climate Change and African Easterly Waves - Geography | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Climate Change and African Easterly Waves
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
geography
📖 Introduction
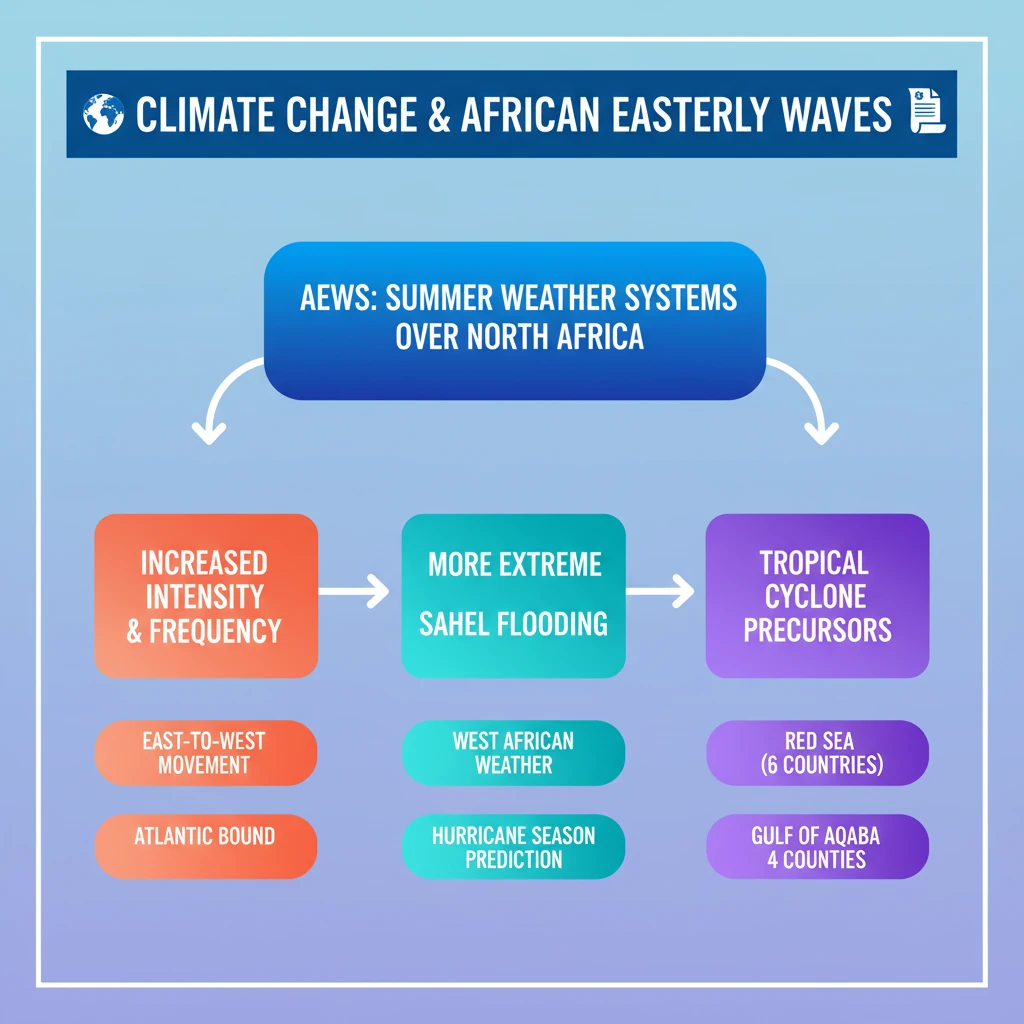
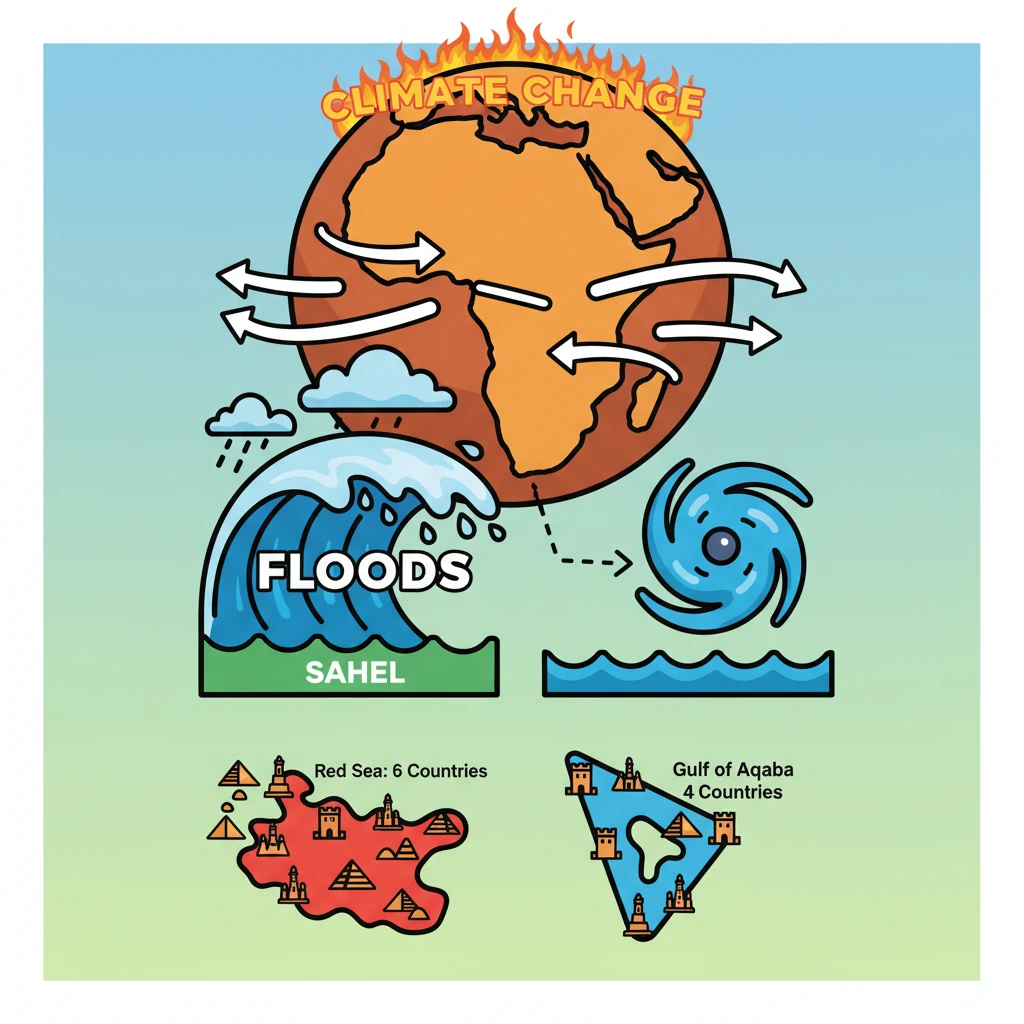
<h4>Introduction to African Easterly Waves (AEWs)</h4><p>A recent study has brought to light critical predictions regarding <strong>climate change</strong> and its impact on the <strong>Sahel region</strong> of Africa.</p><p>The research forecasts a significant increase in the <strong>intensity</strong> and <strong>frequency</strong> of <strong>extreme flooding</strong> events in this vulnerable area.</p><div class='info-box'><p>This projection is directly linked to anticipated changes in <strong>African Easterly Waves (AEWs)</strong>, as detailed in a study published in <strong>Communications Earth & Environment</strong>.</p></div><h4>Definition and Characteristics of AEWs</h4><p><strong>African Easterly Waves (AEWs)</strong> are distinct <strong>weather systems</strong> that play a crucial role in atmospheric dynamics over northern Africa.</p><p>These waves typically form during the <strong>summer months</strong> and exhibit a characteristic movement pattern, propagating from <strong>east to west</strong> towards the <strong>Atlantic Ocean</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>AEWs are known to be significant precursors to the formation of <strong>tropical cyclones</strong> in the Atlantic basin, influencing weather patterns across <strong>West Africa</strong>.</p></div><h4>Projected Climate Change Impacts</h4><p>The study specifically predicts that alterations driven by <strong>climate change</strong> will intensify these waves.</p><p>This intensification will, in turn, lead to a higher occurrence and severity of <strong>extreme flooding</strong> in the <strong>Sahel region</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding the dynamics of <strong>AEWs</strong> and their climate change linkages is crucial for <strong>UPSC Mains GS Paper 1 (Physical Geography)</strong> and <strong>GS Paper 3 (Disaster Management, Environment)</strong>.