International Big Cat Alliance - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

International Big Cat Alliance
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)</h4><p>The <strong>International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)</strong> is a significant global initiative focused on the conservation of the world's most majestic feline predators. It was officially launched by the <strong>Prime Minister of India</strong> in <strong>2023</strong>.</p><p>India's formal joining of the <strong>IBCA</strong> underscores its commitment to global wildlife protection efforts. The alliance's primary goal is to safeguard <strong>big cats</strong> and their vital habitats across the globe.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>While India initiated and launched the <strong>IBCA</strong> as a global institution, it is crucial to remember that India must still <strong>sign and ratify its Framework Agreement</strong>. This process is similar to how India approaches other major international agreements and bodies, such as the <strong>Paris Agreement</strong>, the <strong>Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)</strong>, and the <strong>Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO)</strong>.</p></div><h4>Coordination and Structure of IBCA</h4><p>The <strong>IBCA</strong> operates as a multi-country, multi-agency coalition. It brings together <strong>96 big cat range countries</strong> and non-range countries under a common umbrella for conservation.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)</strong> is coordinated by several key international organizations:</p><ul><li><strong>Conservation International (CI)</strong></li><li><strong>International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)</strong></li><li><strong>Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission-UNESCO (IOC-UNESCO)</strong></li></ul></div><h4>Governance Framework</h4><p>The governance structure of the <strong>IBCA</strong> is designed for effective global coordination and implementation. It mirrors the successful model of the <strong>International Solar Alliance (ISA)</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Key components of the <strong>IBCA's governance structure</strong> include:</p><ul><li>An <strong>Assembly of Members</strong> for overall strategic direction.</li><li>A <strong>Standing Committee</strong> for ongoing oversight and decision-making.</li><li>A <strong>Secretariat</strong>, which is strategically based in <strong>India</strong>.</li></ul><p>A <strong>Director-General (DG)</strong> for the Secretariat is appointed by the <strong>Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)</strong>.</p></div><h4>Core Objectives of the IBCA</h4><p>The <strong>IBCA</strong> is driven by a comprehensive set of objectives aimed at holistic big cat conservation:</p><ul><li>To actively <strong>prevent the illegal wildlife trade</strong> involving the seven designated big cat species.