Biodiversity Credits for Environment Conservation - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Biodiversity Credits for Environment Conservation
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Context and Recent Developments</h4><p>A recent <strong>study</strong> published in the journal <strong>Proceedings of the Royal Society B</strong> has raised significant concerns regarding the effectiveness of the emerging <strong>biodiversity credit market</strong>.</p><p>This study challenges the notion that biodiversity credits are a guaranteed solution for <strong>biodiversity conservation</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The research highlighted deep uncertainties within the market and questioned whether the benefits designed to offset biodiversity loss truly outweigh the potential harms.</p></div><h4>Understanding Biodiversity Credits</h4><p><strong>Biodiversity credits</strong> are a novel financial instrument designed to incentivize and fund positive outcomes for nature and biodiversity.</p><p>They are <strong>verifiable, quantifiable</strong>, and <strong>tradable</strong>, allowing for market-based approaches to conservation.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Definition:</strong> A <strong>biodiversity credit</strong> represents a unit of positive impact on nature, such as the conservation of a specific species, restoration of an ecosystem, or protection of natural habitats, created and sold over a fixed period.</p><ul><li>Can be <strong>land-based</strong> or <strong>ocean-based</strong>.</li><li>Aims to reward positive nature and biodiversity outcomes.</li></ul></div><h4>Mechanism of Biodiversity Credits</h4><p>The operational mechanism of biodiversity credits draws parallels with the well-established system of <strong>carbon credits</strong>.</p><p>When an entity, such as a <strong>company</strong> or a <strong>government</strong>, causes harm or degradation to biodiversity, they can utilize biodiversity credits to offset this damage.</p><p>This offset is achieved by <strong>paying for conservation efforts</strong> undertaken elsewhere, effectively balancing the ecological impact.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The core idea is to achieve an overall net-zero or net-positive impact on biodiversity by compensating for losses through targeted conservation and restoration activities, while also attracting vital <strong>private funding for conservation</strong>.</p></div><h4>Global Initiatives and Future Potential</h4><p>The <strong>World Economic Forum (WEF)</strong> has actively promoted this concept by launching the <strong>Biodiversity Credits Initiative</strong>.</p><p>This initiative aims to unlock new financial streams to support measurable positive outcomes for nature globally.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Market Projections:</strong></p><ul><li>Current estimated worth (WEF): <strong>USD 8 billion</strong>.</li><li>Projected worth by <strong>2030</strong>: <strong>USD 2 billion</strong>.</li><li>Projected worth by <strong>2050</strong>: <strong>USD 69 billion</strong>.</li></ul></div><p>The landmark <strong>Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework 2022</strong> explicitly advocates for diverse financing mechanisms.</p><p>These mechanisms include <strong>ecosystem service payments, green bonds</strong>, and <strong>biodiversity credits</strong>, aiming to mobilize <strong>USD 200 billion annually by 2030</strong> for global biodiversity goals.</p><p>In alignment with these ambitious targets, the <strong>Biodiversity Credit Alliance (BCA)</strong> was subsequently launched to further develop and promote the market.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Mains:</strong> Understanding the <strong>Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework</strong> and its financing mechanisms like <strong>biodiversity credits</strong> is crucial for questions on global environmental governance and sustainable development (<strong>GS Paper 3</strong>).</p></div>
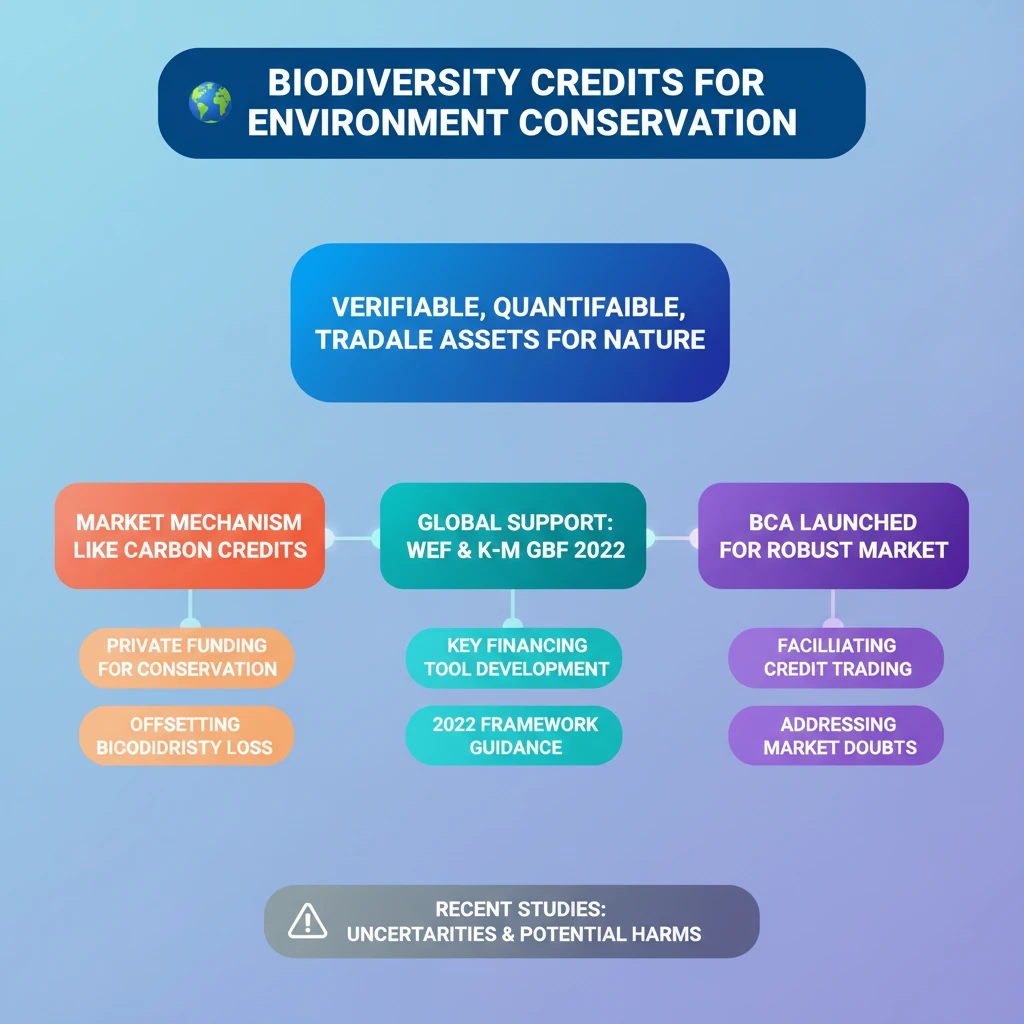
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Biodiversity credits are verifiable, quantifiable, and tradable financial instruments rewarding positive nature outcomes.
- •Their mechanism is similar to carbon credits, aiming to offset biodiversity loss by attracting private funding for conservation.
- •The World Economic Forum (WEF) and the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework 2022 support their development as key financing tools.
- •The Biodiversity Credit Alliance (BCA) was launched to facilitate a robust market for these credits.
- •Recent studies, however, cast doubt on their effectiveness, highlighting deep uncertainties and questioning if benefits truly outweigh potential harms.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Proceedings of the Royal Society B (general journal reference)
•World Economic Forum reports (general reference)
•Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework 2022 (general reference)