Adverse Effects of Lithium Mining - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Adverse Effects of Lithium Mining
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
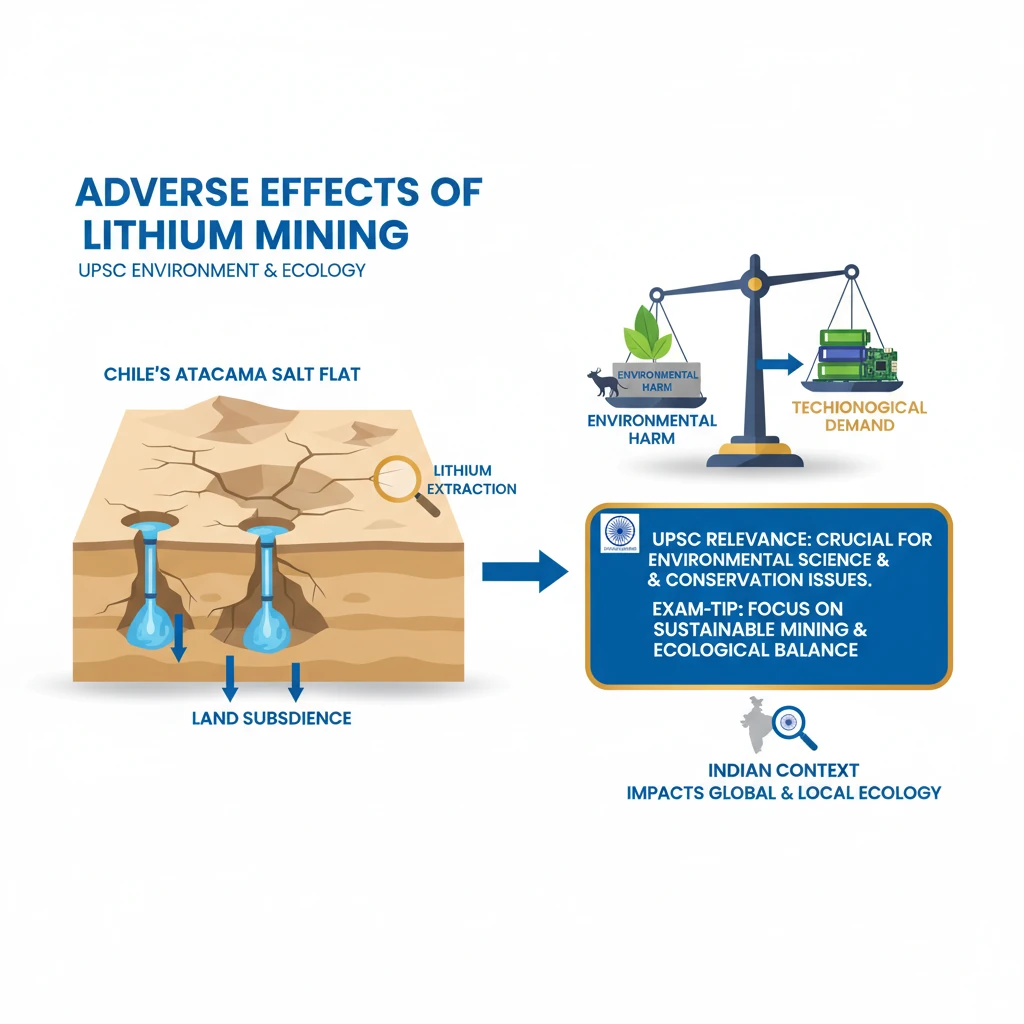
<h4>Introduction to Lithium Mining Impacts</h4><p>Recent studies have brought to light significant environmental concerns associated with <strong>lithium mining</strong>, particularly in ecologically sensitive regions. A new study highlights that <strong>land subsidence</strong> is actively occurring in <strong>Chile's Atacama salt flat</strong> due to intensive <strong>lithium extraction activities</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Relevance:</strong> This topic is crucial for <strong>GS Paper 3 (Environment & Ecology)</strong>, covering environmental degradation, pollution, and conservation. It can also be linked to resource management and sustainable development.</p></div><h4>Key Findings of the Study</h4><p>The study reveals a concerning rate of geological change in the <strong>Atacama salt flat</strong>. This vital ecosystem is experiencing a measurable decline in elevation.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Rate of Sinking:</strong> The <strong>Atacama salt flat</strong> in <strong>Chile</strong> is sinking at an alarming rate of <strong>1 to 2 centimetres per year</strong>.</p></div><p>This subsidence is directly attributed to the process of <strong>lithium brine extraction</strong>. This method involves pumping vast quantities of salt-rich water from underground.</p><p>The underlying cause is the unsustainable rate of extraction. <strong>Lithium-rich brine</strong> is being removed significantly faster than the natural recharge rate of the underground <strong>aquifers</strong>, leading to the observed geological depression.