</li><li>To vigorously <strong>promote the conservation of natural habitats</strong> essential for these seven big cats.</li><li>To effectively <strong>mobilise financial and technical resources</strong> to bolster conservation and protection efforts globally.</li><li>To proactively work towards <strong>mitigating the adverse effects of climate change</strong> on big cat populations and their ecosystems.</li><li>To strongly <strong>advocate for policy initiatives</strong> that seamlessly integrate biodiversity conservation with local community needs, contributing to <strong>United Nations-mandated Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)</strong> within member countries.</li></ul><h4>Focus Species of the Alliance</h4><p>The <strong>IBCA</strong> concentrates its conservation efforts on <strong>seven iconic big cat species</strong>, recognizing their ecological importance and vulnerability.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>seven big cat species</strong> at the heart of the IBCA's mission are:</p><ul><li><strong>Tigers</strong></li><li><strong>Lions</strong></li><li><strong>Leopards</strong></li><li><strong>Snow Leopards</strong></li><li><strong>Cheetahs</strong></li><li><strong>Jaguars</strong></li><li><strong>Pumas</strong></li></ul><p>Out of these seven, <strong>five species</strong>—the <strong>tiger, lion, leopard, snow leopard, and cheetah</strong>—are naturally found in <strong>India</strong>. The <strong>puma</strong> and <strong>jaguar</strong> are not native to India.</p></div><h4>Member Countries and Financial Support</h4><p>The alliance is growing, with several nations formally committing to its cause. Early members play a crucial role in establishing its operational framework.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Currently, the <strong>IBCA</strong> counts <strong>four countries</strong> as its members:</p><ul><li><strong>India</strong></li><li><strong>Nicaragua</strong></li><li><strong>Eswatini</strong></li><li><strong>Somalia</strong></li></ul></div><p>To ensure the operational viability of the alliance, significant financial backing has been pledged by the Indian government.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>Union Cabinet</strong> has approved a substantial <strong>one-time budgetary support</strong> of <strong>Rs 150 crore</strong> for the <strong>IBCA</strong>. This allocation will cover a period of <strong>five years</strong>, from the fiscal year <strong>2023-24 to 2027-28</strong>.</p></div><h4>Ecological Significance of Big Cats</h4><p>Big cats are not just magnificent creatures; they are vital components of their ecosystems, playing critical roles in maintaining ecological balance.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Ecological Roles:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Keystone Species:</strong> Big cats are often <strong>keystone species</strong>, meaning their presence or absence significantly impacts the entire ecosystem structure and function.