</p></div><h4>Geographical Context: Red Sea and Surrounding Regions</h4><p>The <strong>Red Sea</strong> is a vital waterway, strategically bordering six countries, which are divided between its eastern and western shores.</p><ul><li>To the <strong>east</strong>, it borders <strong>Yemen</strong> and <strong>Saudi Arabia</strong>.</li><li>To the <strong>west</strong>, it borders <strong>Egypt</strong>, <strong>Sudan</strong>, <strong>Eritrea</strong>, and <strong>Djibouti</strong>.</li></ul><p>The <strong>Gulf of Aqaba</strong>, an important northern inlet of the Red Sea, is bordered by four nations: <strong>Egypt</strong>, <strong>Israel</strong>, <strong>Jordan</strong>, and <strong>Saudi Arabia</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Prominent Islands</strong> in the Red Sea region include <strong>Tiran</strong> (near the Gulf of Aqaba), <strong>Shadwan</strong> (at the Gulf of Suez), and <strong>Yemen-controlled islands</strong> such as <strong>Kamaran</strong>, <strong>Perim</strong>, <strong>Hanish</strong>, and <strong>Socotra</strong>.</p></div><p>The largest groups of islands are the <strong>Farasan Islands</strong> located in the east and the <strong>Dahlak Archipelago</strong> situated in the west.</p>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •African Easterly Waves (AEWs) are summer weather systems over northern Africa, moving east to west towards the Atlantic.
- •A recent study predicts climate change will increase AEW intensity and frequency, leading to more extreme flooding in the Sahel region.
- •AEWs are significant precursors to the formation of many Atlantic tropical cyclones.
- •The Red Sea borders six countries (Yemen, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea, Djibouti), and the Gulf of Aqaba borders four (Egypt, Israel, Jordan, Saudi Arabia).
- •Understanding AEWs is crucial for predicting West African weather and Atlantic hurricane seasons.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Communications Earth & Environment (cited study)