</p><h4>Environmental Impacts of Lithium Mining</h4><p><strong>Lithium mining</strong>, while essential for modern technologies, carries substantial environmental costs, primarily impacting water resources and soil integrity.</p><ul><li><strong>Massive Water Usage:</strong> The extraction process is incredibly water-intensive. Producing just <strong>one ton of lithium</strong> requires an estimated <strong>2,000 tons of fresh water</strong>.</li><li><strong>Exacerbated Water Scarcity:</strong> In arid regions like the <strong>Atacama Desert</strong>, this massive water consumption severely intensifies existing <strong>water scarcity</strong>. This impacts both the delicate local <strong>ecosystems</strong> and the livelihoods of indigenous <strong>local communities</strong>.</li><li><strong>Chemical Contamination:</strong> The methods used in lithium extraction involve various harsh chemicals. Substances such as <strong>sulfuric acid</strong> and <strong>sodium hydroxide</strong> are commonly employed.</li><li><strong>Ecosystem Harm:</strong> These chemicals pose a significant threat, leading to the contamination of both <strong>soil and water bodies</strong>. Such pollution can severely harm sensitive <strong>ecosystems</strong> and endanger various plant and animal <strong>species</strong>.</li></ul>
💡 Key Takeaways
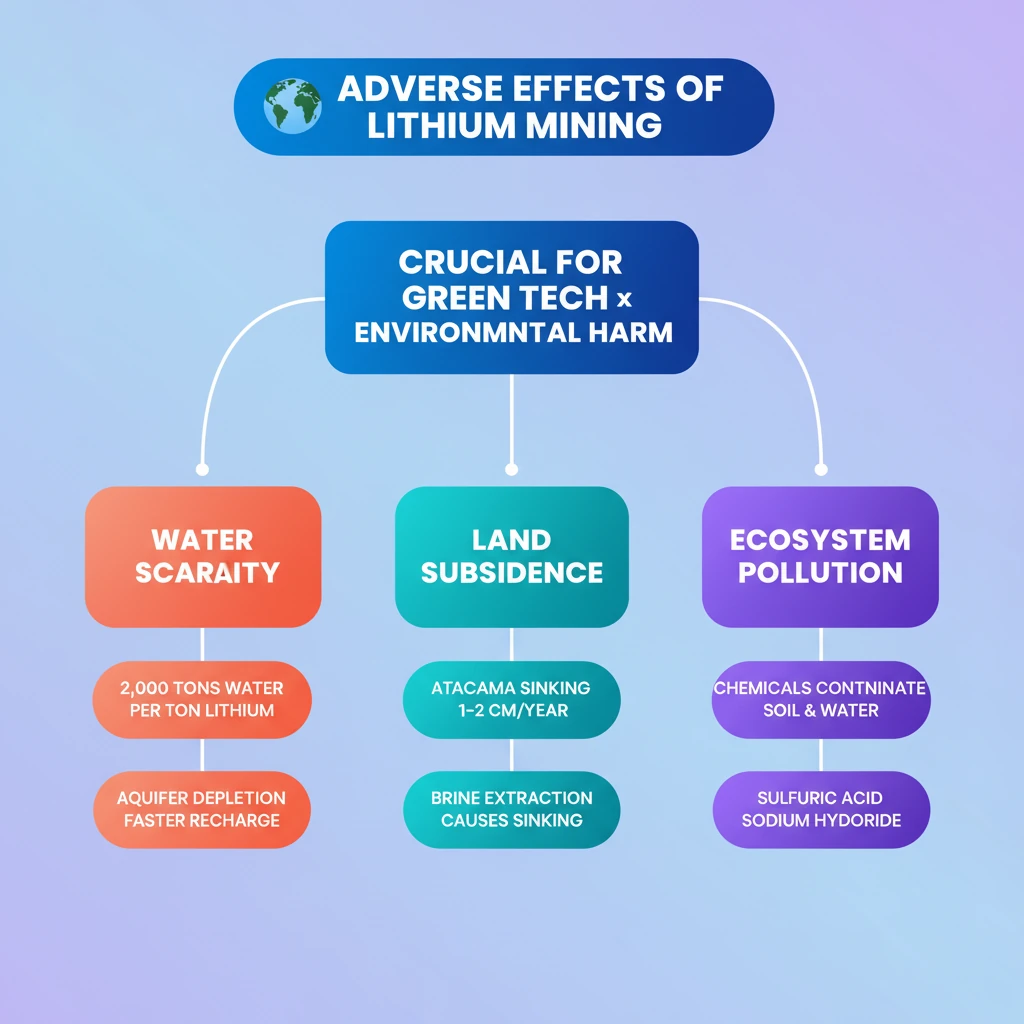
- •Lithium mining, crucial for green tech, causes significant environmental harm.
- •Chile's Atacama salt flat is sinking 1-2 cm/year due to lithium brine extraction.
- •Extraction depletes aquifers faster than natural recharge, leading to land subsidence.
- •Process consumes massive fresh water (2,000 tons per ton of lithium), exacerbating scarcity.
- •Chemicals like sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide contaminate soil and water, harming ecosystems.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Study on land subsidence in Chile's Atacama salt flat (as cited by Drishti IAS)