</li><li><strong>Ecosystem Health Indicators:</strong> They serve as <strong>critical indicators of ecosystem health</strong>. A decline in big cat populations often signals broader environmental degradation.</li><li><strong>Apex Predators:</strong> As <strong>apex predators</strong>, they regulate prey populations, preventing overgrazing and maintaining biodiversity within their habitats.</li></ul></div><p>Despite their importance, big cat populations face severe threats globally, jeopardizing their survival and the health of the ecosystems they inhabit.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Major threats to big cat survival include:</p><ul><li><strong>Poaching:</strong> Illegal hunting for their body parts, often for traditional medicine or trophies.</li><li><strong>Illegal Wildlife Trade:</strong> A lucrative black market driven by demand for exotic pets and animal products.</li><li><strong>Habitat Loss and Fragmentation:</strong> Due to human encroachment, agriculture, and infrastructure development.</li><li><strong>Human-Wildlife Conflict:</strong> Retaliatory killings due to livestock depredation.</li></ul></div><h4>Unique Characteristics of Big Cats</h4><p>While often grouped, big cats exhibit diverse behaviors and social structures.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Distinctive Traits:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Social Structure:</strong> <strong>Lions</strong> are the only big cats that live in complex <strong>social groups called prides</strong> and exhibit cooperative hunting behaviors. Most other big cats are largely <strong>solitary</strong>, except for mothers raising cubs.</li><li><strong>Size and Status:</strong> The <strong>Siberian tiger</strong> is renowned as the <strong>largest of all big cats</strong>. Unfortunately, it is currently listed as <strong>endangered</strong>, primarily due to threats like <strong>trophy hunting</strong> and its use in <strong>traditional Chinese medicine</strong>.</li></ul></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
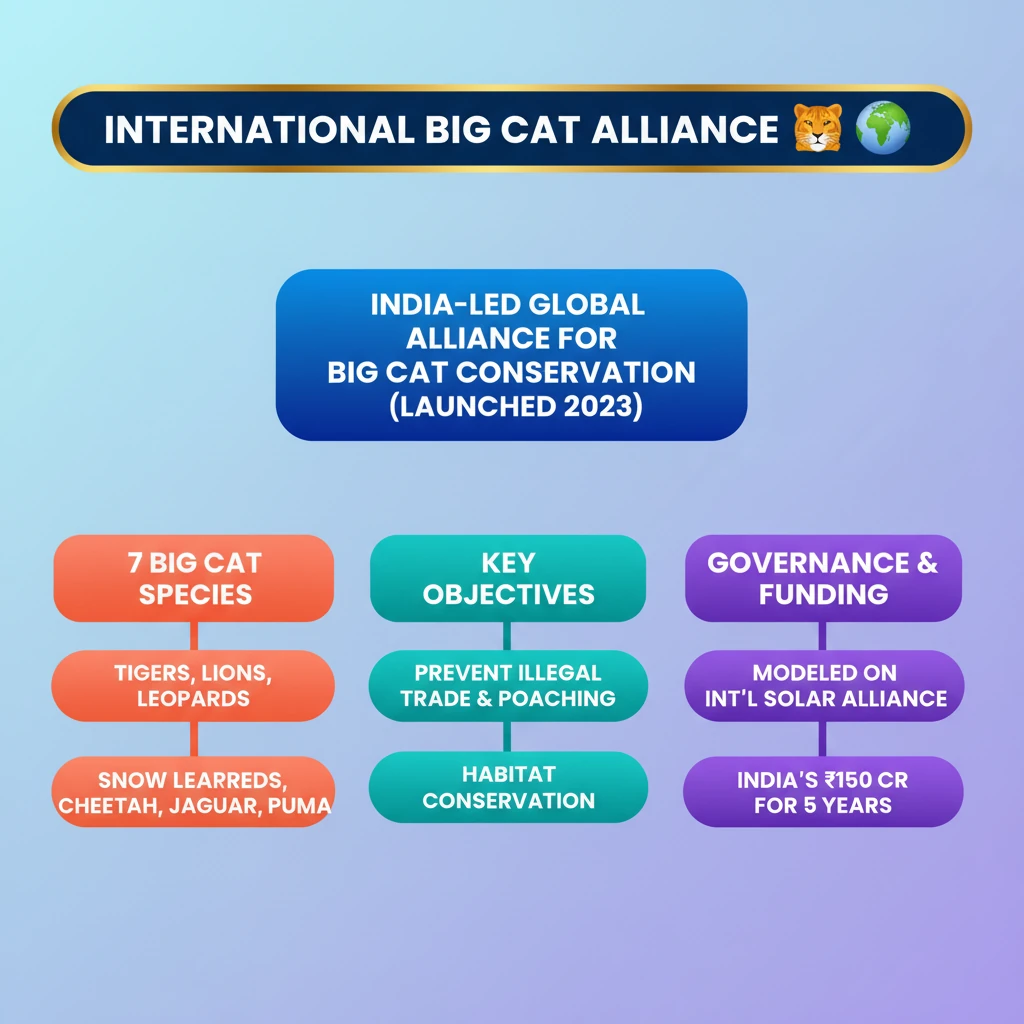
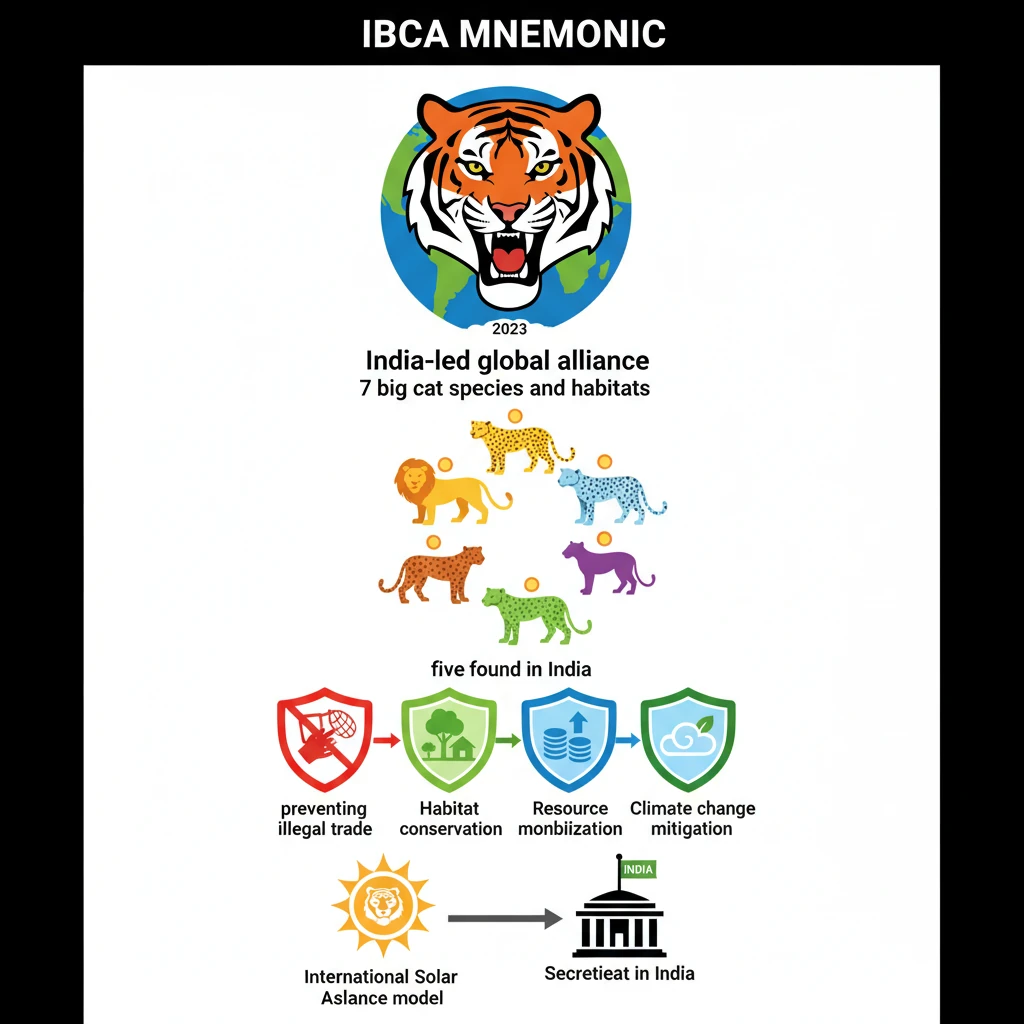
- •IBCA is an India-led global alliance launched in 2023 to conserve 7 big cat species and their habitats.
- •Focuses on Tigers, Lions, Leopards, Snow Leopards, Cheetah, Jaguar, and Puma; five of these are found in India.
- •Objectives include preventing illegal trade, habitat conservation, resource mobilization, and climate change mitigation.
- •Governance structure is modelled after the International Solar Alliance (ISA), with a Secretariat in India.
- •India has committed Rs 150 crore for five years as budgetary support.
- •Big cats are keystone species and indicators of ecosystem health, facing threats from poaching, trade, and habitat loss.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content