What are the Key Points From the Greenwashing Guidelines? - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are the Key Points From the Greenwashing Guidelines?
Medium⏱️ 9 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
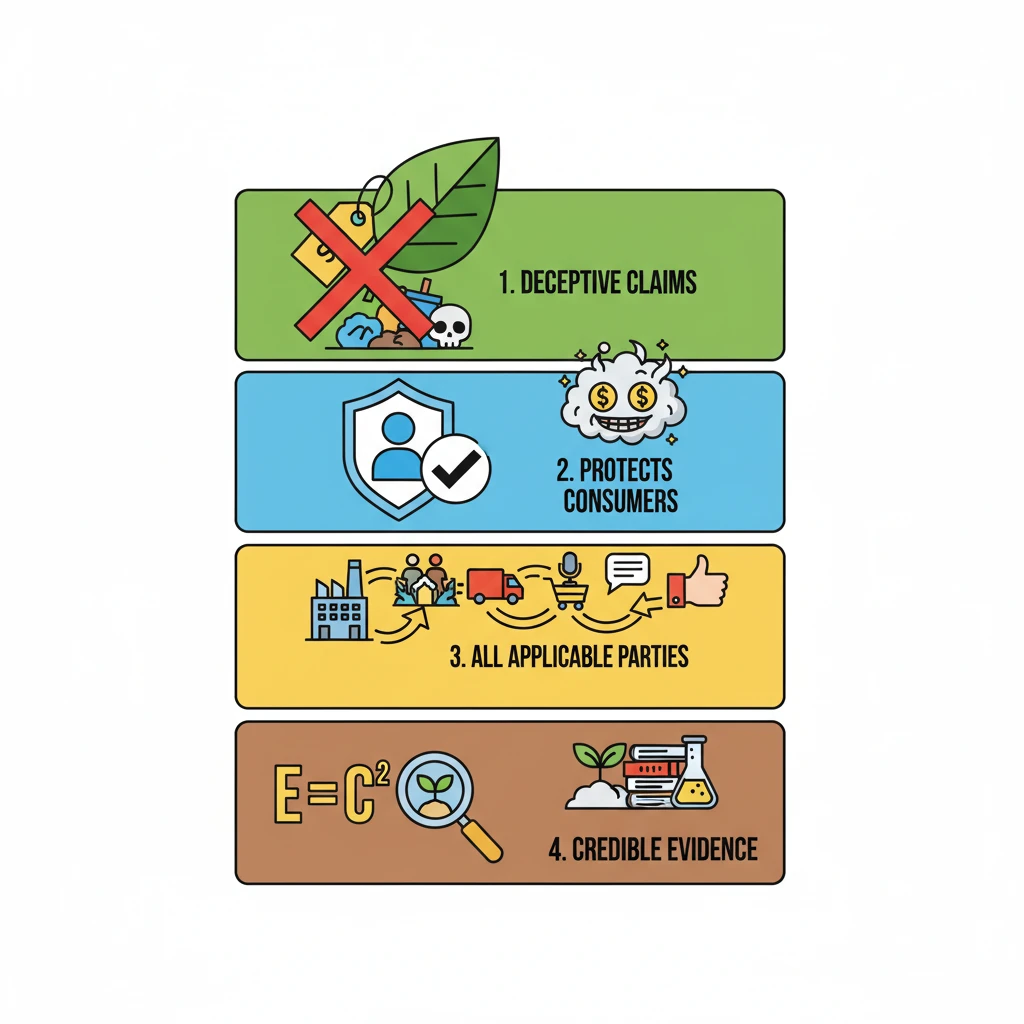
<h4>Objective of the Greenwashing Guidelines</h4><p>The primary aim of the <strong>Greenwashing Guidelines</strong> is to effectively combat <strong>greenwashing</strong>. This practice involves companies falsely promoting their products or services as environmentally friendly without providing credible, verifiable proof.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The core purpose is to protect <strong>consumers</strong> from deceptive marketing tactics and ensure transparency in environmental claims made by businesses.</p></div><h4>Scope and Applicability</h4><p>These guidelines have a broad scope, targeting various entities involved in the production and promotion of goods and services. They apply to <strong>manufacturers</strong>, <strong>service providers</strong>, <strong>traders</strong>, <strong>ad agencies</strong>, and <strong>endorsers</strong>.</p><p>A fundamental requirement is that all environmental claims made by these entities must be properly <strong>substantiated</strong> with credible evidence. This ensures accountability across the entire supply and marketing chain.</p><h4>Specific Requirements for Environmental Claims</h4><p>Terms commonly used to denote environmental benefits, such as <strong>eco-friendly</strong>, <strong>green</strong>, <strong>sustainable</strong>, and <strong>natural</strong>, must be backed by concrete evidence. Companies are required to avoid vague or misleading descriptions that could confuse consumers.</p><div class='info-box'><p>For instance, claims like <strong>100% eco-friendly</strong> or <strong>zero emissions</strong> are not allowed without precise, qualifying information. This information must detail the specific aspects of the product or service that justify such a claim.</p></div><p>It is important to note that these guidelines do not apply to general advertisements or communications that are not specific to a particular product or service. The focus remains on tangible product-related environmental claims.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the specific terms requiring substantiation and the entities covered is crucial for questions on consumer protection and environmental governance in <strong>GS-II</strong> and <strong>GS-III</strong>.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Greenwashing is deceptive marketing of products as environmentally friendly without credible proof.
- •Guidelines aim to combat greenwashing, protecting consumers from misleading environmental claims.
- •Applicable to manufacturers, service providers, traders, ad agencies, and endorsers.
- •All environmental claims (e.g., 'eco-friendly', 'zero emissions', 'natural') must be backed by credible evidence.
- •Vague, generic, or misleading environmental descriptions are prohibited.
- •Guidelines do not apply to general advertisements not specific to a product or service.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•General knowledge of Consumer Protection (Greenwashing) Guidelines and regulatory frameworks (e.g., CCPA, ASCI in India, FTC in USA, ASA in UK)